GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Arithmetic Powers and roots BIDMAS SubstitutionThis topic is relevant for:

Function Notation
Here we will learn about function notation, including different forms of function notation, how to evaluate functions for given values and how to manipulate algebraic expressions using functions.
There are also function notation worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is function notation?
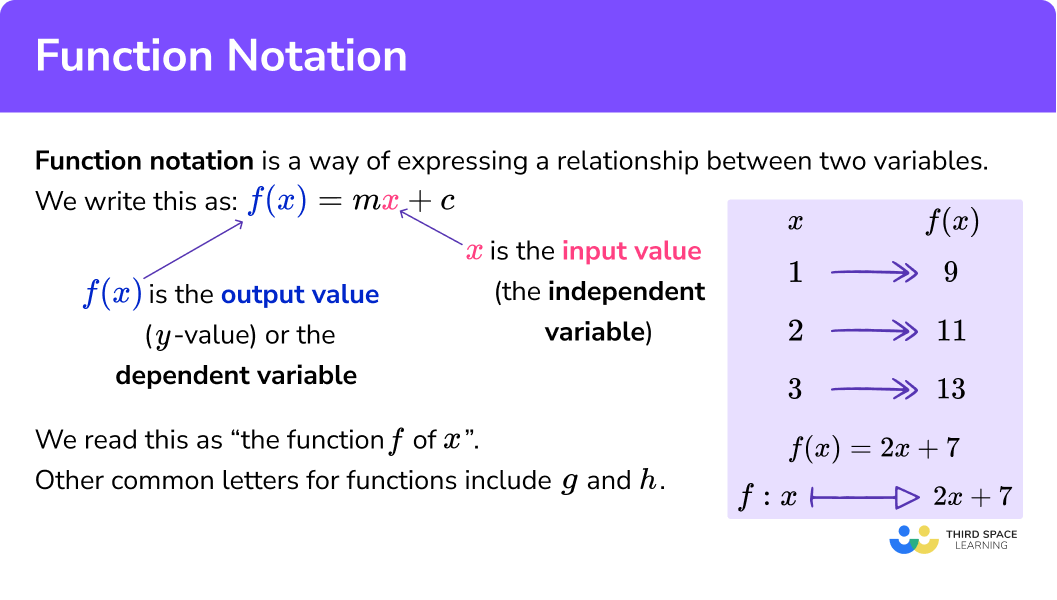
Function notation is a way of expressing a relationship between two variables.
We are used to writing equations of straight lines in the form y = mx + c .
Using function notation we can write this as f(x) = mx + c , by replacing y with f(x) .
We can read this as “ the function f of x ”.
“f” can be thought of as the “name” of the function. We do not always have to use f for the name of the function; other common names include function g or function h.
The x is the input value known as the independent variable.
f(x) is the output value ( y -value) known as the dependent variable.
To use function notation we just substitute the values of x into the expression and evaluate it.
The diagram shows the value of a function for different x -values:
There are different types of function notation. As well as examples like g(x) = x^2 + 2 , we may also see it given as g : x → x^2 + 2 . This type of function notation that is more common in A level mathematics.
Function notation is also used in the table function of a scientific calculator. The table function is useful for finding values when graphing linear equations, quadratics, cubics and other polynomials.
What is function notation?
How to use function notation
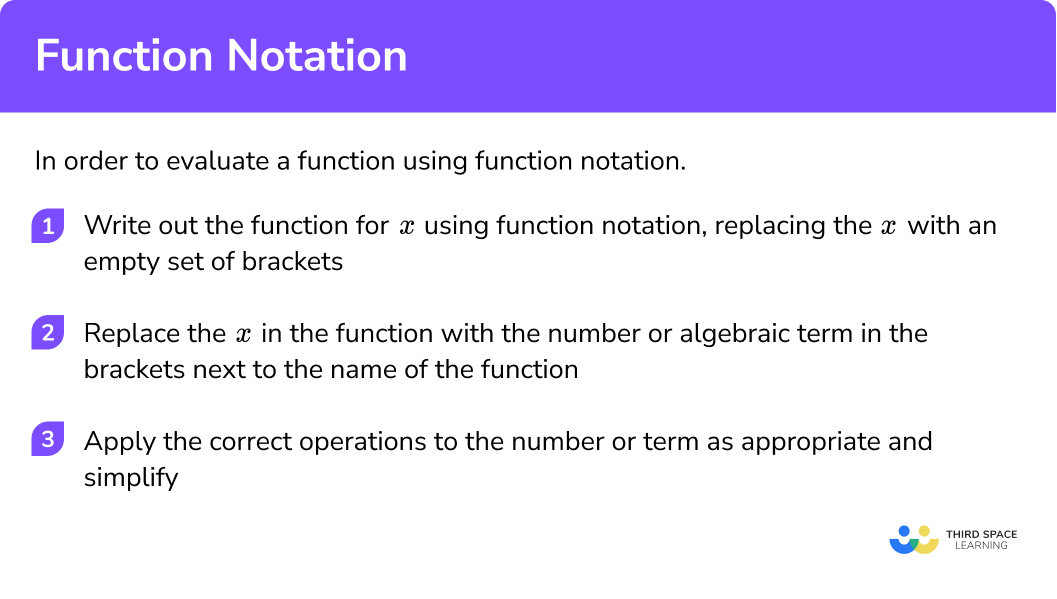
In order to evaluate a function using function notation:
- Write out the function for x using function notation, replacing the x with an empty set of brackets (parentheses).
- Replace the x in the function with the number or algebraic term in the brackets next to the name of the function.
- Apply the correct operations to the number or term as appropriate and simplify.
Explain how to use function notation

Function notation worksheet

Get your free function notation worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Function notation worksheet

Get your free function notation worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on functions in algebra
Function notation is part of our series of lessons to support revision on functions in algebra. You may find it helpful to start with the main functions in algebra lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Function notation examples
Example 1: evaluating linear functions for numerical values
Find f(3) when f(x)= 4x - 1
- Write out the function for x using function notation, replacing the x with an empty set of brackets.
2Replace the x in the function with the number or algebraic term in the brackets next to the name of the function.
f\left( 3 \right)=4\left( 3 \right)-13Apply the correct operations to the number or term as appropriate and simplify.
f\left( 3 \right)=11Example 2: evaluating quadratic functions for numerical values
Find g(-2) when g(x) = x^2 + 4
Write out the function for x using function notation, replacing the x with an empty set of brackets.
Replace the x in the function with the number or algebraic term in the brackets next to the name of the function.
Apply the correct operations to the number or term as appropriate and simplify.
Example 3: evaluating cubic functions for numerical values
Find h(8) when h(x) = x^3 - 3x
Write out the function for x using function notation, replacing the x with an empty set of brackets.
Replace the x in the function with the number or algebraic term in the brackets next to the name of the function.
Apply the correct operations to the number or term as appropriate and simplify.
Example 4: evaluating linear functions for algebraic expressions
Find f(2m) when f(x) = 5x + 7
Write out the function for x using function notation, replacing the x with an empty set of brackets.
Replace the x in the function with the number or algebraic term in the brackets next to the name of the function.
Apply the correct operations to the number or term as appropriate and simplify.
Example 5: evaluating quadratic functions for algebraic expressions
Find g(a+3) when g(x) = x^2 - 1
Write out the function for x using function notation, replacing the x with an empty set of brackets.
Replace the x in the function with the number or algebraic term in the brackets next to the name of the function.
Apply the correct operations to the number or term as appropriate and simplify.
Common misconceptions
- Function notation is mistaken for a product
It is common for f(x) to be thought of as “ f times x ” rather than “ f of x ”.
This confusion can lead to incorrect evaluations of values.
E.g.
When finding f(2) when f(x)=x+3 , a mistake may be to think that f(2) means 2(x+3) .
Whereas the correct solution is:
\begin{aligned} &f(x)=x+3 \\ &f(2)=2+3 \\ &f(2)=5 \end{aligned}Practice function notation questions
1. Find f(4) when f(x)=2x+8




Replace the x with 4 and simplify.
2. Find g(7) when g(x)=5(x-1)




Replace the x with 7 and simplify.
3. Find h(-5) when h(x)=x^2+x+3




Replace the x with -5 and simplify.
4. Find f(3n) when f(x)=6(x+2)




Replace the x with 3n , expand the brackets and simplify.
5. Find g(4k+1) when g(x)=5x-2




Replace the x with 4k+1 , expand the brackets and simplify.
6. Find h(a-2) when h(x)=x^2+5




Replace the x with a-2 , expand the brackets and simplify.
Function notation GCSE questions
1. Given that f(x)=5x-2
(a) Find f(-4)
(b) Find x when f(x)=8
(3 marks)
(a)
(1)
(b)
Equation formed 5x-2=8
(1)
Answer x=2
(1)
2. (a) If f(x)=4x+1 , write a simplified expression for f(2a-1)
(b) If h(x)=x^2+2x-3 , write a simplified expression for h(2m+3)
(5 marks)
(a)
Substitution seen 4(2a-1)+1
(1)
8a-3
(1)
(b)
Substitution seen (2m+3)^2+2(2m+3)-3
(1)
Expanded brackets 4m^2+12m+9+4m+6-3
(1)
Simplified expression 4m^2+16m+12
(1)
3. Given that f(x)=x^2+2 and g(x)=3(x+4).
Find the value of x which satisfies f(x)=g(x)
(4 Marks)
Set equal x^2+2=3(x+4)
(1)
Form quadratic x^2-3x-10=0
(1)
Factorise (x-5)(x+2)=0
(1)
Both solutions x=5,-2
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Where appropriate, interpret simple expressions as functions with inputs and outputs
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.
Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.