GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Arithmetic Laws of indices Square numbers and square roots BIDMASThis topic is relevant for:

Algebraic Terms
Here we will learn about algebraic terms, including how to distinguish them, state their variables and coefficients, and identify like terms.
There are also algebraic terms worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are algebraic terms?
Algebraic terms are individual letters, groups of letters, or groups of letters and numbers separated by addition or subtraction in algebraic expressions.
For example, this is an algebraic expression with three algebraic terms.

Term 1 \;\;\; Term 2 \;\;\; Term 3
Individual algebraic terms can look very different to one another, so here is a list of some of the types you may come across.
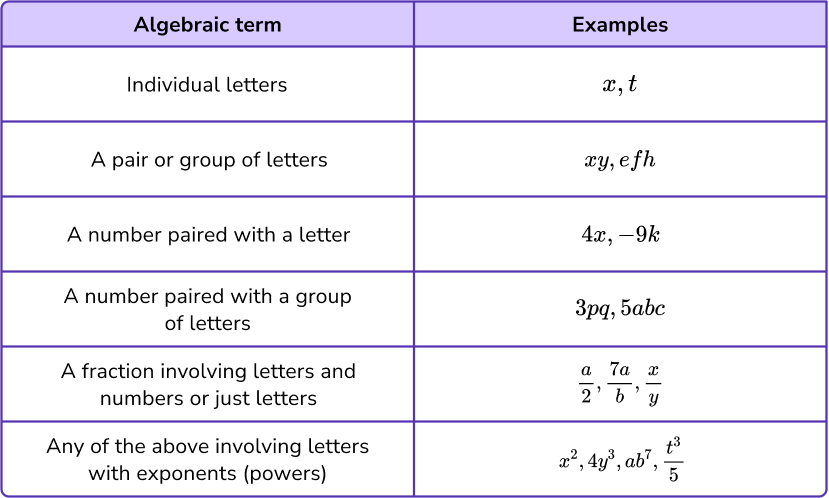
Note that individual numbers are known as constant terms, such as 8 or \frac{4}{9}.
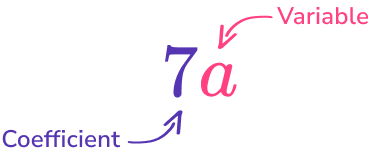
Coefficients and variables
Every algebraic term has a coefficient (the number in the term) and a variable (the letter or letters in the term).
Here are some examples,
For the term 3x
The variable is x.
The coefficient of this ‘ x -term’ is 3.
For the term -5ab
The variables are a and b.
The coefficient of this ‘ ab -term’ is -5.
For the term 7h^2
The variable is h^2.
The coefficient of this ‘ h^2 -term’ is 7.
For the term \frac{y}{4}
The variable is y.
The coefficient of this ‘ y -term’ is \frac{1}{4}.
(Note that \frac{y}{4} can also be written as \frac{1}{4}y.)
For the term t
The variable is t.
The coefficient of this ‘ t -term’ is 1.
(Note that the coefficient of 1 is never written next to the variable in an algebraic term.)
Like terms
Like terms are terms that have the same variable or variables. They can however have different coefficients.
For example, 7h, \ -2h and h are all ‘like terms’ because they all have the same variable ‘ h ’.
For example, 3a^5, \ 12a^5 and \frac{a^5}{7} are all ‘like terms’ because they all have the same variable ‘ a^5 ‘.
Note that 3a and 7ab are not like terms. Although they both have variable a, to be like terms all variables must match.
Note that all constant terms are like terms.
Once you can identify like terms the next step is to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms.
Step-by-step guide: Collecting like terms
Algebraic expressions
Algebraic expressions are made up of one or more algebraic terms which are separated by addition or subtraction signs. Algebraic expressions may also include constant terms.
Monomial expressions have one term.
For example, 6n.
Binomial expressions are made up of two terms.
For example, 3x-12.
Trinomial expressions are made of three terms.
For example, x^2 + 2x - 3.
Step-by-step guide: Algebraic expressions
Note that algebraic expressions do not have equal signs. If algebraic expressions or individual terms are written as equal to each other then the result would be an algebraic equation.
For example, 5x-8=12.
Step-by-step guide: Solving equations
See also: Rearranging equations
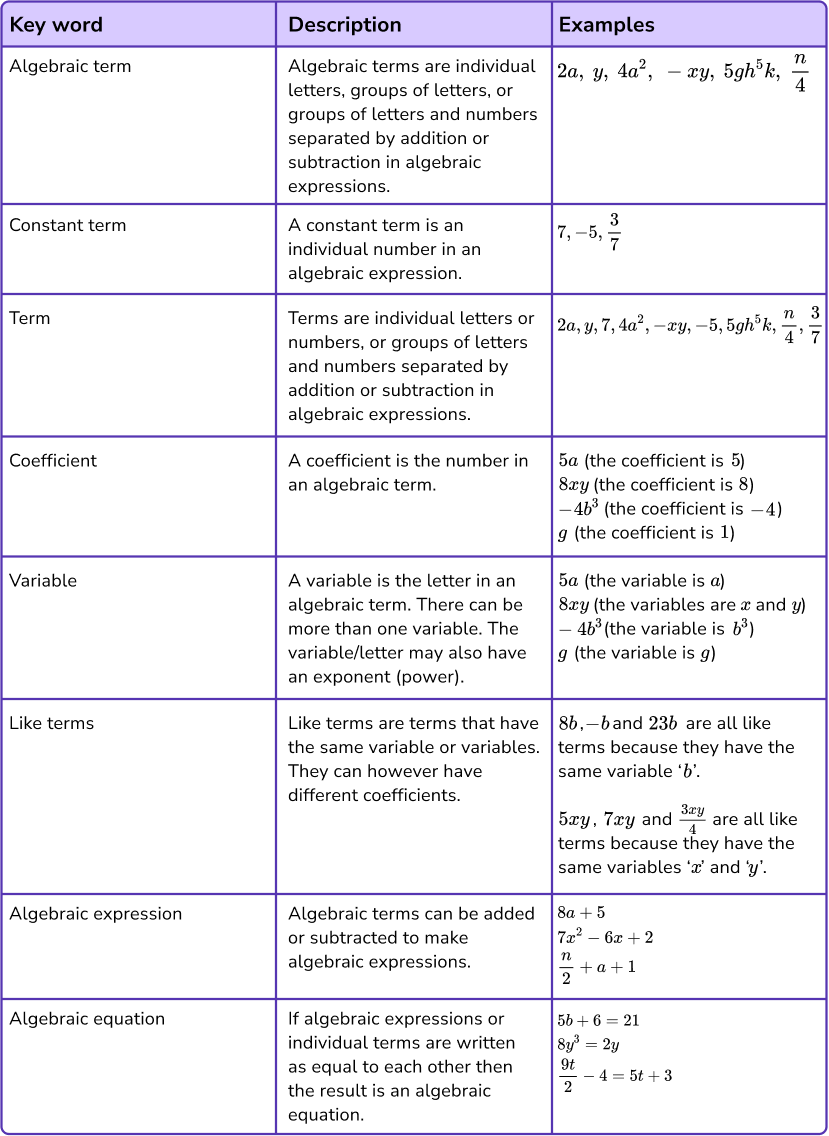
Keyword Summary
Here is a summary of the key words often used when working with algebraic terms.
Additional notes about algebraic terms
- In algebra, when numbers and letters are written next to each other it indicates that they are multiplied together. For example, the algebraic term 5a means 5 \times a.
- When letters, or numbers and letters, are written in fraction form, it means one is being divided by the other. For example, the algebraic term \frac{x}{4} means x \div 4.
- If an algebraic term is made up of a letter and a number, the number always goes at the start of the term. For example, for a \times 4 you should write 4a and not a4.
- If an algebraic term has more than one letter then the letters should be placed in alphabetical order. For example, 5ba is incorrect and should be written as 5ab.
- When a term is subtracted in an algebraic expression, that term must be considered ‘negative’ when identifying separate terms. In other words, the sign before the term belongs to that term. For example, 5a-7b. The first term is 5a and the second term is -7b, not just 7b.
- Multiplication is commutative; therefore reordering letters and numbers that are written next to each other does not change the overall value of the algebraic term.
Step-by-step guide: Simplifying expressions
What are algebraic terms?
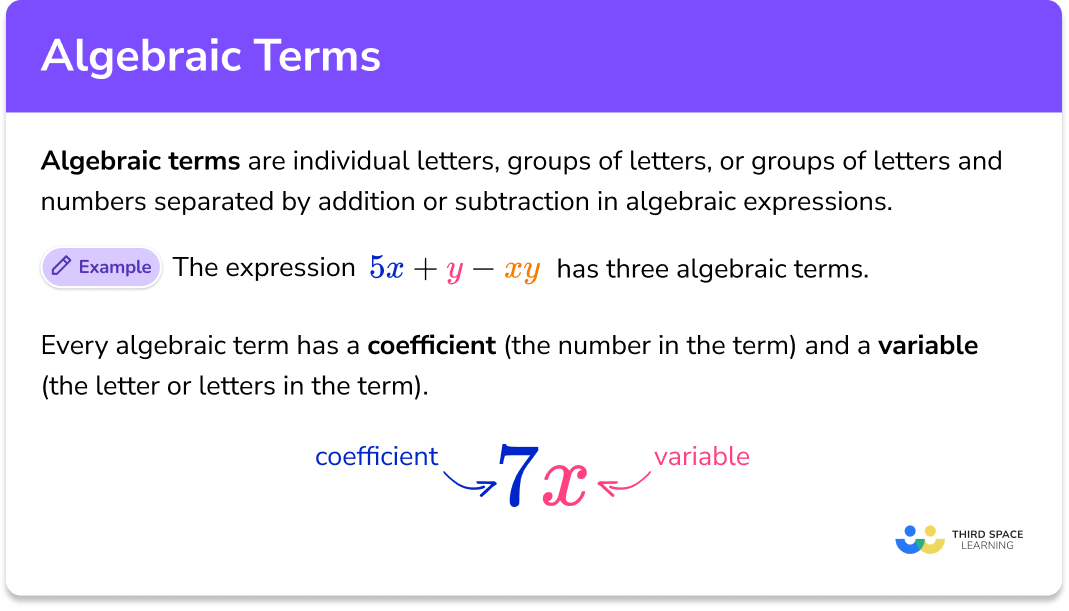
How to identify and describe algebraic terms
In order to identify and describe algebraic terms in algebraic expressions:
- Count the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
- State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
- Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
Explain how to identify and describe algebraic terms

Algebraic expressions worksheet (includes algebraic terms)

Get your free algebraic terms worksheet of 20+ algebraic expressions questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Algebraic expressions worksheet (includes algebraic terms)

Get your free algebraic terms worksheet of 20+ algebraic expressions questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREEAlgebraic terms examples
Example 1: linear algebraic expression with integer coefficients
For this algebraic expression, state the number of terms, the coefficient and variable/s of each term and identify if there are any like terms.
5a+7ab-6- Count the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
There are three terms in this expression.
2State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
Term 5a. Variable is a. Coefficient is 5.
Term 7ab. Variables are a and b. Coefficient is 7.
Term -6. This is a constant term.
3Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
None of the terms have identical variables so there are no like terms.
Example 2: linear algebraic expression with integer coefficients
For this algebraic expression, state the number of terms, the coefficient and variable/s of each term and identify if there are any like terms.
8x+4x-x+3Count the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
There are four terms in this expression.
State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
Term 8x. Variable is x. Coefficient is 8.
Term 4x. Variable is x. Coefficient is 4.
Term -x. Variable is x. Coefficient is -1.
Term 3. This is a constant term.
Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
Terms 8x, \ 4x and -x all have the variable x and are therefore like terms.
We can collect like terms by adding the coefficients together.
8+4+-1=11
Therefore the expression can be simplified to 11x+3.
Example 3: non-linear algebraic expression with integer coefficients
For this algebraic expression, state the number of terms, the coefficient and variable/s of each term and identify if there are any like terms.
n^{3}+5nCount the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
There are two terms in this expression.
State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
Term n^{3}. Variable is n^{3}. Coefficient is 1.
Term 5n. Variable is n. Coefficient is 5.
Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
Although both terms have the letter ‘ n ’, the variables are not identical. n^{3} and n are different variables. So there are no like terms in this expression.
Example 4: linear algebraic expression including non-integer coefficients
For this algebraic expression, state the number of terms, the coefficient and variable/s of each term and identify if there are any like terms.
3k+\frac{k}{2}-4Count the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
There are three terms in this expression.
State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
Term 3k. Variable is k. Coefficient is 3.
Term \frac{k}{2}. Variable is k. Coefficient is \frac{1}{2}. Note that \frac{k}{2} can be written as \frac{1}{2}k. Remember dividing by 2 is the same as multiplying by a half.
Term -4. This is a constant term.
Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
Terms 3k and \frac{k}{2} have the variable k and are therefore like terms.
We can collect like terms by adding the coefficients together.
3+\frac{1}{2}=3\frac{1}{2}=\frac{7}{2}
Therefore the expression can be simplified to \frac{7k}{2}.
Example 5: non-linear algebraic expression including non-integer coefficients
For this algebraic expression, state the number of terms, the coefficient and variable/s of each term and identify if there are any like terms.
6x^{2}-7xy^{2}+\frac{6x^{2}y}{7}+x^{2}+\frac{7}{6}Count the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
There are 5 terms in this expression.
State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
Term 6x^{2}. Variable is x^{2}. Coefficient is 6.
Term -7xy^{2}. Variable is x and y^{2}. Coefficient is -7.
Term \frac{6x^{2}y}{7}. Variable is x^{2} and y. Coefficient is \frac{6}{7}.
Term x^{2}. Variable is x^{2}. Coefficient is 1.
Term \frac{7}{6}. This is a constant term.
Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
Terms 6x^{2} and x^{2} have the variable x^{2} and are therefore like terms.
We can collect like terms by adding the coefficients together.
6+1=7
Therefore 6x^{2}+x^{2}=7x^{2}
and the full expression can simplify to
7x^{2}-7xy^{2}+\frac{6x^{2}y}{7}+\frac{7}{6}.
Example 6: algebraic expression involving brackets and fractions
For this algebraic expression, state the number of terms, the coefficient and variable/s of each term and identify if there are any like terms.
\frac{5a-3}{2}+4(a+1)Count the number of individual terms that are separated by addition/subtraction in the algebraic expression.
This expression needs to be visually altered in order to count the number of terms. First we need to write the fraction as two separate fractions as there is a subtraction sign in the numerator. Then we need to expand the brackets.
\frac{5a-3}{2}+4(a+1)=\frac{5a}{2}-\frac{3}{2}+4a+4
We can now see that the expression has 4 terms.
State the coefficient (the number) and variable/s (the letter/s) of each algebraic term identified in step 1. Also note any constant terms.
Term \frac{5a}{2}. Variable is a. Coefficient is \frac{5}{2}.
Term -\frac{3}{2}. This is a constant term.
Term 4a. Variable is a. Coefficient is 4.
Term 4. This is a constant term.
Check if any of the terms have identical variables and if so, state that they are like terms.
Terms \frac{5a}{2} and 4a have the variable a and are therefore like terms.
We can collect like terms by adding the coefficients together.
\frac{5}{2}+5=\frac{5}{2}+\frac{8}{2}=\frac{13}{2}
Therefore
\frac{5a}{2}+4a=\frac{13a}{2}.
Terms -\frac{3}{2} and 4 are both constant terms.
We can therefore add these together.
-\frac{3}{2}+4=\frac{-3}{2}+\frac{8}{2}=\frac{5}{2}
The full expression can simplify to
\frac{13a}{2}+\frac{5}{2} \ or \ \frac{13a+5}{2}.
Step-by-step guide: Expanding brackets
Common misconceptions
- Forgetting to state the coefficient as negative when a term is subtracted in an algebraic expression
For example, for the expression 7a-8b students may incorrectly state the coefficient of the b- term as 8. Remember that the sign written before a term belongs to that term. The correct coefficient for the b- term is -8.
- Thinking the coefficient is missing when actually it is 1
Students can sometimes think the coefficient is missing or perhaps it is 0 when there is no number written in front of the variable/s, for example, terms abc and n^{2}.
However both of these terms actually have coefficients of 1.
Also, watch out for negative terms, for example the term -x has a coefficient of -1.
- Incorrectly identify like terms because terms have a letter in common
For example, students may think 5x and 3xy are like terms because they both have the letter x. This is incorrect. Variables must be identical for terms to be considered like terms.
Another common error involves variables with exponents.
For example some students may think a^2 and a are like terms because they both have the letter a and no other letters/variables. However, a^{2} and a are distinct variables and are not like terms.
Practice algebraic terms questions
1. What is the coefficient of the algebraic term 5ab?




A coefficient is the number in the term.
2. How many terms does this algebraic expression have?
6a+b-3




The first term is 6a, the second term is b and the third term is -3. So there are 3 terms.
3. What is the coefficient of the x- term in this algebraic expression?
4xy + 6x + 2




An x- term is a term which has an ‘ x ’ in it and no other letters or exponents. The question is referring to the term 6x, and therefore the coefficient (the number in the term) is 6.
4. How many terms are in this expression?
6x+k^{3}+c-7




The first term is 6x, the second term is k^{3}, the third term is c and the fourth term is -7. So there are 4 terms.
5. What is the coefficient of the a- term in this algebraic expression?
7ab+a-b+4




An a- term is a term which has an ‘ a ’ in it and no other letters or exponents. The letter a is written on its own without a number. This indicates that there is only one a, and therefore the coefficient is 1.
6. How many terms are in this expression?
4(x+5)-y




Expanding the brackets gives 4x+20-y.
The first term is 4x, the second term is 20 and the third term is -y. So there are 3 terms.
7. What is the coefficient of the x^{2}- term in this algebraic expression?
4-4xy-12x^{2}




An x^{2}- term is a term which has an ‘ x^{2} ’ in it and no other letters or exponents. The question is referring to the term -12x^{2}, and therefore the coefficient (the number in the term) is -12.
Remember that the sign written before a term belongs to that term which is why the answer is -12 and not just 12.
8. Which of the following are like terms with 7ah?
All three of these terms.




7ah and 5ah are like terms because they have exactly the same variables. They both have a and h with no other letters or exponents.
9. What is the constant term in this algebraic expression?
9b+\frac{4}{b}+7




The constant term is 7 because it is an individually written number with no letters attached to it.
10. Are any of the terms in this expression like terms?
8fg+2f-8g+2g^{2}
Yes, 8fg and -8g

Yes, 8fg+ 2f-8g

No

Yes, 8g+2g^{2}

None of these terms are like terms because they don’t have identical variables. Some terms have a letter in common but to be like terms they must have exactly the same letters and exponents.
Algebraic terms GCSE questions
1. Here are five algebraic terms.

(a) What is the coefficient of term 1?
(b) Which two terms are like terms?
(2 marks)
(a) \frac{5}{2} \ or \ 2.5 .
(1)
(b) Term 1 and Term 5 .
(1)
2. Here is an algebraic expression.
2y(3y+4)
(a) Expand the brackets.
(b) What is the coefficient of the y- term in the algebraic expression?
(3 marks)
(a) 6y^{2}+8y
(2)
(b) 8
(1)
3. The table shows some algebraic terms.
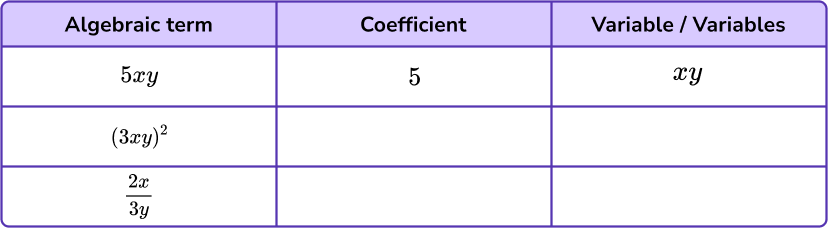
(a) Complete the table. The first one has been done for you.
(b) Dylan says “All the terms in the table are like terms because they all have an x and a y in them”.
Is Dylan correct? Give reasons for your answer.
(5 marks)
(a)
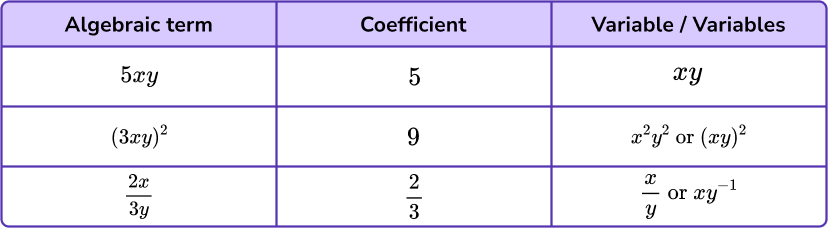
For both coefficients correct.
(1)
One mark for each correct variable.
(2)
(b) Dylan is incorrect.
(1)
None of the terms in the table are like terms because they don’t have identical variables.
They all use the same letters but to be like terms they must have exactly the same letters and exponents.
OR
The terms have the same letters but they have different exponents (powers) so they are not identical and are therefore not like terms.
OR
The terms have the same letters but the second term has its letters squared and the third term has a fraction.
Therefore they are not identical variables so they are not like terms.
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Identify algebraic terms and state their variables and coefficients
- Count the number of algebraic terms and constant terms in algebraic expressions
- Identify like terms
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.
Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.