High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Substitution Perimeter Areas of a circle Area of composite shapes Area of a quadrilateral Circumference of a circleSurface area of a cylinder
Here you will learn about the surface area of a cylinder, including how to calculate the lateral surface area of a cylinder given its radius and its perpendicular height.
Students will first learn about the surface area of a cylinder as part of geometry in th grade.
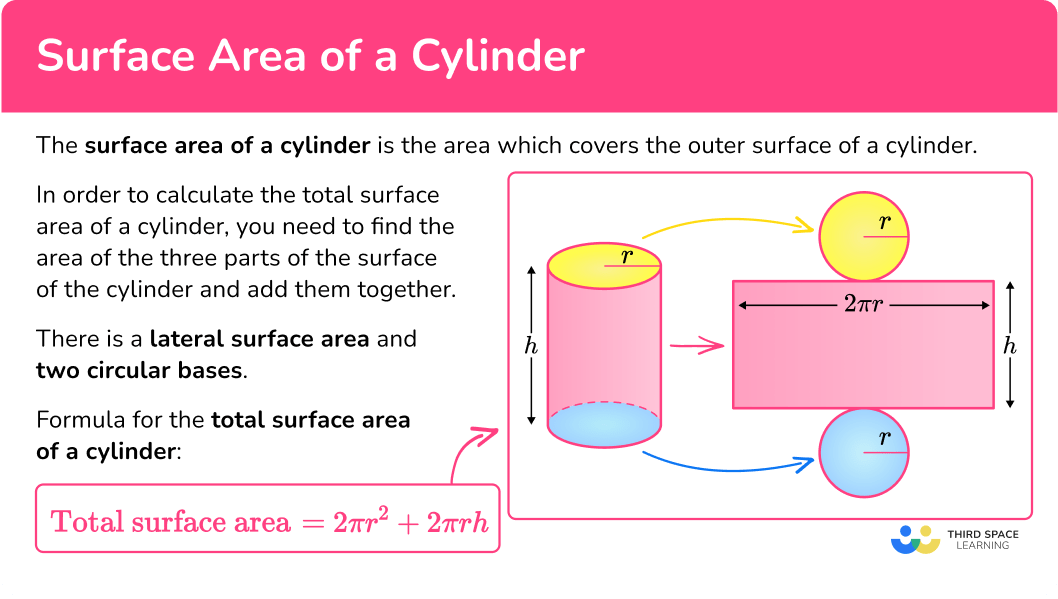
What is the surface area of a cylinder?
The surface area of a cylinder is the area that covers the outer surface of a cylinder.
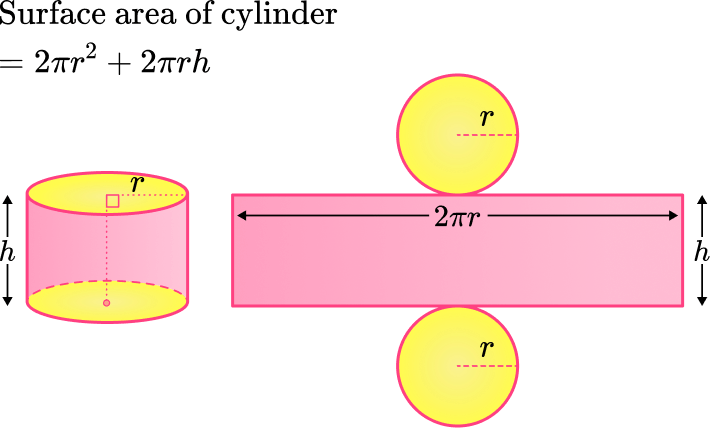
In order to calculate the total surface area of a cylinder you need to find the area of the three parts of the surface and add them together.
There is a lateral surface area and two circular bases.
(The lateral surface area of a cylinder is also referred to as the curved surface area of a cylinder).
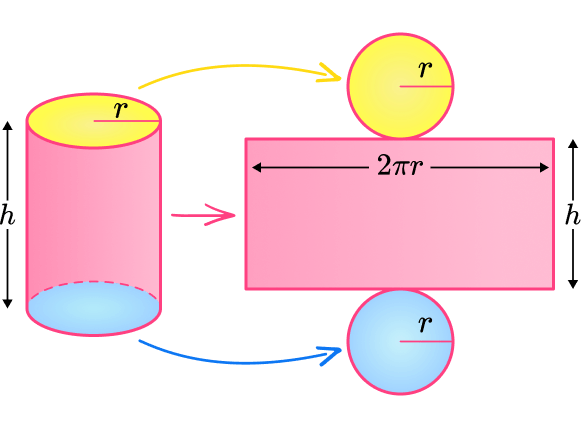
is the radius of the cylinder. The lateral surface area of a cylinder is a rectangle.
The circumference of the circle is the length of the rectangle. The height of a cylinder is the height of the rectangle.
Note: The examples on this page are for right circular cylinders. However, the formula above can be used for oblique cylinder if slant height is used for the value of
Let’s look at each part of the surface of a cylinder.
Lateral surface area
The lateral surface area of a cylinder is a rectangle.
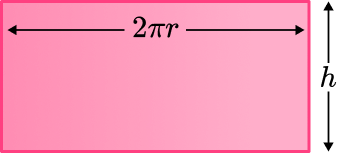
is the formula for the area of the rectangle.
The base of the rectangle is the circumference of the circle:
The height of the rectangle is height of the cylinder given by
To find the area of a rectangle you need to multiply the base by the height
This gives us the formula for the lateral surface area of a cylinder:
Base area
Then you need to calculate the area of the base of the cylinder, this is a circle.
Formula for the area of circle:
The area of the top and the area of the base of a cylinder are the same.
Total surface area of a cylinder
So to find the total surface area, you can add the lateral surface area to the area of the two circles:
For example,
Calculate the total surface area of this cylinder with radius of the base and perpendicular height
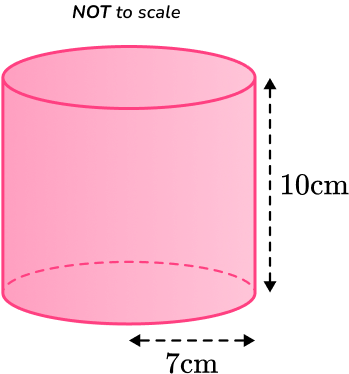
First, you need to find the lateral surface area of the cylinder:
You then need to find the area of the base of the cylinder:
The area of the top of the cylinder is the same as the area of the base so,
Total surface area:
Since the measurements of the cylinder are in cm, the surface area will be measured in
The surface area of the cylinder is rounded to the nearest tenth.
What is the surface area of a cylinder?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to th grade math?
- Grade 8 – Geometry (8.G.C.9)
Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
![[FREE] Surface Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Surface-Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Surface Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6)
![[FREE] Surface Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Surface-Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 students’ understanding of surface area. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th grade surface area topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Surface Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Surface-Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Surface Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6)
![[FREE] Surface Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Surface-Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 students’ understanding of surface area. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th grade surface area topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to calculate the surface area of a cylinder
In order to calculate the surface area of a cylinder:
- Calculate the area of each face.
- Add the areas together.
- Write the answer, including the units.
Surface area of a cylinder examples
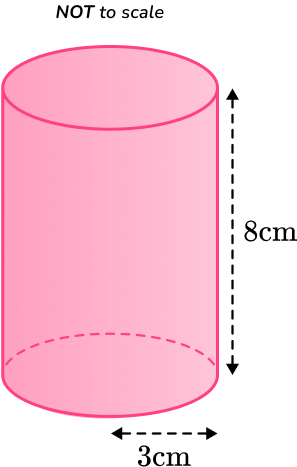
Example 1: lateral surface area (lsa)
Calculate the lateral surface area of the cylinder below, with radius and perpendicular height
Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
- Calculate the area of each face.
This question is only asking us for the lateral surface area, so you only need to find the area of the curved surface that is between the circular bases.
2Add the areas together.
Since you are only calculating the lateral surface area, you do not need to add any other areas.
3Write the answer, including the units.
You need to round the answer to the nearest tenth and include the units – square centimeters.
The lateral surface area of the cylinder is:
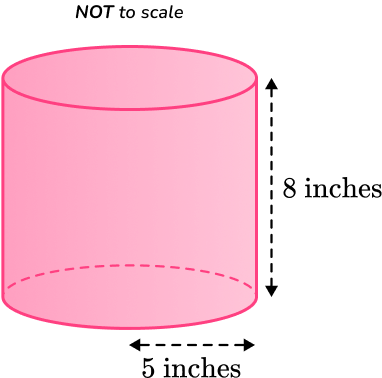
Example 2: lateral surface area – in terms of π
Calculate the lateral surface area of the cylinder below, with radius and perpendicular height
Leave your answer in terms of
Calculate the area of each face.
This question is only asking us for the lateral surface area, so you only need to find the area of one face.
Add the areas together.
Since you are only calculating the lateral surface area, you do not need to add any other areas.
Write the answer, including the units.
You need to leave the answer in terms of and include the units – square inches.
Lateral surface area =
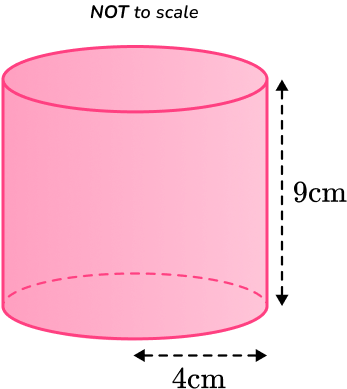
Example 3: total surface area (tsa)
Calculate the surface area of the cylinder below, with radius and perpendicular height
Round your answer to the nearest whole.
Calculate the area of each face.
This question is asking us for the total surface area of the cylinder. You need to find the area of each face and add them together.
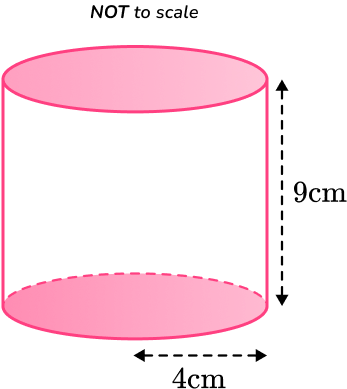
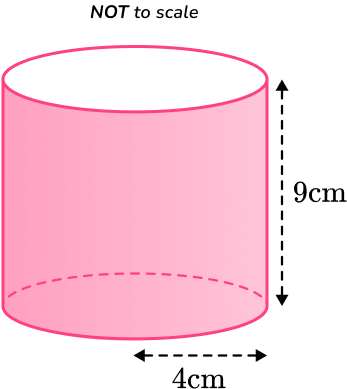
The top face is the same as the bottom face, so the area of the top is also
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is
Write the answer, including the units.
You need to round to the nearest whole number and include units.
The total surface area of the cylinder is:
Example 4: decimal radius of a cylinder
Calculate the surface area of the cylinder below.
Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
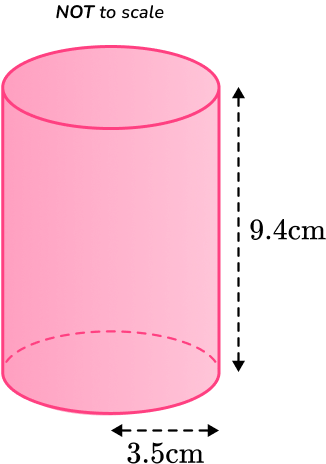
Calculate the area of each face.
This question is asking us for the total surface area of the cylinder. You need to find the area of each face and add them together.
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is
Write the answer, including the units.
You need to round to the nearest whole number and include units.
The TOTAL surface area of the cylinder is:
Example 5: total surface area (tsa)
Calculate the surface area of the cylinder below.
Leave your answer in terms of
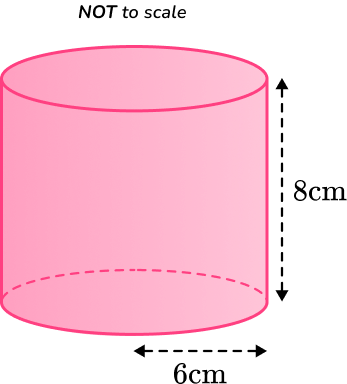
Calculate the area of each face.
This question is asking us for the answer in terms of When calculating the area of each face, you need to leave the answers in terms of
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is
Write the answer, including the units.
You need to leave the answer in terms of and include the units.
The TOTAL surface area of the cylinder is:
Example 6: total surface area (tsa)
Calculate the surface area of the cylinder below.
Leave your answer in terms of
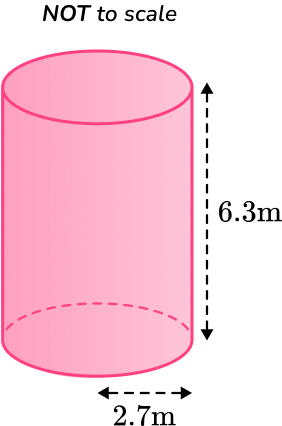
Calculate the area of each face.
This question is asking us for the answer in terms of When calculating the area of each face, you need to leave the answers in terms of
Add the areas together.
The sum of the areas is
Write the answer, including the units.
You need to leave the answer in terms of and include the units.
The TOTAL surface area of the cylinder is:
Teaching tips for surface area of a cylinder
- Before using worksheets, give students opportunities to work with real world cylindrical shapes, like aluminum cans or food canisters. Have them estimate what they think the surface area is and then brainstorm ways to measure. Finally, introduce the formula and have students compare it to their estimate and brainstorming ideas.
- Have students compare how calculating the surface area of a cylinder is similar and different from calculating the surface area of other -dimensional shapes.
- Calculating the surface area of a cylinder can extend beyond math classes and be applied to activities in science classes, art classes, and beyond. When teaching this topic, be sure that other teachers who work with your students are aware that this is something they can integrate into their curriculum as well.
Easy mistakes to make
- Rounding too soon
It is important to not round the answer until the end of the calculation. Rounding beforehand can make your answer less precise.
- Confusing the radius or the diameter
It is a common error to mix up radius and diameter. Remember, the radius is half of the diameter, and the diameter is double the radius.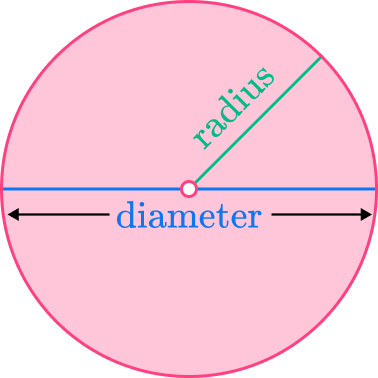
- Not using the correct units
For area, you use square units such as For volume, you use cube units such as
Practice surface area of a cylinder questions
1. Calculate the lateral surface area of a cylinder with the radius of and the perpendicular height of
Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
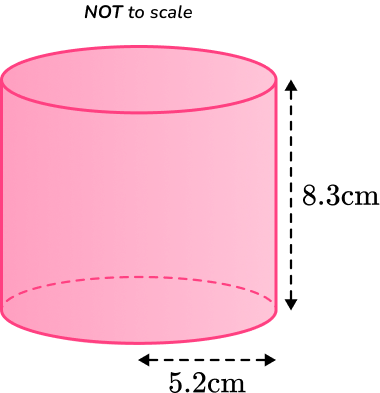




You are calculating the lateral surface area of a cylinder, so you substitute the values of and into the formula.
2. Calculate the lateral surface area of a cylinder with the radius of and the perpendicular height of
Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
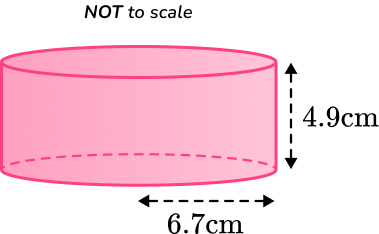




You are calculating the lateral surface area of a cylinder, so you substitute the values of and into the formula.
3. Calculate the lateral surface area of the cylinder below.
Leave your answer in terms of
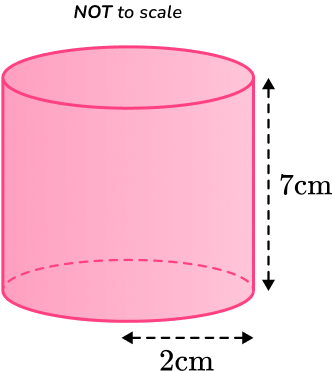




You are calculating the lateral surface area of a cylinder, so you substitute the values of and into the formula.
4. Calculate the surface area of the cylinder below.
Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
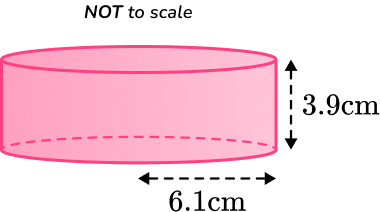




You are calculating the TOTAL surface area of the cylinder, so you find the area of each face and add them together.
Total surface area:
Surface area (rounded to the nearest whole number)
5. Calculate the TOTAL surface area of the cylinder below.
Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
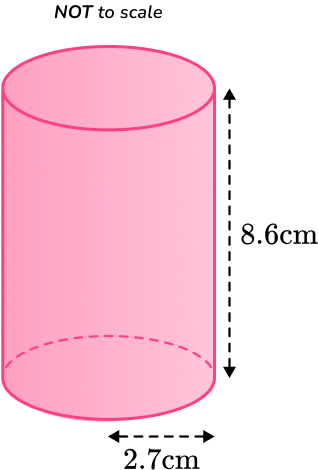




You are calculating the TOTAL surface area of a cylinder, so you find the area of each face and add them together.
Total surface area:
Surface area (rounded to the nearest whole number)
6. Calculate the TOTAL surface area of the cylinder below.
Leave your answer in terms of
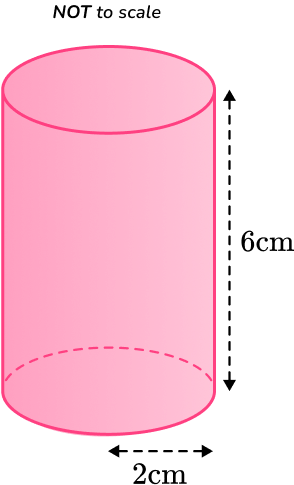




You are calculating the TOTAL surface area of a cylinder, so you find the area of each face and add them together.
Total surface area:
Surface area of a cylinder FAQs
To find the volume of a cylinder, find the area of the base, a circle and multiply it by the height. You can do this with the formula The total surface area is found by adding the area of the two bases and the lateral side.
The lateral side is measured by the height of the cylinder and the circumference of the circle. You can use the surface area of a cylinder formula to solve for any cylinder.
The next lessons are
- Pythagorean theorem
- Trigonometry
- Circle math
- Volume of a cylinder
- Sphere shape
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!