GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Segment of a circle Circles, sectors and arcs Parts of a circleThis topic is relevant for:

How To Draw A Hexagon
Here we will learn about how to draw a hexagon using a pencil, a ruler and a pair of compasses.
There are also constructions worksheets, including how to draw a hexagon, based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
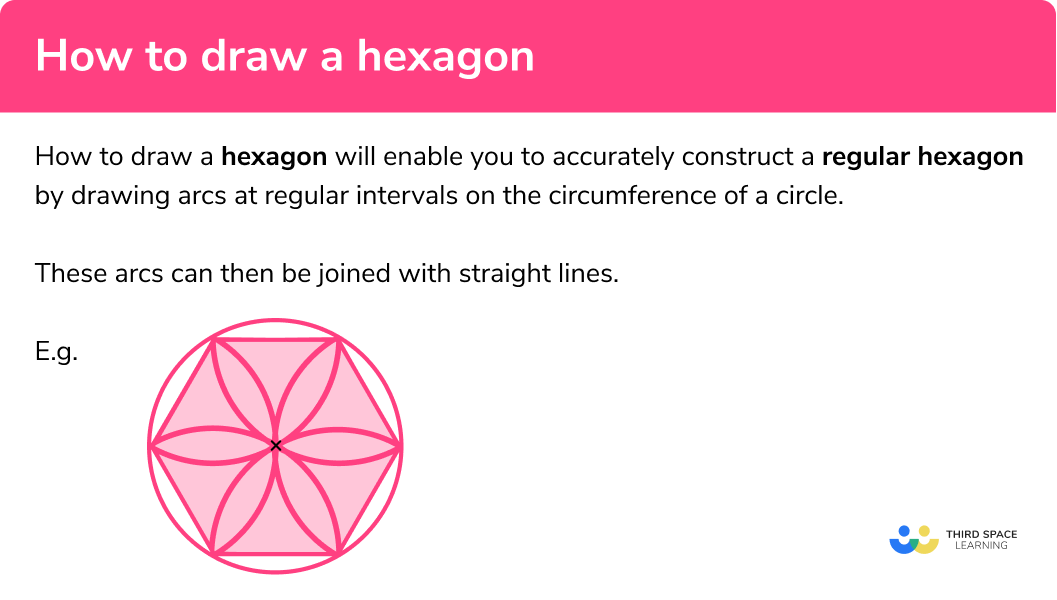
How to draw a hexagon
In order to draw a hexagon you need to accurately construct 6 arcs at regular intervals on the circumference of a circle. These arcs can then be joined with straight lines.
To do this we need to use a pencil, a ruler (a straight-edge) and compasses.
E.g.
A regular hexagon is a regular polygon with 6 sides and 6 vertices. It has equal sides and equal angles.
An equilateral triangle can be constructed in a similar way.
Equilateral triangles, squares and regular hexagons along with other regular polygons including regular pentagons, regular heptagons and regular octagons can be constructed and have been used in art for many centuries.
What is how to draw a hexagon?
How to draw a hexagon
In order to draw hexagons:
- Draw a circle.
- Make arcs around the circle.
- Join the points.
How to draw a hexagon

Construction worksheet (includes how to draw a hexagon)

Get your free how to draw a hexagon worksheet of 20+ construction questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Construction worksheet (includes how to draw a hexagon)

Get your free how to draw a hexagon worksheet of 20+ construction questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on constructions
How to draw a hexagon is part of our series of lessons to support revision on construction and loci and construction. You may find it helpful to start with the main loci and construction lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
How to draw a hexagon examples
Example 1: draw a hexagon
Construct a hexagon
- Draw a circle.
Here is the first how to draw a hexagon step. Use compasses to draw a circle and mark the centre point with a cross.
2Make arcs around the circle.
Keep the compasses set the same, make a starting mark A and then draw arcs. Keep moving the compasses on until there are 6 marks on the circumference of the circle.
3Join the points.
With a straight-edge join the point where the arcs cross the circle.
By joining together the end points of the arcs we create a hexagon shape with equal side lengths.
Common misconceptions
- The compasses must be kept at the same setting
The circumference of a circle is approximately 6 times the length of the radius, so that is why we can have 6 arcs with the compasses around the circumference of the circle. When they are joined together this will give us 6 as the number of sides.
- The pencil should be sharp
A sharp pencil helps your diagram to be accurate. Using a small pencil in compasses can also be helpful.
- The points joined must be where the arcs cross the circle
Join up the intersections of the arcs for an accurate construction of the regular hexagon.
Practice how to draw a hexagon questions
How to draw a hexagon GCSE questions
1. Use compasses and a ruler to construct a hexagon.
Use this circle.
You must show all your construction lines.
(2 marks)
for 6 equally spaced arcs (the first may be a mark).
(1)
for the perfect hexagon drawn with straight lines and the construction arcs.
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Draw a perfect hexagon using constructions
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.
Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.

