GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
BIDMAS Substitution Solving equations Squares and square rootsThis topic is relevant for:

Composite Functions
Here we will learn about composite functions including how to evaluate composite functions and how to solve problems involving composite functions.
There are also composite functions worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are composite functions?
Composite functions are when the output of one function is used as the input of another.
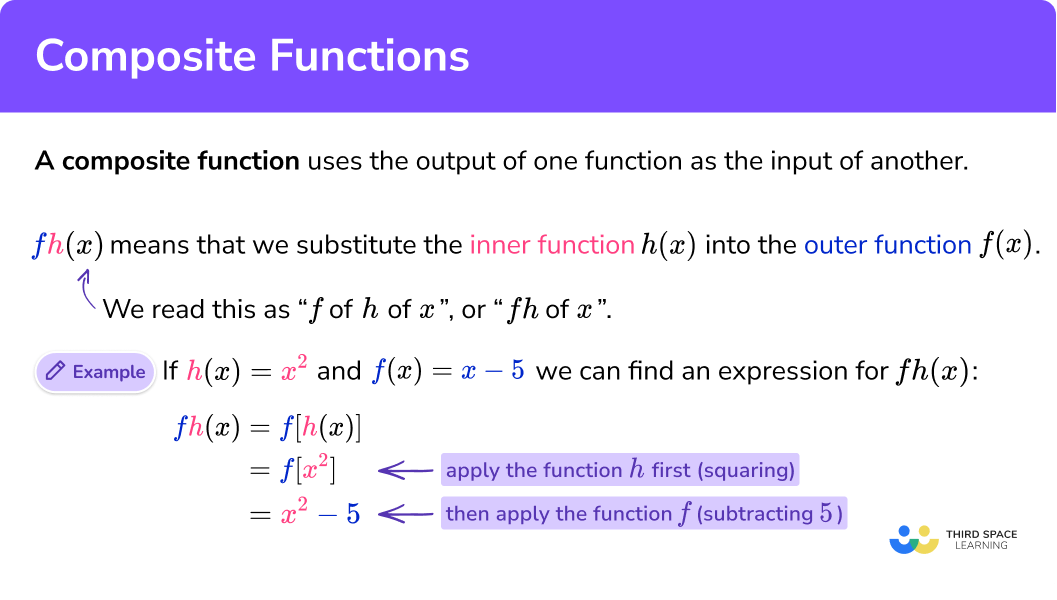
If we have a function f and another function g , the function fg(x) ,
said as “ f of g of x ”, or “ fg of x ”, is the composition of the two functions.
The order of how the functions are applied is important.
We are finding a function of a function, and if we have two or more functions, there could be many different permutations of those functions leading to many different composite functions.
fg(x) could be written as f[g(x)] which shows that the inner function must be applied before the outer function. We can evaluate composite functions for numerical values or find the algebraic expression for the new function.
To evaluate a composition of functions for a numerical value we can just substitute the value into the inside function and then use the result of that function to substitute into the outside function.
E.g.
Here the function h is described by h(x)=x^2 and the function f by f(x)=x-5 .
We can find hf(2) by finding f(2) , which gives us −3 ,
and then finding h(−3) which gives us 9.
If we want to find the expression for the function fh(x) , we can replace the x in the expression for f(x) with the expression for h(x) .
There are other types of notation that can be used for composite functions.
E.g.
The composition of functions f and g can be written using a small circle,
(f ∘ g)(x)=fg(x) .
In A level mathematics we look at composite functions in more depth by finding the derivatives of composite functions using a process called the chain rule. The derivative of a function gives us an expression for the function’s gradient at any point.
What are composite functions?
How to evaluate composite functions
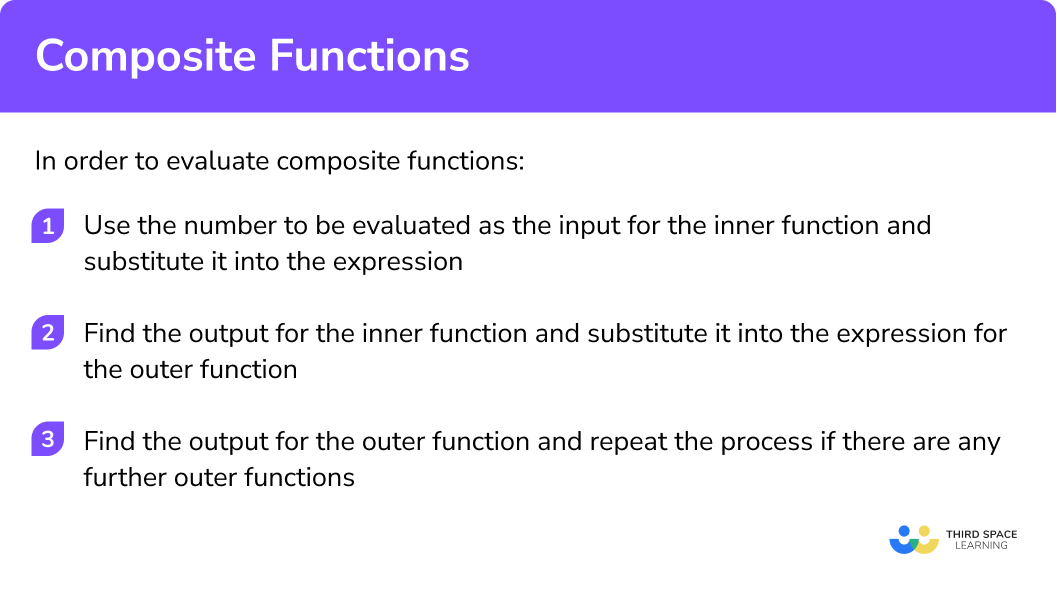
In order to evaluate composite functions:
- Use the number to be evaluated as the input for the inner function and substitute it into the expression.
- Find the output for the inner function and substitute it into the expression for the outer function.
- Find the output for the outer function and repeat the process if there are any further outer functions.
Explain how to evaluate composite functions
Composite functions worksheet

Get your free composite functions worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Composite functions worksheet

Get your free composite functions worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on functions in algebra
Composite functions is part of our series of lessons to support revision on functions in algebra. You may find it helpful to start with the main functions in algebra lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Evaluating composite functions examples
Example 1: Evaluating composite functions
If f(x)=4x and g(x)=x^2-1 , find fg(4) :
- Use the number to be evaluated as the input for the inner function and substitute it into the expression.
2Find the output for the inner function and substitute it into the expression for the outer function.
\begin{aligned} & g\left( 4 \right)=15 \\ \\ & f\left( 15 \right)=4\left( 15 \right) \end{aligned}3Find the output for the outer function and repeat the process if there are any further outer functions.
f(15)=60, \text{ so } fg(4)=60Example 2: Evaluating composite functions
If f(x)=2x+1 find ff(3) :
Use the number to be evaluated as the input for the inner function and substitute it into the expression.
Find the output for the inner function and substitute it into the expression for the outer function.
Find the output for the outer function and repeat the process if there are any further outer functions.
Example 3: Evaluating composite functions
If f(x)=3x+2, g(x)=x^{2} and h(x)=\frac{x}{2}, find hfg(-5) :
Use the number to be evaluated as the input for the inner function and substitute it into the expression.
Find the output for the inner function and substitute it into the expression for the outer function.
Find the output for the outer function and repeat the process if there are any further outer functions.
Repeat Step 2 for h(77)
h(77)=\frac{77}{2}=38.5
So hfg(-5)=38.5
How to find composite functions
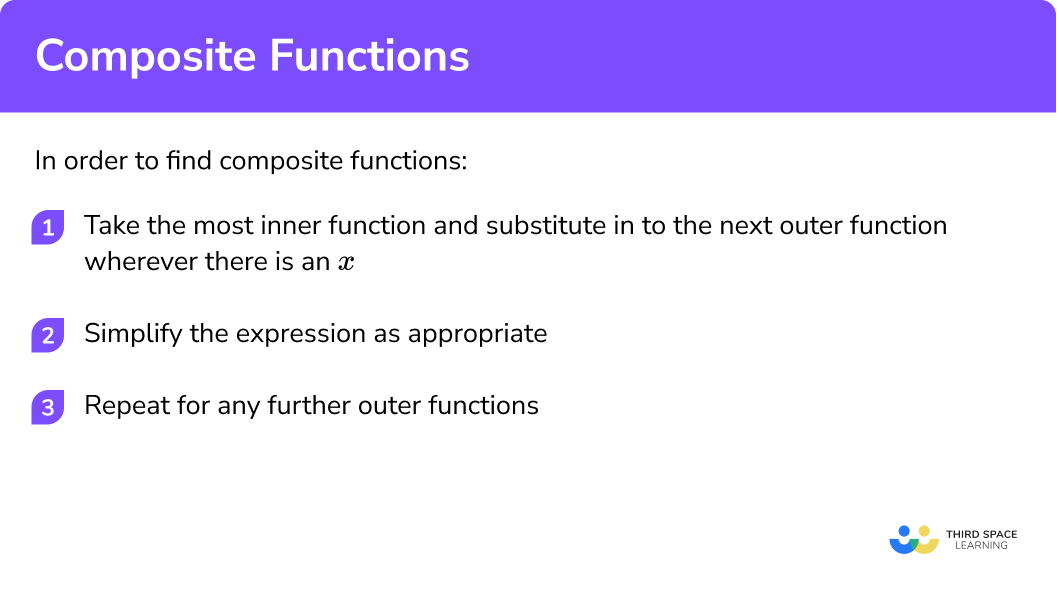
In order to find composite functions:
- Take the most inner function and substitute in to the next outer function wherever there is an x .
- Simplify the expression as appropriate.
- Repeat for any further outer functions.
Explain how to find composite functions
Finding composite functions examples
Example 4: Finding composite functions
If f(x)=3x-1 and g(x)=x^2+2, find fg(x) :
Take the most inner function and substitute in to the next outer function wherever there is an x.
Simplify the expression as appropriate.
Repeat for any further outer functions.
No further outer functions, so fg(x)=3x^2+5 .
Example 5: Finding composite functions
If f(x)=2x+1 and g(x)=x^2, find gf(x) :
Take the most inner function and substitute in to the next outer function wherever there is an x.
Simplify the expression as appropriate.
Repeat for any further outer functions.
No further outer functions, so gf(x)=4x^2+4x+1.
Example 6: Finding composite functions
If f(x)=x+2, g(x)=x^2+1 and h(x)=3x, find fgh(x):
Take the most inner function and substitute in to the next outer function wherever there is an x.
Simplify the expression as appropriate.
Repeat for any further outer functions.
So, fgh(x)=9x^2+3 .
Common misconceptions
- Mistaking composite functions for the product of the functions
A common mistake is to think that fg(x) means f(x) \times g(x) .
E.g.
If f(x)=x+1 and g(x)=2x-3 , the error will be to think that
fg(x)=(x+1)(2x-3) , rather than the correct answer of fg(x)=2x-2 .
- The functions are applied from left to right instead of right to left
A common error is to apply the functions in the wrong order.
fgh(x) means we should apply the functions in the order h , then g , then f , which is right to left.
A common mistake is to apply them from left to right. Thinking of fgh(x) as f[g(h(x))] can help to use the functions in the correct order, i.e. starting with the innermost function and working outwards.
Practice composite function questions
1. Evaluate gf(2) when f(x)=3x+5 and g(x)=2x-1




f(2)=11 , then g(11)=21.
2. Evaluate fg(-3) when f(x)=5x-2 and g(x)=x^2+1




g(-3)=10 , then f(10)=48.
3. Evaluate ghf(4) when f(x)=x-3, g(x)=x^2 and h(x)=5x




f(4)=1 , then h(1)=5, then g(5)=25.
4. Find gf(x) when f(x)=4x+6 and g(x)=\frac{x}{2}-3




5. Find fg(x) when f(x)=x^2-1 and g(x)=2x+3




6. Find hgf(x) when f(x)=x+1, g(x)=x^2 and h(x)=7x




Composite functions GCSE questions
1. f(x)=3x+1 and g(x)=x^2+2 .
(a) Find gf(-2)
(b) Find an expression for fg(x).
(4 marks)
(a)
f(-2)=-5
(1)
g(-5)=27
(1)
(b)
g(x) substituted into f, 3(x^2+2)+1
(1)
3x^2+7
(1)
2. f(x)=2x^2-1, g(x)=x+6, h(x)=3(x-4)
(a) Find ghg(3)
(b) Write an expression for hfg(x).
(6 marks)
(a)
hg(3)=15
(1)
ghg(3)=21
(1)
(b)
g correctly substituted into f, fg(x)=2(x+6)^2-1
(1)
fg(x) simplified , fg(x)=2x^2+24x+71
(1)
fg correctly substituted into h
(1)
Fully simplified answer hfg(x)=6x^2+72x+201
(1)
3. f(x)=2x+1 and g(x)=x^2-2
(a) Find fg(x)
(b) Find when fg(x)=gf(x)
(6 marks)
(a)
2(x^2-2)+1
(1)
2x^2-3
(1)
(b)
gf(x)=(2x+1)^2-2
(1)
Set equal 2x^2-3=4x^2+4x-1
(1)
Attempt to solve/ factorise
2(x+1)(x+1)=0
(1)
x=-1(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Where appropriate, interpret simple expressions as functions with inputs and outputs
- Interpret the succession of two functions as a ‘composite function’
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.
Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.