GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
This topic is relevant for:

Enlargement
Here we will learn about enlargement, including how to enlarge a 2D shape by a scale factor and how to describe an enlargement in detail.
There are also enlargement worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is enlargement?
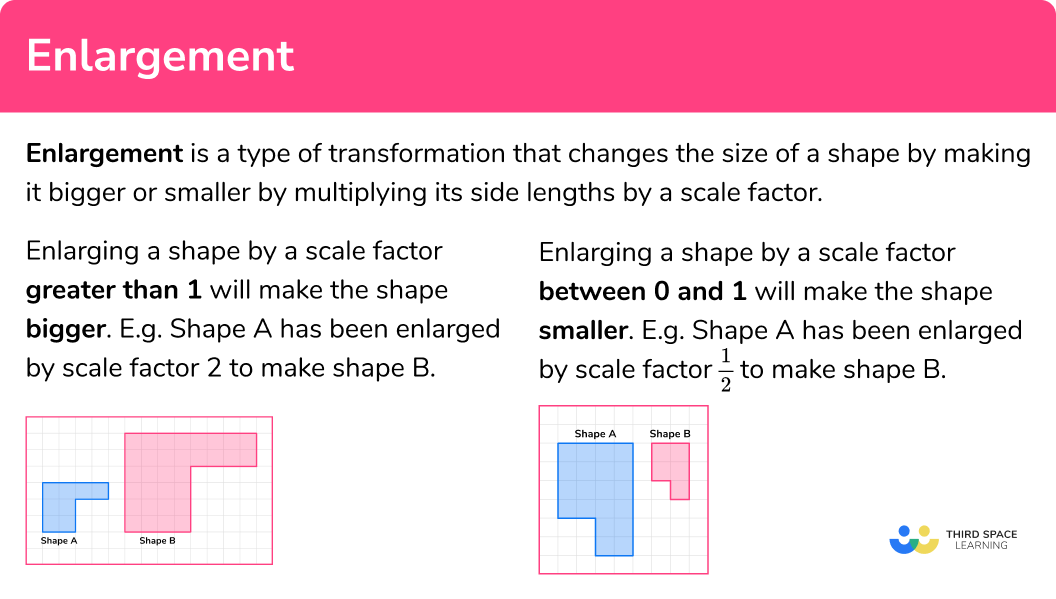
Enlargement is a type of transformation that changes the size of a shape by making it bigger or smaller by multiplying its side lengths by a scale factor.
Enlargements have real life functions, such as changing the size of photographic prints or pictures in documents.
- Enlarging a shape by a scale factor greater than
1 will make the shape bigger.
E.g.
Shape A has been enlarged by scale factor 2 to make shape B.
The corresponding angles are identical but each side in shape B is double the size of the original shape.
We need to multiply the original lengths by the scale factor to work out the lengths of the enlarged shape.
- Enlarging a shape by a scale factor between
0 and1 will make the shape smaller.
This is often written as a fraction and is known as a fractional scale factor.
E.g.
Shape A has been enlarged by scale factor \frac{1}{2} to make shape B.
The corresponding angles are identical but each side in shape B is half the size of the original shape.
The object is the name of the original shape. The image is the name of the shape after it has been translated. When an object is enlarged the object and the image are similar shapes.
What is enlargement?
Centre of enlargement
The centre of enlargement places the enlargement in a specific place.
To use a centre of enlargement we need to draw straight lines from the centre of enlargement through the vertices of the original shape. These are called ray lines.
E.g.
Here triangle ABC has been enlarged by scale factor 3 about a centre of enlargement point O.
The new triangle is labelled A’B’C’.
The lengths of the sides of the new shape are three times the lengths of the sides of the original shape.
The pairs of corresponding sides are parallel lines.
The angles in the two shapes are the same.
The triangles are similar triangles.
Step-by-step guide: Centre of enlargement
Step-by-step guide: Scale factor
How to use enlargement
Points to consider:
- The side lengths of the shape are enlarged depending on the scale factor
- To work out the length scale factor – compare corresponding sides
- If there is not a centre of enlargement, the enlarged shape can be drawn anywhere on the grid
- If there is a centre of enlargement, ray lines can help to make sure the enlarged shape in the correct position on the grid
Enlargement maths worksheet

Get your free enlargement maths worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Enlargement maths worksheet

Get your free enlargement maths worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREEEnlargement maths examples
Example 1: use a scale factor to enlarge a shape
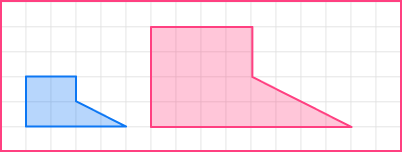
Enlarge the shaded shape by scale factor 2 .
Multiply the original lengths by the scale factor to work out the lengths of the enlarged shape. It is easier to start with horizontal or vertical lines.
Step-by-step guide: Scale factor (coming soon)
Example 2: calculating a scale factor
Shape A has been enlarged to make shape B. Calculate the scale factor.
To calculate the scale factor we need to divide an enlarged length by the corresponding original length.
\text{scale factor } = \frac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\frac{6}{2}=3Example 3: with a centre of enlargement on a grid
Enlarge the shaded shape with scale factor 3 about the point.
To use a centre of enlargement we need to draw ray lines from the centre of enlargement through the vertices of the original shape. Use the ray lines to help you enlarge the shape.
Step-by-step guide: Centre of enlargement
Example 4: with a centre of enlargement on a coordinate grid
Enlarge the shaded shape by scale factor 2 about the point (1,2)
Plot the centre of enlargement on the coordinate grid. Then draw ray lines from the centre of enlargement through the vertices of the original shape. Use the ray lines to help you enlarge the shape.
Example 5: find a centre of enlargement
Shape A has been enlarged to make shape B. Find the centre of enlargement.
Find pairs of corresponding vertices and draw ray lines going through the points.
Example 6: negative scale factor (higher)
Enlarge the shaded shape with scale factor -2 about the point.
There are also negative scale factors in the higher GCSE only. These are an extension of positive scale factors.
Draw ray lines from the centre of enlargement through the vertices of the original shape. Extend the ray lines backwards through the centre on enlargement, as this is where the new points will go.
Common misconceptions
- Accuracy
Use a sharp pencil and make use of the grid lines to help you to be accurate.
- Diagonal lines
Diagonal lines can be tricky to enlarge, so it is best to use horizontal and vertical lines.
- The origin
The origin of a coordinate grid has the coordinates (0,0) . It is commonly denoted as O. It is used often as the centre of enlargement.
- Describe a single transformation
If you are asked to give a single transformation – make sure it is a single transformation, not 2 or more. Also make sure that you state the type of transformation and give full details.
E.g.
For enlargements state scale factor and the coordinates of the centre of enlargement.
Practice enlargement maths questions
1. Enlarge the shaded shape by scale factor \frac{1}{2}.




The scale factor is \frac{1}{2} so all the sides need to be halved.
2. Shape A has been enlarged to make shape B. Calculate the scale factor.
Scale factor is 3

Scale factor is 2.5

Scale factor is 2

Scale factor is \frac{1}{2}

To calculate the scale factor we need to divide an enlarged length by the corresponding original length. If we use the heights of the rectangles:
\text{scale factor } = \frac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\frac{6}{3}=2
3. Enlarge the shaded shape with scale factor 2 about the point.




The two triangles should be similar. The pairs of corresponding sides are parallel lines. Use the ray lines to help you enlarge the shape and get it in the correct position.
4. Enlarge the shaded shape by scale factor 3 about the point (8,8)




Make sure you have the centre of enlargement plotted correctly. Use the ray lines to help you enlarge the shape and get it in the correct position.
5. Shape A has been enlarged to make shape B. Find the centre of enlargement.




Find pairs of corresponding vertices and draw ray lines going through the points.
6. Enlarge the shaded shape with scale factor -1 about the point. (higher)




Draw ray lines from the centre of enlargement through the vertices of the original shape. Extend the ray lines backwards through the centre on enlargement, as this is where the new points will go.
Enlargement maths GCSE questions
1. On the grid, draw an enlargement of the rectangle with scale factor 3.
(2 marks)
For 2 sides correctly enlarged
(1)
For all 4 sides correctly enlarged
(1)
2. Enlarge the shape with scale factor 2, centre (1,1).
(3 marks)
For one correct vertex
(1)
For second correct vertex
(1)
For fully correct triangle
(1)
3. Describe fully the single transformation that maps shape A onto shape B.
(3 marks)
For stating that it is an enlargement
(1)
For the correct scale factor (scale factor 3)
(1)
For the correct coordinates of the centre of enlargement (8,8)
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Enlarge a shape by a scale factor on a grid
- Calculate a scale factor
- Use a centre of enlargement to enlarge a shape on a grid
- Use a centre of enlargement to enlarge a shape with a fractional scale factor
- Find a centre of enlargement
- Use a centre of enlargement to enlarge a shape with a negative scale factor (higher)
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.