High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
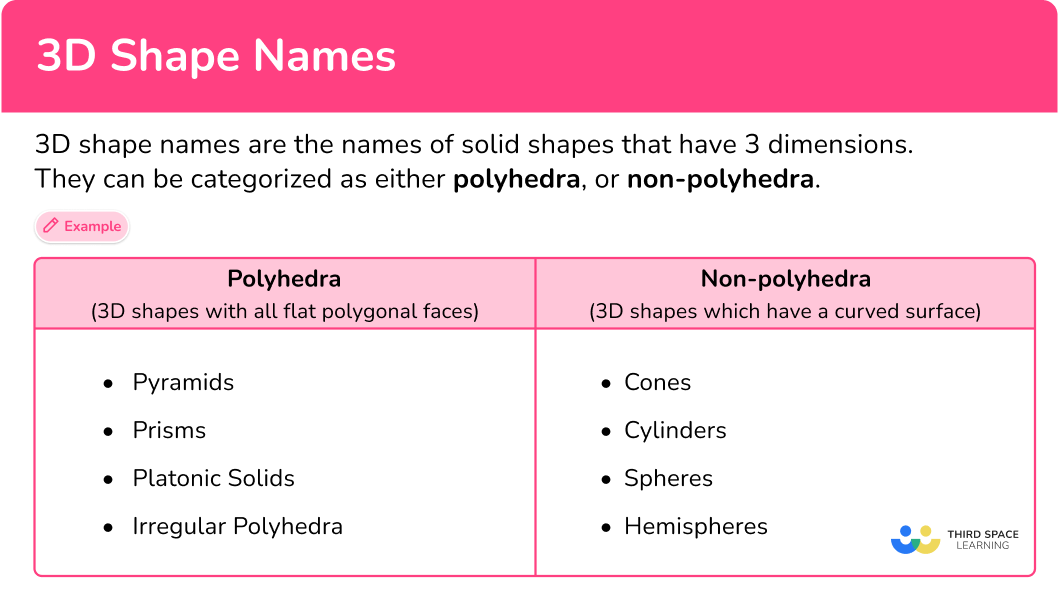
3D shape names
Here you will learn about 3D shape names, including types of polyhedra (prisms, pyramids, platonic solids, irregular), non-polyhedra (cones, cylinders, spheres, hemispheres) and compound 3D shapes.
Students will first learn about 3D shape names as part of geometry in 1 st grade. They expand their learning in 6 th grade when they find surface area of 3D shapes and solve real world problems involving 3D shapes.
What are 3D shape names?
3D shape names are the names of solid shapes that have 3 dimensions (height, width and depth). They can be categorized as either polyhedra, or non-polyhedra.
The properties of 3D shapes can help you classify them and recall their names.
3D Shape \hspace{1.5cm}
| Polyhedra (3D shapes with all flat polygonal faces) | Non-polyhedra (3D shapes which have a curved surface) |
|---|---|
● Pyramids | ● Cones and other pyramids with |
Polyhedra
Polyhedra are 3D shapes with flat faces, straight sides (edges), and sharp vertices.
All polyhedra can then be categorized as prisms, pyramids, platonic solids, or irregular polyhedra.
Here are some examples of polyhedra.
| Prism | Pyramid | Platonic solid | Irregular polyhedron |
|---|---|---|---|
 (Triangular prism) |  (Square based | 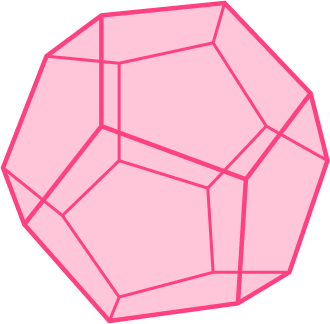 (Dodecahedron) | 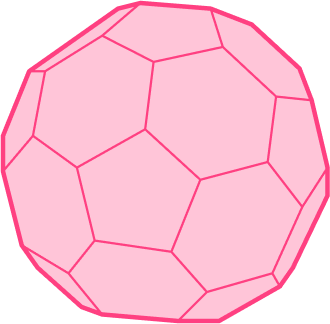 |
Some 3D shapes can fit into more than one category. For example, a tetrahedron is one of the platonic solids, but it is also a triangular based pyramid.
Non-polyhedra
Non-polyhedra are 3D shapes that include curved surfaces. They may also have some flat faces, edges or vertices.
Here are some examples of non-polyhedra.
| Sphere | Cone | Cylinder | Conical Frustum |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
Platonic solids
Some of the most famous polyhedra are called the Platonic solids named after the Greek philosopher and Mathematician, Plato.
The platonic solids can also be referred to as regular polyhedra because their faces are regular polygons; each solid is made up of one type of regular polygon and can be inscribed inside a sphere.
In practical terms, this means that the solid can be used as a fair dice, where there is an equal chance of landing on each face.
For example,
| Name | Tetrahedron | Cube | Octahedron | Dodecahedron | Icosahedron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picture |  | 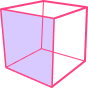 |  |  |  |
| Face shape | Equilateral | Square | Equilateral | Regular | Equilateral |
| Number of faces | 4 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 20 |
| Additional information | This solid | This solid | This solid |
Prisms
A prism is a polyhedron that has congruent cross sections. In non-mathematical words, it is a 3D shape that can be sliced like a loaf of bread, and each slice will look like the same flat shape.
For example,
The rectangular prism below has a rectangular cross section that is the same for the entire depth of the shape.
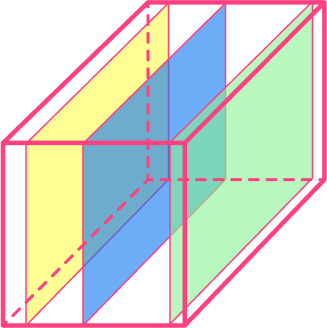
For example,
The triangular prism below has a triangular cross section that is the same for the entire depth of the shape.
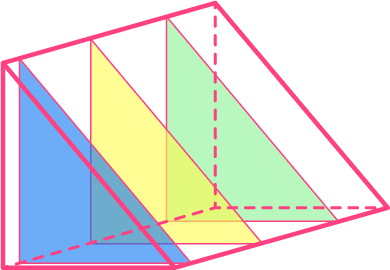
Questions involving prisms may ask you to calculate the volume, calculate the surface area, draw the net, or count the number of edges, faces, and vertices.
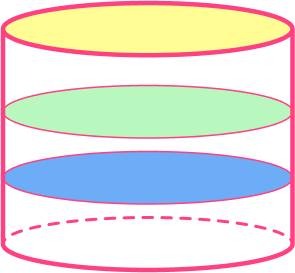
Cylinders
Geometrically, a cylinder is like a prism. The cross sections of a cylinder are congruent circles.
Face, edges, and vertices
Faces, edges, and vertices are words to describe different parts of 3D shapes.
| Face
A flat 2D shape | Edge
A straight line where | Vertex
A point where two |
|---|---|---|
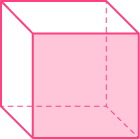 | 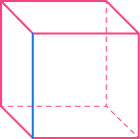 | 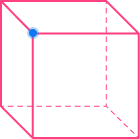 |
The cube in the table above has \bf{6} faces, \bf{12} edges, and \bf{8} vertices.
Pyramids
A pyramid is a polyhedron that has a flat polygonal base shape and an apex. It has triangular side faces which slope to meet each other at the apex.
| Base shape | Apex |
|---|---|
 |  |
Regular pyramids
The base shape of a regular pyramid is a regular polygon (A 2D shape with straight equal sides).
All the lateral edges (edges leading from the base to the apex) are equal in length.
Irregular pyramids
The base shape of an irregular pyramid is an irregular polygon (A 2D shape with straight sides which vary in length).
The lateral edges may be different in length.
For all types of pyramids, the cross sectional areas are similar to each other.
For example,
| Regular square based pyramid | Irregular hexagonal pyramid |
|---|---|
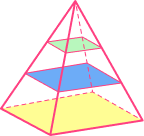 | 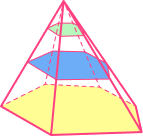 |
 Square base |  Hexagonal base |
Right pyramids
If the apex of the pyramid lies directly on top of the center of the base, the pyramid is a right pyramid.
Oblique pyramids
If the apex of the pyramid does not lie directly on top of the center of the base, the pyramid is an oblique pyramid.
This is illustrated in the diagrams below. The cross sectional areas of both right pyramids and oblique pyramids are similar to each other.
For example,
| Right triangular pyramid | Oblique pentagonal pyramid |
|---|---|
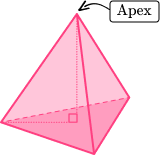 | 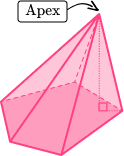 |
Questions involving pyramids may ask you to calculate the volume, calculate the surface area, draw the net, or count the faces, edges, and vertices.
Cones
Cones can be described like pyramids; they have a circular base shape and an apex. Their cross-sectional areas are similar circles. However, unlike pyramids, cones do not have sloping triangular side faces but instead have a curved side surface.
| Cone |
|---|
 |
 |
Frustums
If the apex of a pyramid or cone is sliced off, then the remaining shape is known as a frustum. The mathematical term for ‘slicing off an apex’ is ‘truncating.’ So a frustum can also be described as a truncated pyramid or truncated cone.
| Truncated cone / conical frustum | Truncated square based pyramid |
|---|---|
 |  |
Irregular polyhedra
If a 3D shape is a polyhedron (it is made up of flat polygonal faces) but it cannot be categorized as a prism, pyramid, or platonic solid, then it is an irregular polyhedron. An irregular polyhedron can have faces which are regular polygons or irregular polygons, or a combination of both.
For example,
The 3D shape below is a well recognized irregular polyhedron. This solid is made up of regular pentagons and regular hexagons and has the design of a soccer ball.

Compound solids
A compound solid is a 3D shape that is made up of other identifiable 3D shapes.
Examples
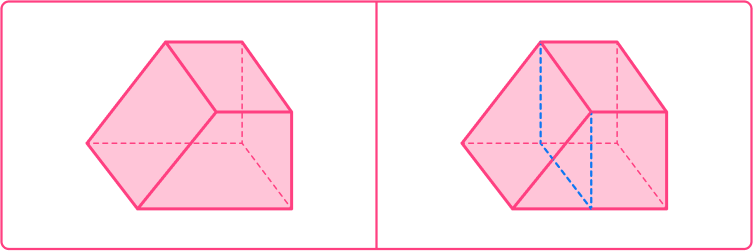
This compound solid is a polyhedra and is made up of a rectangular prism and a triangular prism.
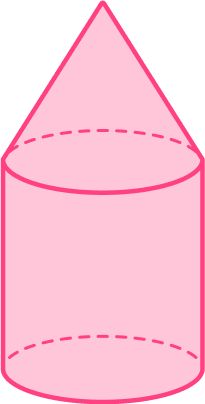
This compound solid is a non-polyhedra and is made up of a cylinder and a cone.
What are 3D shape names?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6 th and 7 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Geometry (6.G.A.4)
Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
- Grade 7 – Geometry (7.G.A.3)
Describe the two-dimensional figures that result from slicing three- dimensional figures, as in plane sections of right rectangular prisms and right rectangular pyramids.
- Grade 7 – Geometry (7.G.B.6)
Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms.
How to categorize and name a 3D shape
In order to categorize and name a 3D shape:
- Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2.
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3. - Identify if all the faces are the same regular shape.
i) If yes, this is one of the Platonic solids (tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron or icosahedron).
ii) If no, continue to step 3. - Identify if the 3D shape is:
a) A pyramid or cone (3D shape with a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas).
b) A prism or cylinder (3D shape with congruent cross-sectional areas).
c) Neither. - Name the shape.
a) For pyramids: the name of the base shape often forms the name of the 3D shape.
b) For prisms: the name of the cross-sectional area often forms the name of the 3D shape.
c) i) For neither (polyhedron): This is an irregular polyhedron or a compound solid.
\: \: \: ii) For neither (non-polyhedron): This is a sphere or hemisphere.
![[FREE] 3D Shape Names Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/3D-Shape-Names-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] 3D Shape Names Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] 3D Shape Names Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/3D-Shape-Names-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 6th grade and 7th grade students’ understanding of 3D shape names. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] 3D Shape Names Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/3D-Shape-Names-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] 3D Shape Names Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] 3D Shape Names Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/3D-Shape-Names-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 6th grade and 7th grade students’ understanding of 3D shape names. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE3D shape names examples
Example 1: naming a 3D shape from its net
What 3D shape can be formed from this net?
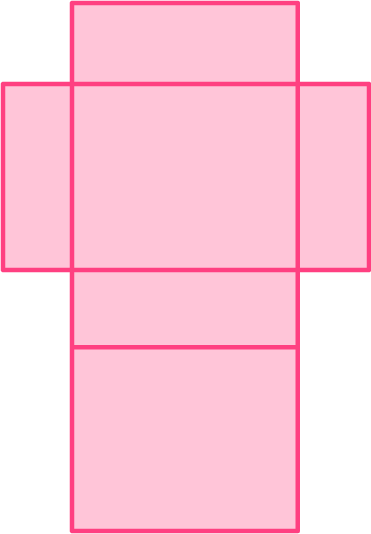
- Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2.
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3.
All the 2D shapes that make up this net are polygons; they are all rectangles. The 3D shape it will form is therefore a polyhedron.
2Identify if all the faces are the same regular shape.
i) If yes, this is one of the Platonic solids (tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron or icosahedron).
ii) If no, continue to step 3.
The faces are not the same; they are different size rectangles.
This is not a platonic solid.
3Identify if the 3D shape is:
a) A pyramid or cone (3D shape with a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas).
b) A prism or cylinder (3D shape with congruent cross-sectional areas).
c) Neither.
Imagine the net folding up into a 3D shape.
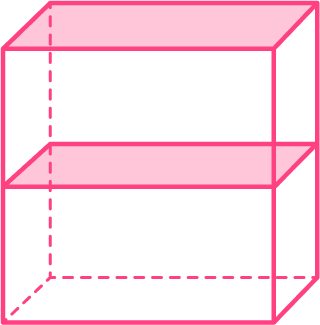
The cross-sectional areas are congruent as shown by these pink rectangles. This 3D shape is a type of prism.
4Name the shape.
For pyramids: the name of the base shape often forms the name of the 3D shape.
For prisms: the name of the cross-sectional area often forms the name of the 3D shape.
i) For neither (polyhedron): This is an irregular polyhedron or a compound solid.
ii) For neither (non-polyhedron): This is a sphere or hemisphere.
This is a rectangular prism, which is also called a cuboid.
Example 2: naming a 3D shape from a 3D image and description
The following 3D shape is made up of 4 equilateral triangles. What is the name of this 3D shape?
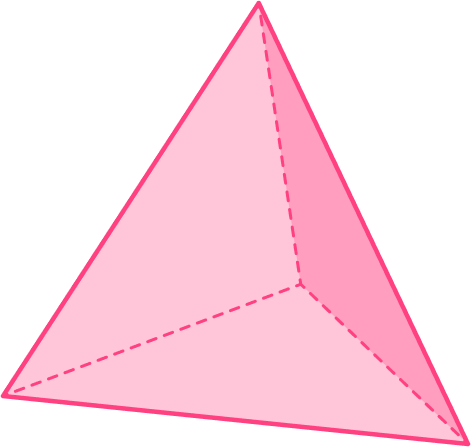
Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3.
All the surfaces are flat and triangular. This 3D shape is therefore a polyhedron.
Identify if all the faces are the same regular shape:
i) If yes, this is one of the Platonic solids (tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron or icosahedron).
ii) If no, continue to step 3.
The faces are all equilateral triangles.
This is a Platonic solid.
This is a tetrahedron.
This can also be described as a triangular based pyramid.
Example 3: naming a 3D shape from a 3D image
What is the name of this 3D shape?
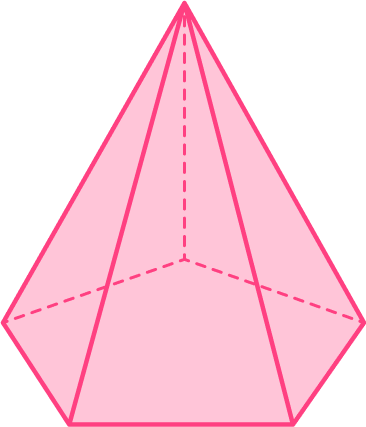
Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2.
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3.
All the surfaces are flat. All the faces are polygons; triangles and a pentagon. This 3D shape is therefore a polyhedron.
Identify if all the faces are the same regular shape:
i) If yes, this is one of the Platonic solids (tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron or icosahedron).
ii) If no, continue to step 3.
The faces are not the same. There are triangles and a pentagon.
This is not a Platonic solid.
Identify if the 3D shape is:
a) A pyramid or cone (3D shape with a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas).
b) A prism or cylinder (3D shape with congruent cross-sectional areas).
c) Neither.
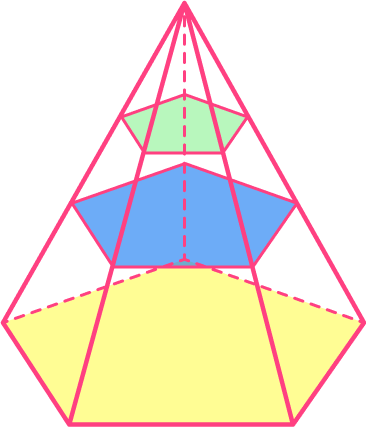
This 3D shape has a pentagon as a base and an apex. The cross-sectional areas are similar as shown by the yellow, blue and green pentagons in this diagram. This 3D shape is therefore a type of pyramid.
Name the shape.
For pyramids: the name of the base shape often forms the name of the 3D shape.
For prisms: the name of the cross-sectional area often forms the name of the 3D shape.
i) For neither (polyhedron): This is an irregular polyhedron or a compound solid.
ii) For neither (non-polyhedron): This is a sphere or hemisphere.
This is a pentagonal based pyramid.
Example 4: naming a 3D shape from a 3D image and description.
The following 3D shape is made up of 8 equilateral triangles. What is the name of this 3D shape?
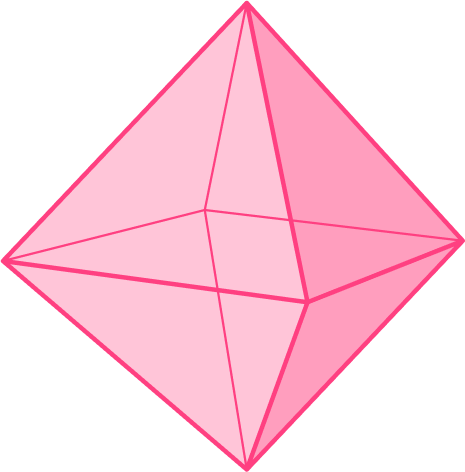
Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2.
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3.
All the surfaces are flat and triangular. This 3D shape is therefore a polyhedron.
Identify if all the faces are the same regular shape.
i) If yes, this is one of the Platonic solids (tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron or icosahedron).
ii) If no, continue to step 3.
The faces are all equilateral triangles.
This is a Platonic solid.
This is an octahedron.
Example 5: naming a 3D shape from its net
What 3D shape can be formed from this net?
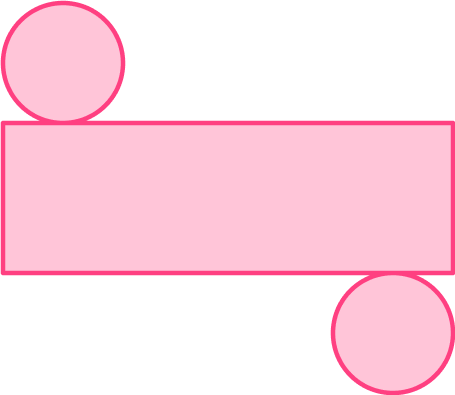
Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2.
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3.
The 2D shapes that make up this net are circles and a rectangle. Because they are not all polygons, the 3D shape this net will form will have a curved surface. It is therefore a non-polyhedron; go to step 3.
Identify if the 3D shape is:
a) A pyramid or cone (3D shape with a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas).
b) A prism or cylinder (3D shape with congruent cross-sectional areas).
c) Neither.
Imagine the net folding up into a 3D shape. The rectangle will curl around the circumference of the circles.
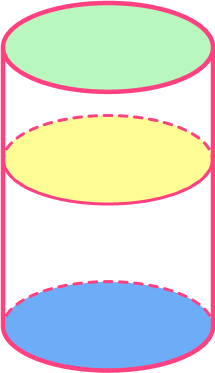
The cross-sectional areas are congruent as shown by these shaded circles. This 3D shape is a prism or cylinder.
Name the shape.
For pyramids: the name of the base shape often forms the name of the 3D shape.
For prisms: the name of the cross-sectional area often forms the name of the 3D shape.
i) For neither (polyhedron): This is an irregular polyhedron or a compound solid.
ii) For neither (non-polyhedron): This is a sphere or hemisphere.
This 3D shape is a cylinder.
Example 6: categorizing and describing a 3D shape
Below is an image of a compound solid.
(a) Is this solid a type of pyramid or prism?
(b) What 3D shapes make up this compound solid?
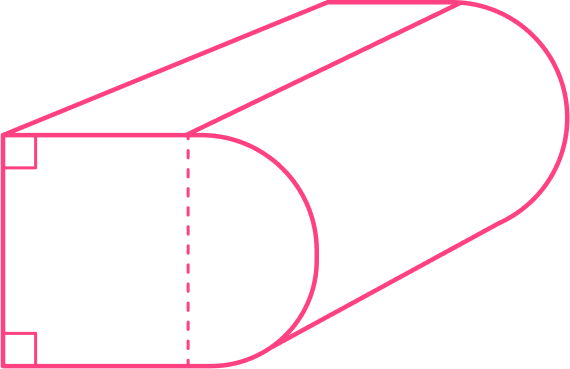
Identify if the 3D shape is:
i) A polyhedron (all flat polygonal faces) – go to step 2.
ii) A non-polyhedron (includes a curved surface) – go to step 3.
Some of the surfaces are flat and rectangular, there is also a curved surface. This 3D shape is therefore not a polyhedron.
Identify if the 3D shape is:
a) A pyramid or cone (3D shape with a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas).
b) A prism or cylinder (3D shape with congruent cross-sectional areas).
c) Neither.

The cross-sectional areas are congruent as shown by the pink shapes, which are made from rectangle and a semicircle. This 3D shape is like a prism, but with a curved face.
Name the shape.
For pyramids: the name of the base shape often forms the name of the 3D shape.
For prisms: the name of the cross-sectional area often forms the name of the 3D shape.
i) For neither (polyhedron): This is an irregular polyhedron or a compound solid.
ii) For neither (non-polyhedron): This is a sphere or hemisphere.
This is a compound 3D shape. It is made up of rectangular prisms and a half of a cylinder.
Teaching tips for 3D shape names
- Utilize visual aids like posters, charts, or flashcards displaying 2D representations of the shapes along with their names. This helps students associate the shapes with their respective names and identify key features.
- Show students pictures or bring in real-world objects that exemplify different 3D shapes. Encourage them to identify the shapes present in those objects. This connects the concept to their everyday experiences and reinforces understanding.
Easy mistakes to make
- Mixing up 2D and 3D shape names
Make sure you know the correct 3D shape names and avoid common mistakes involving 2D shape names like the following examples:
Cube – common incorrect name ‘3D square’.
Rectangular prism – common incorrect name ‘3D rectangle’.
Tetrahedron – common incorrect name ‘3D triangle’.
Related 3D shapes lessons
- Hemisphere shape
- Cone
- Sphere shape
- Triangular pyramid
- Pyramid shape
- Square pyramid
- Cylinder
- Angles of elevation and depression
Practice 3D shape names questions
1. Below is the net of a 3D shape.
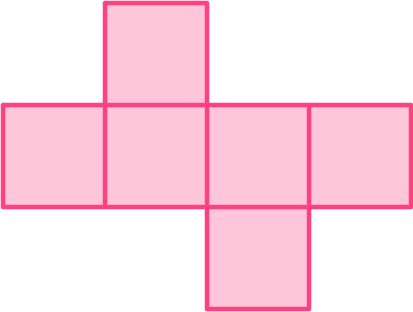
What is the name of the 3D shape that can be formed from this net?
3D square

Cube

Cylinder

Quadrahedron

All the faces are the same regular shape; squares.
Therefore this net will form one of the five platonic solids.
A cube is made up of 6 squares.
2. Below is an image of a 3D shape.
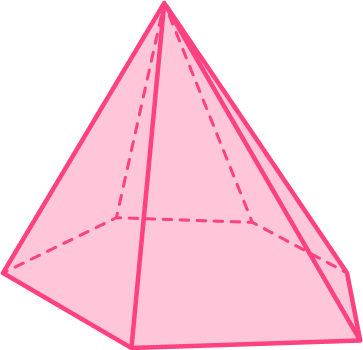
What is the name of this 3D shape?
Hexagon

Hexagonal pyramid

Hexahedron

Hexagonal prism

This 3D shape has a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas: it is therefore a pyramid.
The base shape is a hexagon, hence, it is a hexagonal pyramid.
3. Below is an image of a 3D shape.
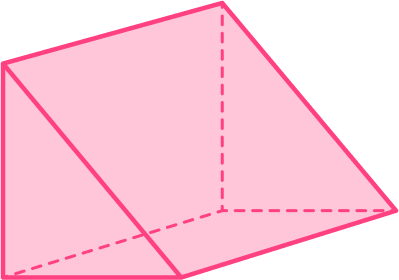
What is the name of this 3D shape?
Right pyramid

Triangular pyramid

Tetrahedron

Triangular prism

This 3D shape has congruent cross-sectional areas: it is therefore a prism.
The shape of the cross-section is a triangle, hence, it is a triangular prism.
4. Below is an image of a 3D shape which is made up of 12 regular pentagons.

What is the name of this 3D shape?
Dodecahedron

Pentagonal prism

Pentahedron

Icosahedron

All the faces are the same regular shape; regular pentagons.
Therefore this 3D shape is one of the five platonic solids.
A dodecahedron is made up of 12 regular pentagons.
5. Below is the net of a 3D shape.
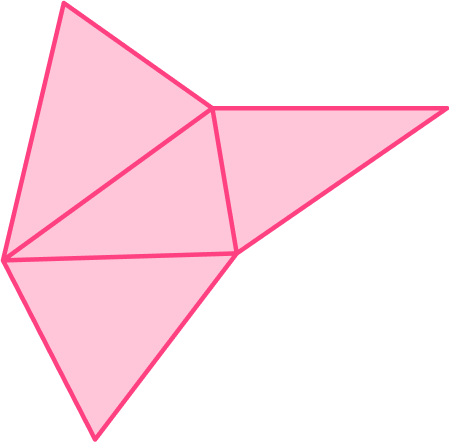
What is the name of the 3D shape that can be formed from this net?
Irregular triangle

Rectangular based pyramid

Triangular based pyramid

Triangular prism

The triangle in the middle of the net will be the base and the other triangles will fold up and meet at an apex.
6. Below is an image of a 3D shape.
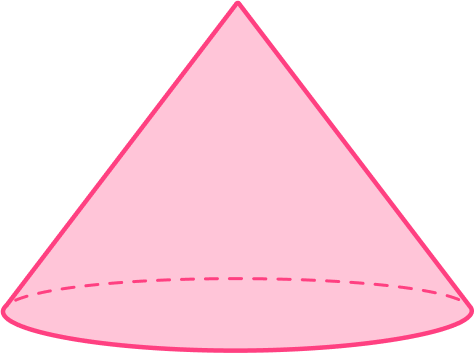
What is the name of this 3D shape?
Cylinder

Circular based pyramid

Sphere

Cone

This 3D shape has a base, an apex and similar cross-sectional areas: it is therefore a pyramid or cone.
A cone can look ‘pyramid-like’ with a circular base.
3D shape names FAQs
The most common 3D shape names are cube, cylinder, sphere, rectangular prism, cone, and pyramid.
In elementary or primary school, children typically learn about basic 3D shapes such as cubes and cylinders. These shapes are often introduced along with their properties such as edges, faces, and vertices. Children learn to identify and describe these shapes, count their faces, edges, and vertices, and understand their basic attributes.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!