High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Quadrilateral Types of quadrilaterals Types of angles Angles of a triangle Straight angle Vertical angles theorem Parallel anglesQuadrilateral angles
Here you will learn about quadrilateral angles, including the sum of quadrilateral angles, how to find missing angles, and how to use these angle facts to generate equations and solve problems.
Students will first learn about quadrilateral angles as part of geometry in high school.
What are quadrilateral angles?
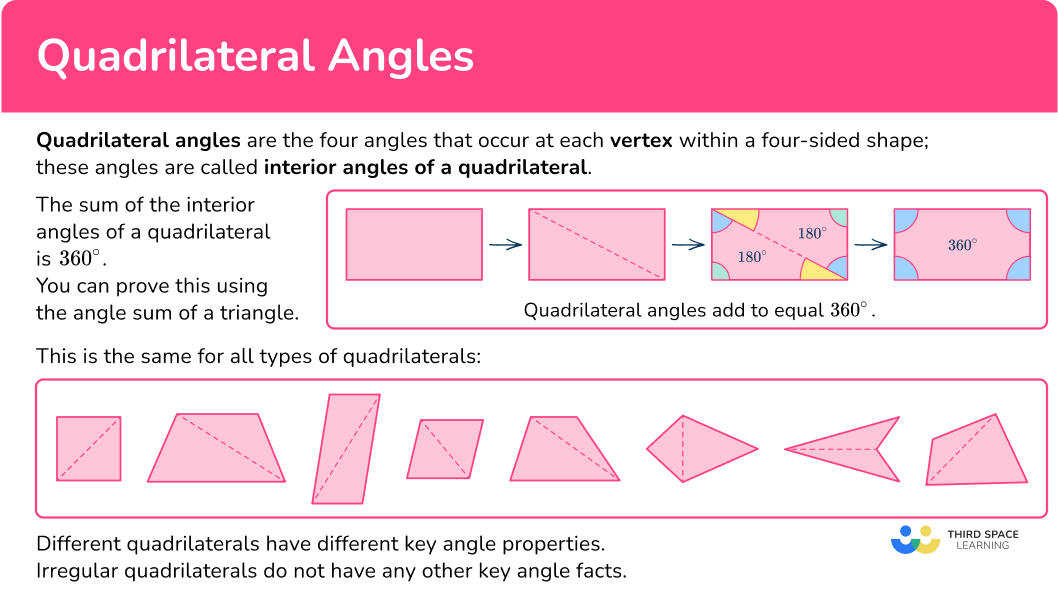
Quadrilateral angles are the four angles that occur at each vertex within a four-sided shape; these angles are called interior angles of a quadrilateral.
The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360^{\circ}. You can prove this using the angle sum of a triangle.
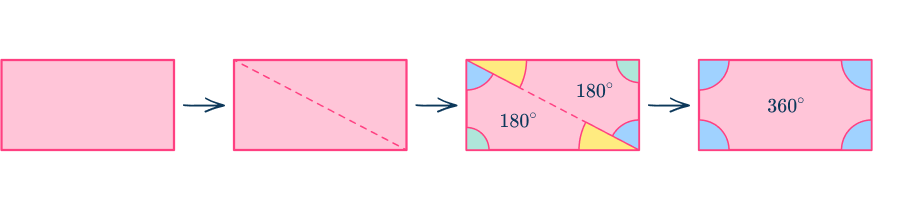
The rectangle above is split into two triangles by joining two vertices together across the diagonal. As the sum of angles in a triangle is 180^{\circ}, you can add two lots of 180^{\circ} together, making the angle sum of a quadrilateral equal to 360^{\circ}.
This is the same for all types of quadrilaterals:

Step-by-step guide: Angles of a triangle
What are quadrilateral angles?
![[FREE] Angles Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Angles-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Angles Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4)
![[FREE] Angles Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Angles-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4 students’ understanding of angles. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 4th grade angles topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Angles Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Angles-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Angles Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4)
![[FREE] Angles Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Angles-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4 students’ understanding of angles. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 4th grade angles topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEAngle properties of quadrilaterals
The four angles in any quadrilateral always add to 360^{\circ}, but there are a few key properties of quadrilaterals that can help us calculate other angles.
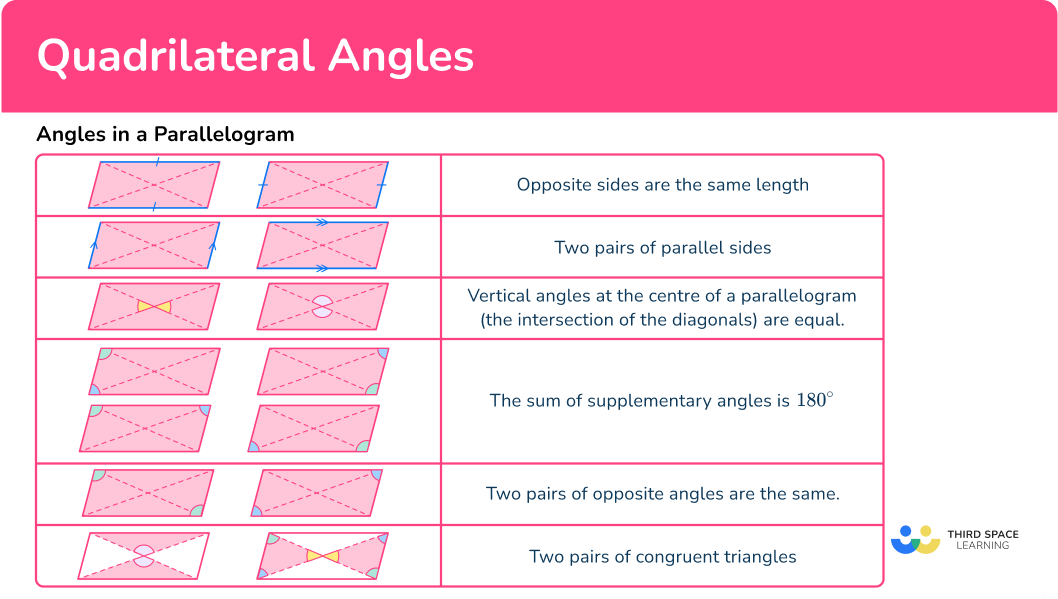
Parallelogram

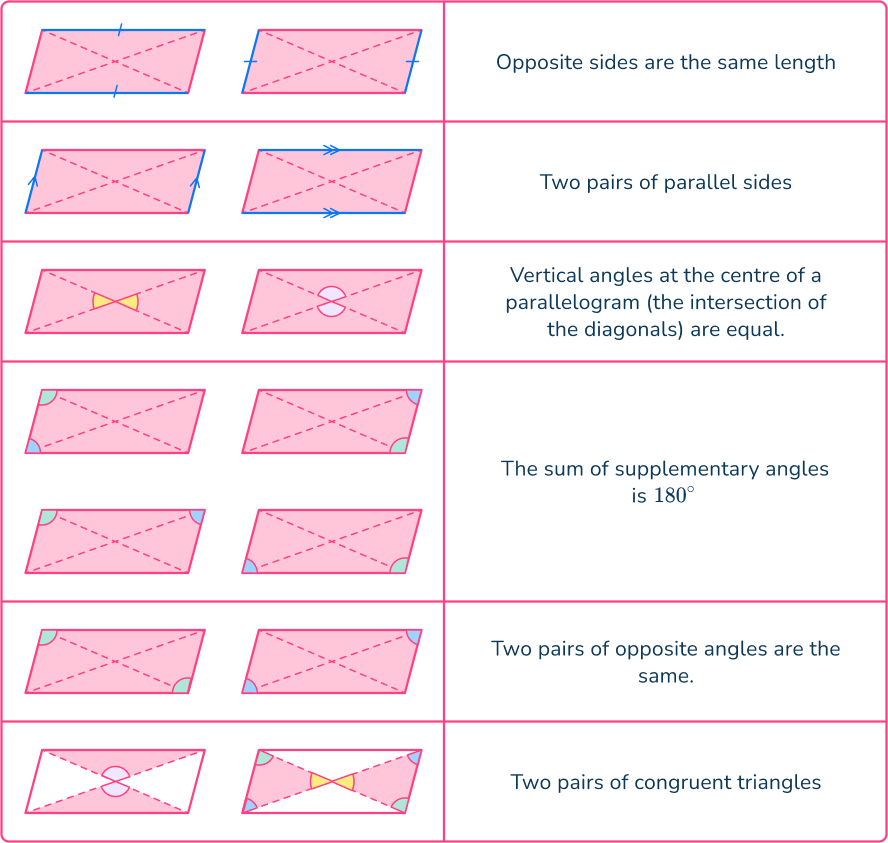
What are angles in a Parallelogram?
Rectangle

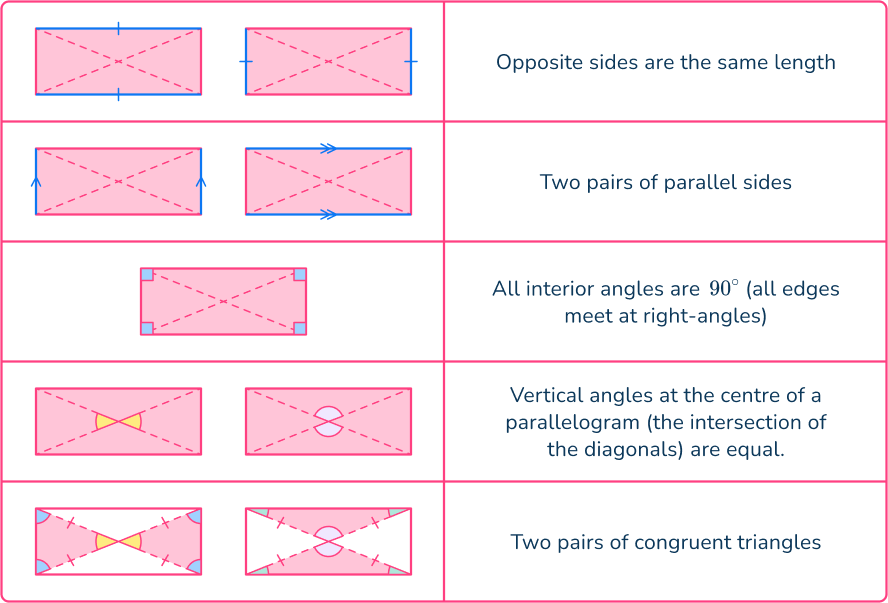
What are angles in a Rectangle?
Kite

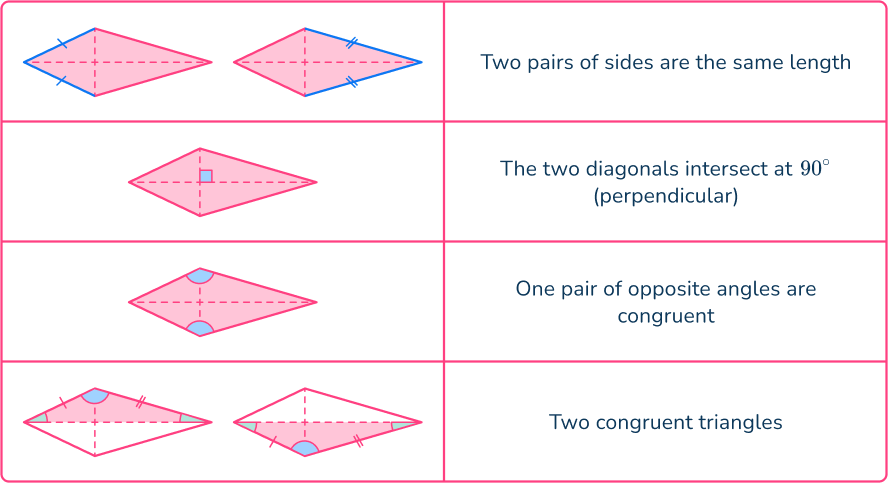
What are angles in a Kite?
Rhombus

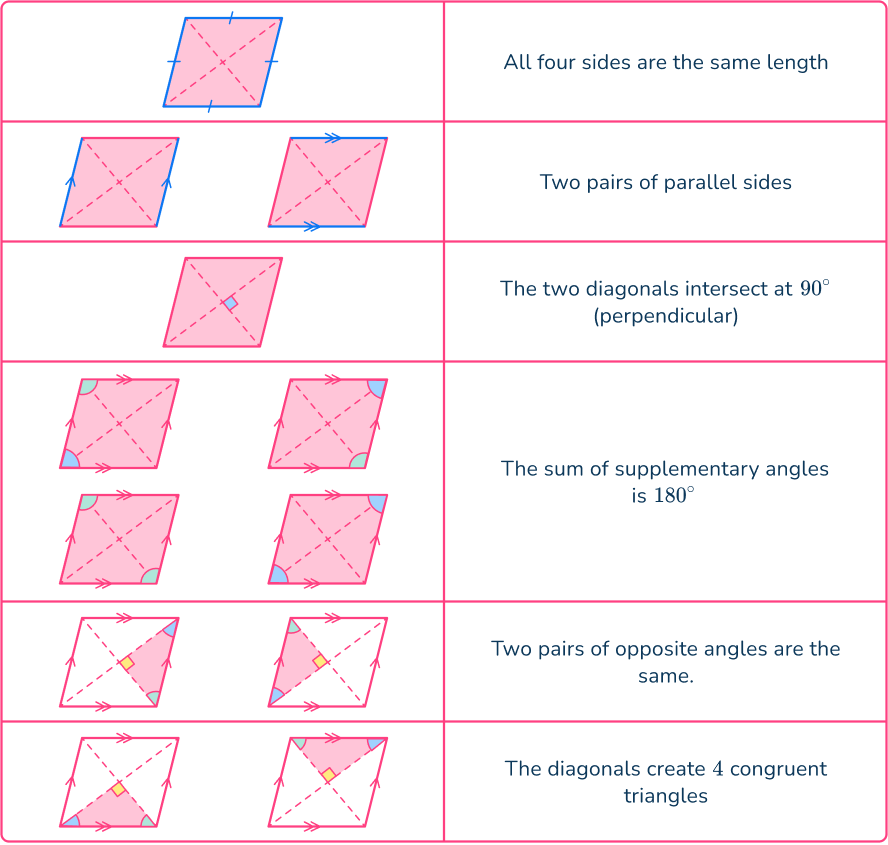
What are angles in a Rhombus?
Square

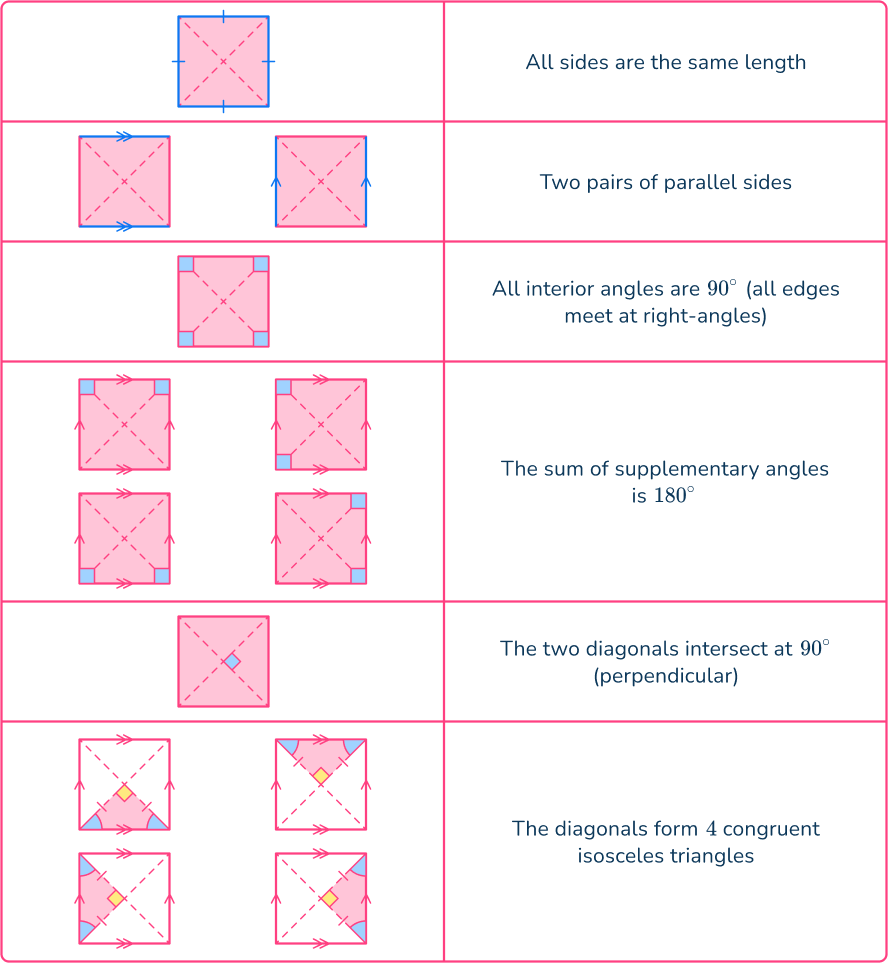
What are angles in a Square?
Trapezoid

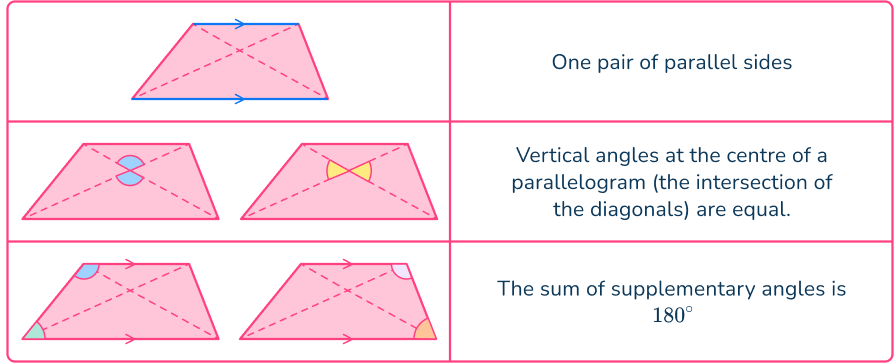
What are angles in a Trapezoid?
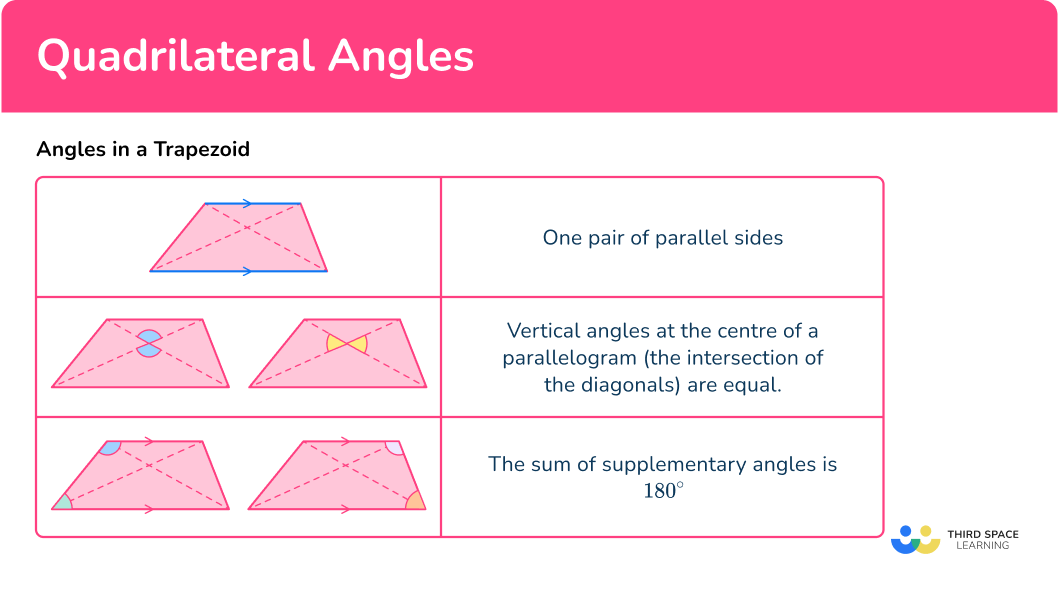
Isosceles trapezoid

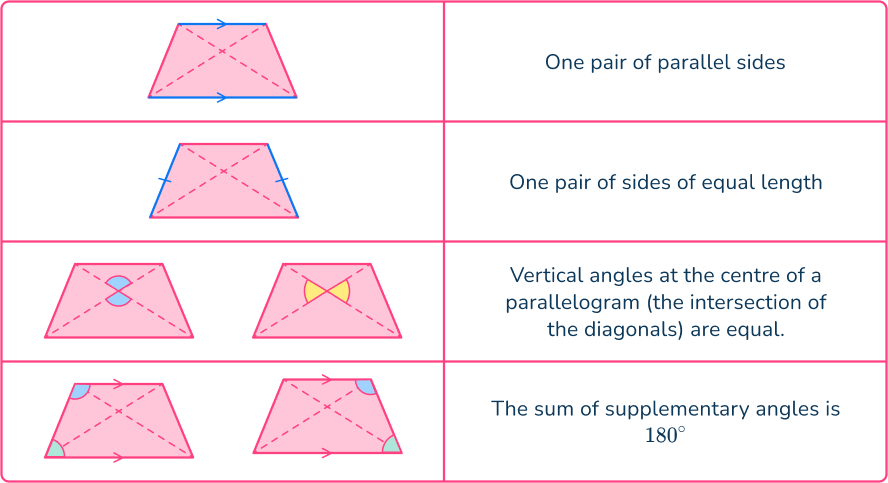
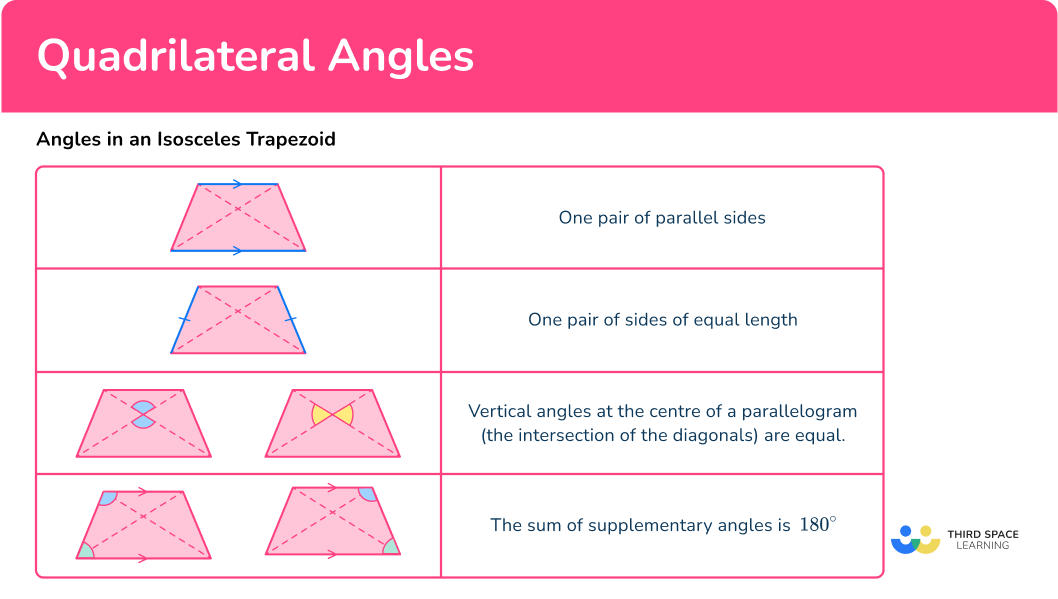
What are angles in an Isosceles Trapezoid?
Arrowhead
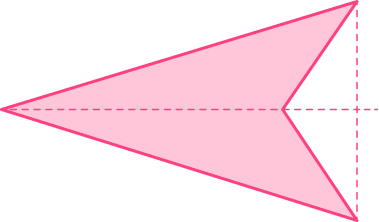
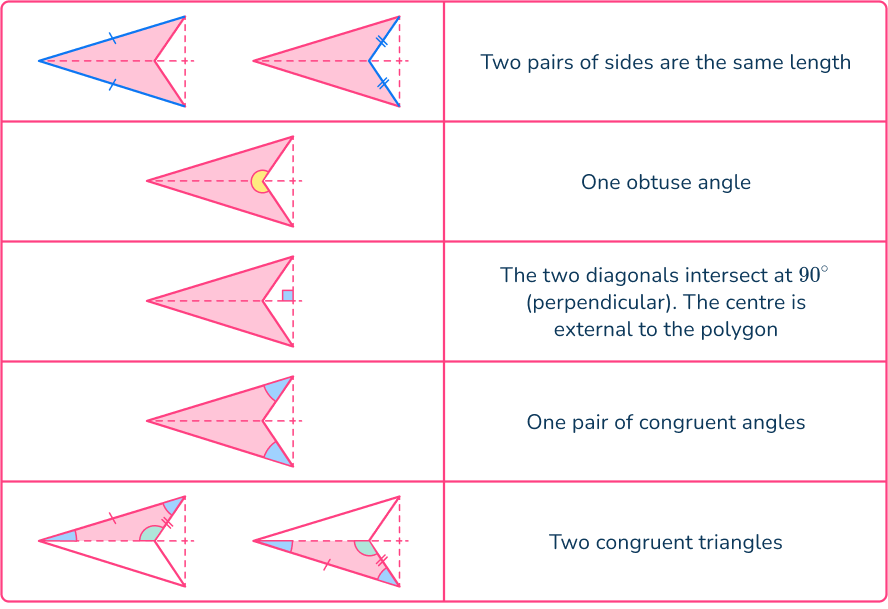
What are angles in an Arrowhead?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to high school math?
- High School – Geometry – Congruence (H.G.CO.C.11)
Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals.
How to find missing quadrilateral angles
In order to find missing quadrilateral angles:
- Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
- Add all known interior angles.
- a: Subtract the angle sum from \bf{360}^{\circ}.
b: Form and solve the equation.
Quadrilateral angles examples
Example 1: trapezoid
ABCD is a trapezoid. Calculate the size of angle BCD, labeled x.
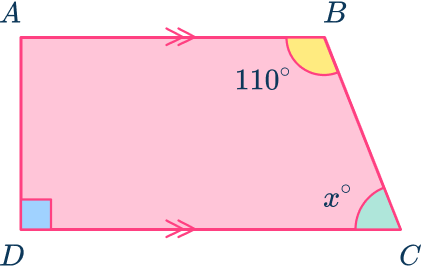
- Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
Angle fact:
- The line AD is perpendicular to lines AB and CD , so angle BAD=90^{\circ}.
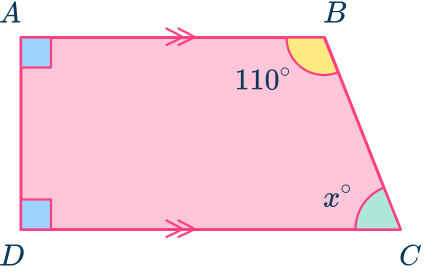
2Add all known interior angles.
90+90+110=290^{\circ}3a: Subtract the angle sum from \bf{360}^{\circ}.
Here, 360-290=70^{\circ}
So x=70^{\circ}.
Example 2: irregular quadrilateral
Find the value of the missing angle x.
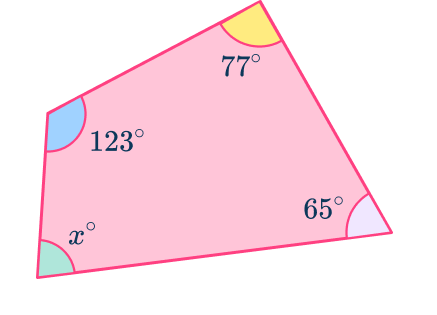
Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
Angle fact:
- Quadrilateral angles add to equal 360^{\circ}.
Add all known interior angles.
a: Subtract the angle sum from \bf{360}^{\circ}.
Here, 360-265=95^{\circ}
So x=95^{\circ}.
Example 3a: parallelogram with one interior angle (form and solve)
Calculate the missing angle for the following parallelogram.
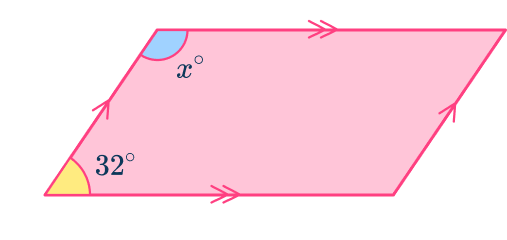
Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
Angle fact:
- Co-interior angles add to equal 180^{\circ}.
Add all known interior angles.
b: Form and solve the equation.
Here,
\begin{aligned}x+32&=180 \\\\
x+32-32&=180-32 \\\\
x&=148^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Example 3b: parallelogram with one interior angle (form and solve)
Calculate the missing angle for the following parallelogram.
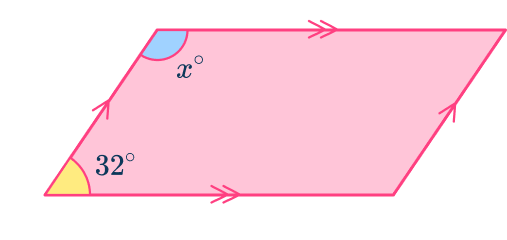
Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
Angle fact:
- Diagonally opposite angles in a parallelogram are equal.
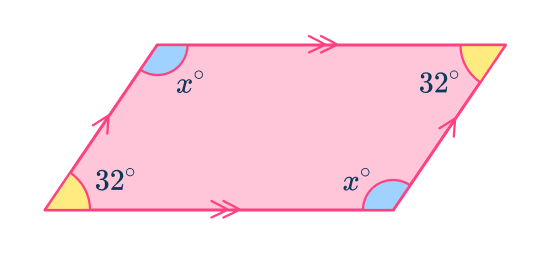
Add all known interior angles.
Simplify this to get 2x+64.
b: Form and solve the equation.
Here,
\begin{aligned}2x+64&=360 \\\\ 2x+64-64&=360-64 \\\\ 2x&=296 \\\\ 2x\div{2}&=296\div{2} \\\\ x&=148^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Example 4: exterior angle given
Calculate the measure of the missing angle for the following quadrilateral.
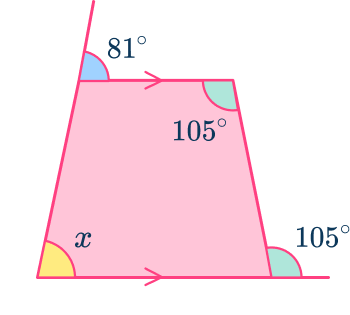
Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
Angle fact:
- Angles on a straight line add to equal 180^{\circ}.
Add all known interior angles.
a: Subtract the angle sum from \bf{360}^{\circ}.
Here, 360-279=81^{\circ}
So x=81^{\circ}.
Example 5: forming and solving equations
By finding the value for x, calculate the value of each angle in the kite drawn below.
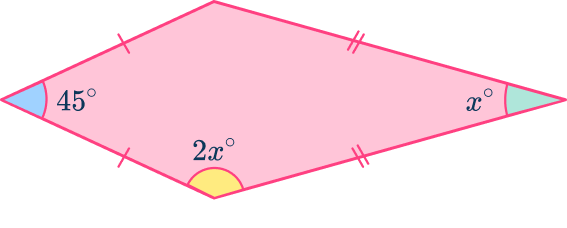
Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
Angle fact:
- One pair of diagonally opposite angles in a kite are the same size.
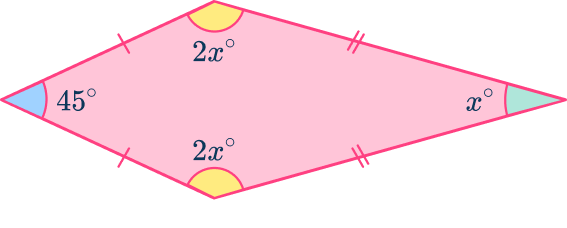
Add all known interior angles.
Simplify this to get 5x+45.
b: Form and solve the equation.
Here,
\begin{aligned}5x+45&=360 \\\\
5x+45-45&=360-45 \\\\
5x&=315 \\\\
5x\div{5}&=315\div{5} \\\\
x&=63^{\circ} \end{aligned}
As x=63^{\circ} , we can find the value for the remaining angles in the kite by substituting the value onto each angle:
2x=2\times{63}=126^{\circ}
So we have the four angles: 45^{\circ}, 126^{\circ}, 126^{\circ}, and 63^{\circ}.
You can check the solution by adding these angles together. They should add to equal 360.
45+126+126+63=360^{\circ}.
Example 6: forming and solving equations
By finding the value for x, calculate the value of each angle in the quadrilateral.
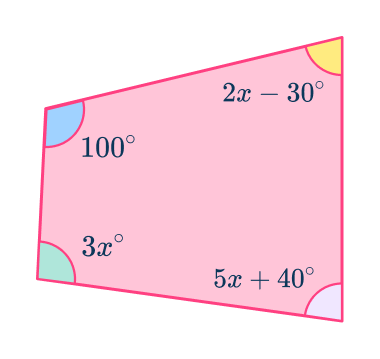
Use angle properties to determine any interior angles.
For an irregular quadrilateral, there is only one angle property.
- Quadrilateral angles add to equal 360^{\circ}.
Add all known interior angles.
This simplifies to be 10x+110.
b: Form and solve the equation.
Here,
\begin{aligned}10x+110&=360 \\\\
10x+110-110&=360-110 \\\\
10x&=250 \\\\
10x\div{10}&=250\div{10} \\\\
x&=25^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Teaching tips for quadrilateral angles
- Encourage students to classify different types of quadrilaterals (square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, rhombus) and compare their angle properties.
- Provide worksheets that involve finding unknown angles in quadrilaterals and applying properties of specific quadrilateral types.
- Students should be familiar with different types of quadrilaterals from elementary school ( 3 rd grade, 4 th grade, 5 th grade) but if needed, provide a quick intro to each type including their properties.
Easy mistakes to make
- Mistaking the sum of quadrilateral angles with the angles in a triangle
The angle sum is remembered incorrectly as 180^{\circ}, rather than 360^{\circ}. The sum of angles in a triangle is equal to 180^{\circ}.
- Joining all the diagonals
When recalling the angle sum in a quadrilateral, students join all the diagonals together, creating 4 triangles. This makes their angle sum 720^{\circ} which is also incorrect.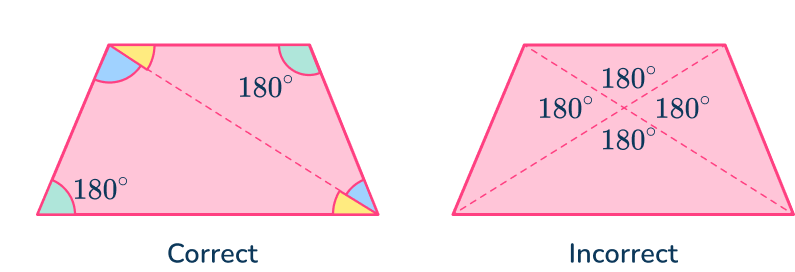
- Using an incorrect angle fact
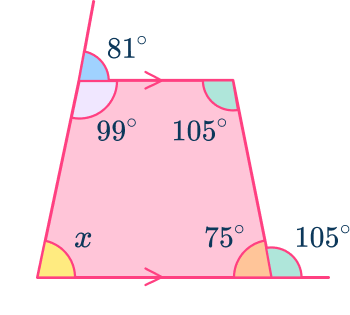
A common mistake is to use the incorrect angle fact or make an incorrect assumption to overcome a problem.
For example, here the trapezoid is assumed to be symmetrical (an isosceles trapezoid) so the interior angles are easy to deduce. This is not always true and so you should use co-interior angles instead.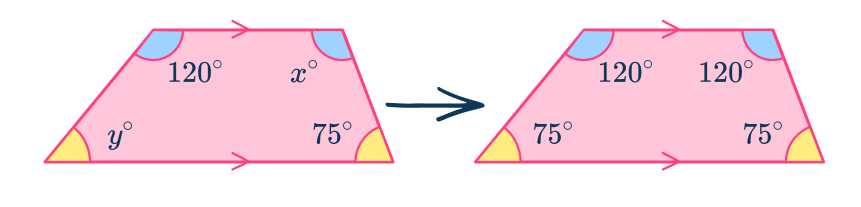
Here, the angle x should be equal to 105^{\circ} and y should be equal to 60^{\circ} due to co-interior angles in parallel lines.
Related angles in polygons lessons
- Interior and exterior angles of polygons
- Interior angles of a polygon
- Sum of exterior angles of a polygon
- Angles of a hexagon
Practice quadrilateral angles questions
1. ABCD is a rhombus. Given that ADC=84^{\circ}, calculate the value of a.
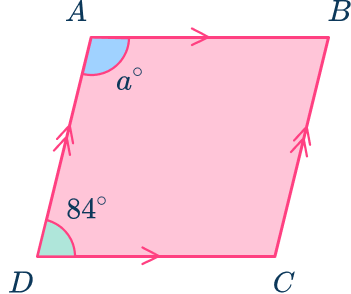




Diagonally opposite angles in a rhombus are equal
Co-interior angles add to equal 180^{\circ}.
180-84=96^{\circ}
2. ABCD is a trapezoid. Use the information below to calculate the value of b.
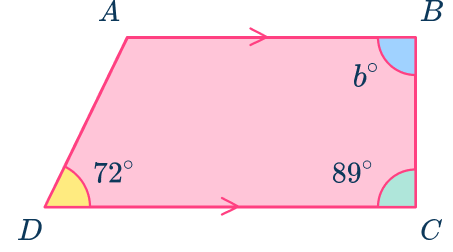




Co-interior angles add to equal 180^{\circ}.
180-89=91^{\circ}
3. ABCD is a parallelogram. Calculate the size of the angle BCD.





The sum of co-interior angles is 180^{\circ} so
\begin{aligned}5x+4x&=180 \\\\ 9x&=180 \\\\ x&=20 \end{aligned}
BCD=5x=100^{\circ}
4. ABCD is a quadrilateral. Given that CE is a straight line, calculate the interior angle at D marked x.
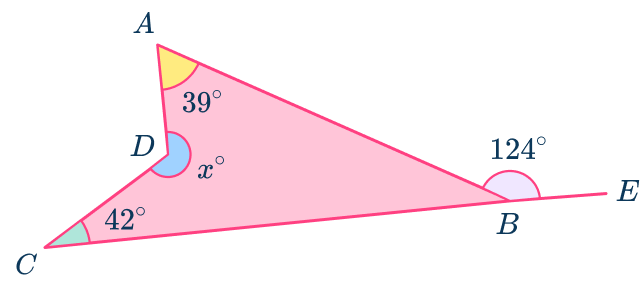




Angles on a straight line add to equal 180^{\circ}.
180-124=56^{\circ}
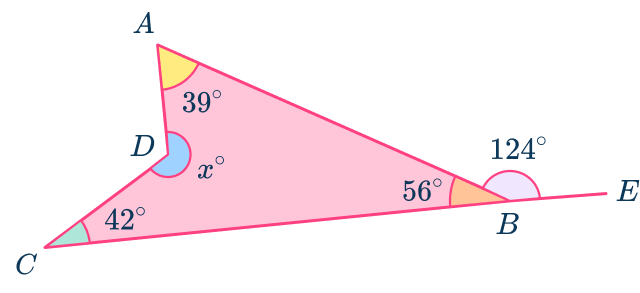
Angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360^{\circ}.
\begin{aligned}39+56+42+x&=360 \\\\ x+130&=360 \\\\ x&=223^{\circ} \end{aligned}
5. ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid. Calculate the value of y.





ADC=BCD so
\begin{aligned}2x+25&=3x-25 \\\\ 2x+50&=3x \\\\ x&=50^{\circ} \end{aligned}
\begin{aligned}y&=180-(3\times{50-25}) \\\\ &=180-125 \\\\ &=55^{\circ} \end{aligned}
6. ABCD is an irregular quadrilateral where BE is a straight line through C. Calculate the exact size of the angle y.
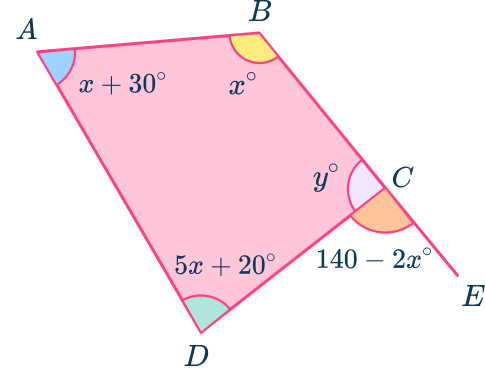




Angles on a straight line add to equal 180^{\circ}.
y=180-(140-2x)=2x+40
x+30+x+5x+20+2x+40=9x+90
Quadrilateral angles add to equal 360^{\circ}.
9x+90=360^{\circ}
\begin{aligned}9x+90-90&=360-90 \\\\ 9x&=270 \\\\ x&=30^{\circ} \end{aligned}
As x=30^{\circ},~y=2x+40=2\times{30+40}=100^{\circ}.
Quadrilateral angles FAQs
A quadrilateral is a closed figure/polygon with four sides and four vertices (corners). The sum of its interior angles is always 360 degrees.
Quadrilaterals can be classified into various types based on their side lengths, angles, and symmetry, including squares, rectangles, parallelograms, rhombuses, trapezoids, and kites. Each type of quadrilateral has its own set of properties and characteristics.
Quadrilateral angles are different from angles of other polygons primarily in their sum.
The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360 degrees, while for other polygons, the sum is calculated using the formula (𝑛−2) \times 180 degrees, where 𝑛 is the number of sides.
For example, a triangle’s angles add up to 180 degrees, and a pentagon’s angles add up to 540 degrees.
In a quadrilateral, adjacent angles are pairs of angles that share a common side (adjacent side). Since a quadrilateral has four sides and four angles, each angle has two adjacent angles.
While some angles in special types of quadrilaterals (like rectangles or squares) can be inferred without measurement due to their known properties (e.g., all angles in a rectangle are 90 degrees), a protractor is necessary for precise measurement, especially in irregular quadrilaterals where the angles are not equal or known in advance.
The next lessons are
- Congruence and similarity
- Transformations
- Mathematical proof
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!