FREE DOWNLOAD
Simple And Compound Interest Worksheet
Help your students prepare for their Maths GCSE with this free simple and compound interest worksheet of 44 questions and answers
- Section 1 of the simple and compound interest worksheet contains 36 skills-based simple and compound interest questions, in 3 groups to support differentiation
- Section 2 contains 4 applied simple and compound interest questions with a mix of worded problems and deeper problem solving questions
- Section 3 contains 4 foundation and higher level GCSE exam style simple and compound interest questions
- Answers and a mark scheme for all simple and compound interest questions are provided
- Questions follow variation theory with plenty of opportunities for students to work independently at their own level
- All questions created by fully qualified expert secondary maths teachers
- Suitable for GCSE maths revision for AQA, OCR and Edexcel exam boards
Unlock access to download your free resource
You can unsubscribe at any time (each email we send will contain an easy way to unsubscribe). To find out more about how we use your data, see our privacy policy.
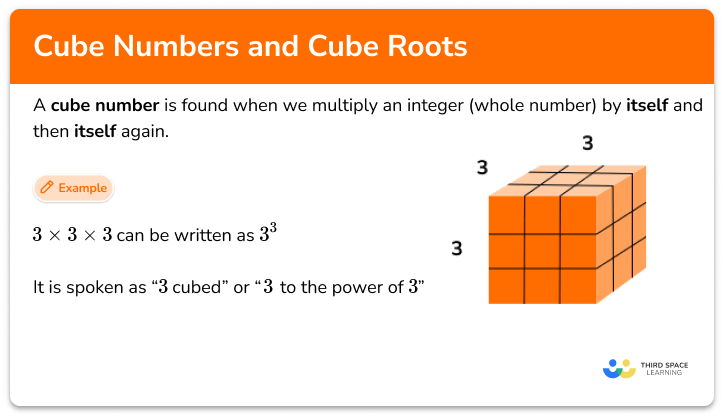
Simple and compound interest at a glance
For GCSE we need to know about two different types of interest – simple and compound.
Simple interest calculates interest based purely on the original amount invested. For example, a savings account with a simple interest rate of 2% and an initial amount of £100, would earn £2 interest each year regardless of the amount of money in the account at the end of each year.
With compound interest, the amount of money in the account at the start of each year is used when calculating interest. For example, if a bank account has an initial investment of £100, and the compound interest rate is 2% per annum (per year), at the end of the first year, the value of the investment will be identical to the simple interest, £102. However, the next year’s interest calculation will be 2% of £102, rather than 2% of the original amount invested. This process will continue for the number of years the money is invested. The total amount of interest is greater when using compound interest than when using simple interest.
The annual compound interest formula is initial amount annual interest rate number of years. Annual interest rate is written as a percentage multiplier, so an interest rate of 2% would be a multiplier of 1.02. If interest is calculated over a different time period, such as semiannually, the ‘number of years’ would change to ‘number of times interest is paid’.
Compound depreciation works in the same way as compound interest, with a slight adjustment to the multiplier.
Looking forward, students can then progress to additional number worksheets, for example a fractions worksheet or a decimals worksheet.

For more teaching and learning support on Number our GCSE maths lessons provide step by step support for all GCSE maths concepts.
Do you have GCSE students who need additional support?
There will be students in your class who require individual attention to help them achieve their target GCSE maths grade. In a class of 30, it’s not always easy to provide.
Help your students feel confident with exam-style questions and the strategies they’ll need to answer them correctly with personalised online one to one tutoring from Third Space Learning
Lessons are selected to provide support where each student needs it most, and specially-trained GCSE maths tutors adapt the pitch and pace of each lesson. This ensures a personalised revision programme that raises grades and boosts confidence.