GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Multiplying fractions Substitution Area How to work out perimeter Rounding decimals Significant figures Volume of a cylinderThis topic is relevant for:

Surface Area Of A Cone
Here we will learn about the surface area of a cone, including how to find the surface area given the radius and the slant height.
There are also cone worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is the surface area of a cone?
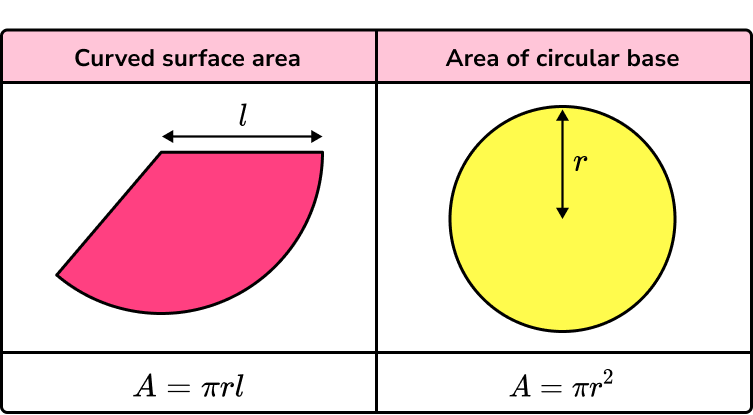
The surface area of a cone is the area which covers the outer surface of the cone.
For any cone, r is the radius of the base of the cone, l is the slant height of the cone, and h is the perpendicular height of the cone.
In order to calculate the total surface area of a cone we need to find the area of the two parts of the surface of the cone and add them together.
There is a curved surface area and a circular base. (The curved surface area of a cone is sometimes referred to as the lateral surface area of a cone).
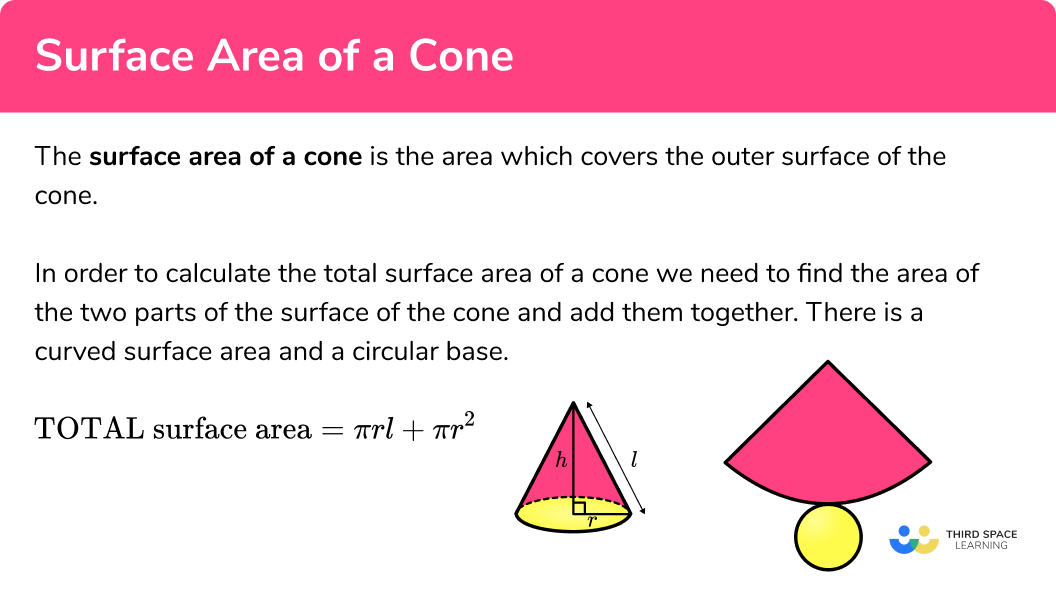
The surface area of a cone is the area of the two parts added together,
\text{Surface area of a cone}=\pi{r}{l}+\pi{r^{2}}
The perpendicular height of a cone h is not required to calculate the surface area of a cone, although it is used to calculate the volume of the cone.
Note: We cannot use the formula for the surface area of a cone written above for an oblique cone. This is because the curved surface area does not have a constant slant height l from the apex (a vertex) to the circular base.
What is the surface area of a cone?
Example
Calculate the surface area of the cone below to 1 decimal place.
Curved surface area =\pi{rl}=\pi\times{6}\times{8}=48\pi
Area of circular base =\pi{r^{2}}=\pi\times{6^{2}}=36\pi
We then add these together to find the total surface area of the cone,
Surface area of the cone = 48\pi + 36\pi = 84\pi = 263.9 cm^2 (1dp)
How to calculate the surface area of a cone
In order to calculate the surface area of a cone:
- Work out the area of each face.
- Add the areas together.
- Write the answer, including the units.
How to calculate the surface area of a cone

Surface area of a cone worksheet

Get your free surface area of a cone worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Surface area of a cone worksheet

Get your free surface area of a cone worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on cones
Surface area of a cone is part of our series of lessons to support revision on cone. You may find it helpful to start with the main cone lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Surface area of a cone examples
Example 1: curved surface area
Find the curved surface area of the cone below, with radius 3cm and slant height 7cm . Write your answer to 1 decimal place.
- Work out the area of each face.
We only need to calculate the area of the curved surface for this question.
2Add the areas together.
We only need to find the curved surface area, so we can move on to step 3 .
3Write the answer, including the units.
We need to round the answer to 1 decimal place and include the units.
21\pi=66.0 (1dp)The curved surface area of the cone is 66.0cm^2 (1dp) .
Note: If the question asks for 1 decimal place, the answer must have 1 decimal place, even if the digit is 0 .
Example 2: total surface area
Find the total surface area of the cone below to 1 decimal place.
Work out the area of each face.
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is
\frac{1547}{25}\pi+\frac{1156}{25}\pi=\frac{2703}{25}\pi .
Write the answer, including the units.
We need to write the answer to 1 decimal place.
\frac{2703}{25}\pi=339.7\ (1dp)The total surface area of the cone is 339.7cm^2 (1dp) .
Example 3: calculate the surface area in terms of pi
A chip shop sells mushy peas in a conical pot. The lid has a radius of 7cm , and the pot has a slant height of 10cm . Calculate the outside surface area of the closed pot, including the lid. Write your answer in terms of \pi .
Work out the area of each face.
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is
70\pi+49\pi =119\pi .
Write the answer, including the units.
We need to write the answer in terms of \pi , and state the units.
The total surface area of the cone is 119\pi cm^2 .
Example 4: surface area in terms of pi
The roof of a tower is a solid cone. The radius of the circular base is 4.5m , and the roof has a slope length of 8.3m . Calculate the surface area of the roof. Write your answer in the form \frac{a}{b}\pi where a and b are integers with no common factors.
Work out the area of each face.
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is equal to
\frac{747}{20}\pi+\frac{81}{4}\pi=\frac{747}{20}\pi+\frac{405}{20}\pi=\frac{1152}{20}\pi .
Write the answer, including the units.
We need to write the answer in the form \frac{a}{b}\pi where a and b are integers with no common factors. By simplifying the fraction fully, we get \frac{1152}{20}\pi=\frac{288}{5}\pi .
The surface area of the solid cone is \frac{288}{5}\pi\text{m}^{2} .
Example 5: calculate the surface area given the diameter
Calculate the surface area of a cone with a base diameter of 4cm and a slant height of 6cm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
Work out the area of each face.
We need to calculate the radius of the circular base first. As the diameter is twice the radius of a circle, we need to divide the diameter of the circle by 2 .
4\div2=2cmWe now have r=2cm .
Add the areas together.
Adding the two areas together, we get 12\pi + 4\pi = 16\pi .
Write the answer, including the units.
We need to write the answer to 3 significant figures, and state the units.
16\pi=50.2\ (3sf)The surface area of the cone is 50.2cm^2 (3sf) .
Example 6: curved surface area given the perpendicular height
A cone has a perpendicular height of 4cm , and a circular base with a radius of 3cm . The apex of the cone is directly above the centre of the circular base. Calculate the area of the curved surface in terms of \pi .
Work out the area of each face.
We need to know the slant height of the cone. Sketching a diagram of the cone with the dimensions given, we have
To find the slant height l , we need to use Pythagoras theorem.
a^2+b^2=c^2 . Given that a=4cm, b=3cm, and c=l , we have
Now we have the value for the slant height, we can find the curved surface area.
Add the areas together.
We only need to calculate the area of the curved surface so we can move on to step 3 .
Write the answer, including the units.
We need to leave the answer in terms of π and include the units.
The curved surface area of the cone is 15\pi cm^2 .
Common misconceptions
- Using the correct formula
There are several formulas that can be used, so we need to match the correct formula to the correct context.
- Rounding
Do not round the answer until the end of the calculation. This will mean your final answer is more accurate.
- Using the radius or the diameter
It is a common error to mix up radius and diameter. Remember the radius is half of the diameter.
- Make sure you have the correct unit
- For area we use square units such as cm^2, m^2 .
- For volume we use cube units such as cm^3, m^3 .
Practice surface area of a cone questions
1. Find the curved surface area of a cone of radius 10cm and slant height 12cm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.




We are finding the curved surface area of a cone so we substitute the value of r and l into the formula.
\text{Curved surface area}=\pi rl\\ =\pi \times 12\times 10\\ =120\pi\\ =376.9911184…\\ =377 \ cm^2 \ \text{(3sf)}
2. A cone has a radius of 7.8mm and a slant height of 9.6mm . Calculate the curved surface area of the cone, to 3 significant figures.




We are finding the curved surface area of a cone so we substitute the value of r and l into the formula.
\text{Curved surface area}=\pi rl\\ =\pi \times 7.8\times 9.6\\ =235.2424579…\\ =235 \ \text{mm}^2 \ \text{(3sf)}
3. A candle is made in the shape of a cone. The radius of the base is 4cm , and the slant height is 7cm . Calculate the surface area of the candle to 1 decimal place.




We are finding the total surface area of a cone so we find the curved surface area and add on the area of the circular base.
\text{Curved surface area}=\pi rl\\ =\pi \times 4 \times 7\\ = 28 \pi
\text{Area of circular base }=\pi r^2\\ =\pi \times 4^2\\ =16 \pi
The total surface area is 28\pi +16\pi =44\pi .
44\pi=138.2\text{cm}^{2}\ (1dp)
4. Find the total surface area of a cone of radius 6.5cm and slant height 9.3cm . Write your answer as a fraction in the form \frac{a}{b}\pi where a and b are integers. State the units in your answer.




We are finding the total surface area of a cone so we find the curved surface area and add on the area of the circular base.
\text{Curved surface area}=\pi rl\\ =\pi \times 6.5\times 9.3\\ =\frac{1209}{20}\pi
\text{Area of circular base }=\pi r^2\\ =\pi \times 6.5^2\\ =\frac{169}{4}\pi
The total surface area is \frac{1209}{20}\pi+\frac{169}{4}\pi=\frac{1207}{10}\pi .
Surface area is equal to \frac{1207}{10}\pi cm^2 .
5. A conical party hat has a diameter of 16cm , and a slant height of 11cm . An image is being placed on the entire outside surface of the party hat. What is the area of the image? Write your answer to in terms of \pi .




The diameter is twice the length of the radius and so r=16\div2=8cm . Substituting the values for r and l into the formula for the curved surface area we get,
\text{Curved surface area}=\pi rl\\ =\pi \times 8\times 11\\ =88\pi\\ =88\pi \ \text{cm}^2
6. A cone has a radius of 5cm and a perpendicular height of 12cm . The apex of the cone is directly above the centre of the circular base. Calculate the surface area of the cone to 3 significant figures.




Use Pythagoras theorem to calculate the slant height of the cone, then determine the surface area.
Pythagoras theorem is a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2} .
a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}\\ 5^{2}+12^{2}=l^{2}\\ 25+144=l^{2}\\ l^{2}=169\\ l=\sqrt{169}\\ l=13\text{cm}
The slant height l=13cm .
\text{Curved surface area}=\pi rl\\ =\pi \times 5\times 13\\ =65\pi
\text{Area of circular base }=\pi r^2\\ =\pi \times 5^2\\ =25\pi
The total surface area is 65\pi+25\pi=90\pi=283\ \text{(3sf)} .
The total surface area of the cone is 283cm^2 (3sf) .
Surface area of a cone GCSE questions
\text{Curved surface area of a cone}=\pi rl
1. Below is a diagram of a cone.
Calculate the curved surface area of the cone.
Write your answer to 3 significant figures.
(2 marks)
(1)
605.636…=606(1)
2. Here is a cone.
Calculate the total surface area of the cone.
Write your answer in terms of \pi .
(3 marks)
(1)
223.79\pi +\pi \times 13.9^{2}(1)
417\pi(1)
3. A cone has a diameter of 6cm and a slant height of 7cm . Calculate the total surface area of the cone. Write your answer to 1 decimal place.
(5 marks)
(1)
\pi \times 3 \times 7=21\pi(1)
\pi \times 3^{2}= 9\pi(1)
21\pi + 9\pi = 30\pi(1)
30\pi=94.2\text{cm}^{2}\ (1dp)(1)
4. A cone has a circular base with an area of 25\pi and a slant height of 6cm . Calculate the total surface area of the cone in terms of \pi .
(3 marks)
(1)
\pi\times{5}\times{6}=30\pi(1)
30\pi+25\pi=55\pi(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Calculate surface areas of cones
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.
Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.