High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Equilateral triangle Right triangle Area of a square Area of a rectangleArea of equilateral triangle
Here you will learn about how to find the area of equilateral triangles, including what formula to use and why it works.
Students will first learn about the area of equilateral triangles as part of geometry in 6th grade.
What is the area of an equilateral triangle?
The area of an equilateral triangle is the amount of the space inside an equilateral triangle.
An equilateral triangle is a triangle where all angles and sides are equal – making it a regular polygon.
Since the angles in a triangle add up to 180^{\circ}, each of the interior angles (internal angles) in an equilateral triangle is 60^{\circ}.
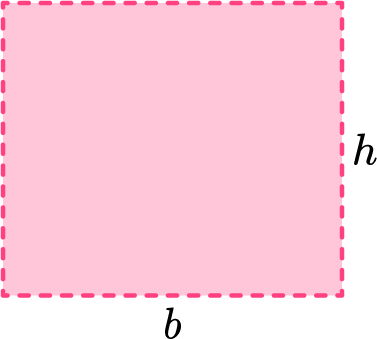
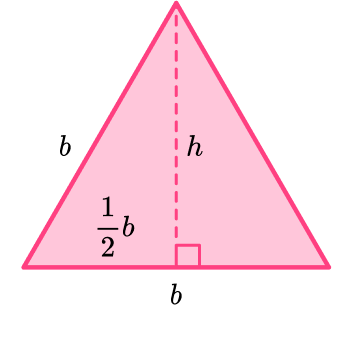
In order to find the area of an equilateral triangle, start with the area of a rectangle.
The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying the \text {base } \times \text { height }.
Within certain rectangles, there is an equilateral triangle. It can be shown by drawing lines from a midpoint of the rectangle to the corners.
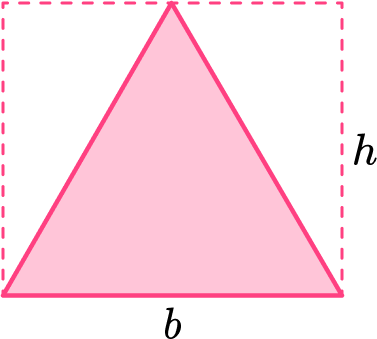
Creating the equilateral triangle (in pink) also creates two congruent right triangles (in green).
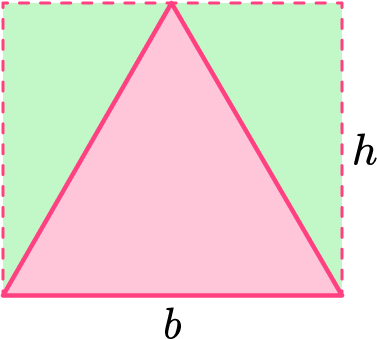
If you rotate the two right triangles and place them back to back, they form an equilateral triangle that is the same area as the blue equilateral triangle.
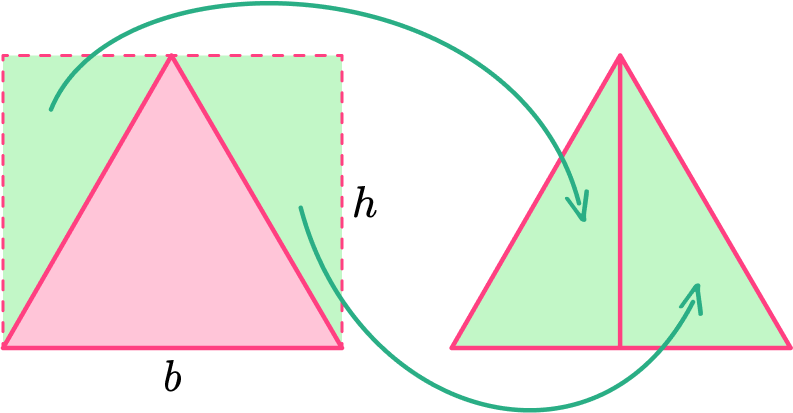
The area of the rectangle is the same as two congruent equilateral triangles. This means the area of each equilateral triangle is exactly half the area of the rectangle.
![[FREE] Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4 to 6)
![[FREE] Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4 to 6 students’ understanding of area. 15+ questions with answers covering a range of 4th, 5th and 6th grade area topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4 to 6)
![[FREE] Area Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 4 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Area-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4 to 6 students’ understanding of area. 15+ questions with answers covering a range of 4th, 5th and 6th grade area topics to identify areas of strength and support!
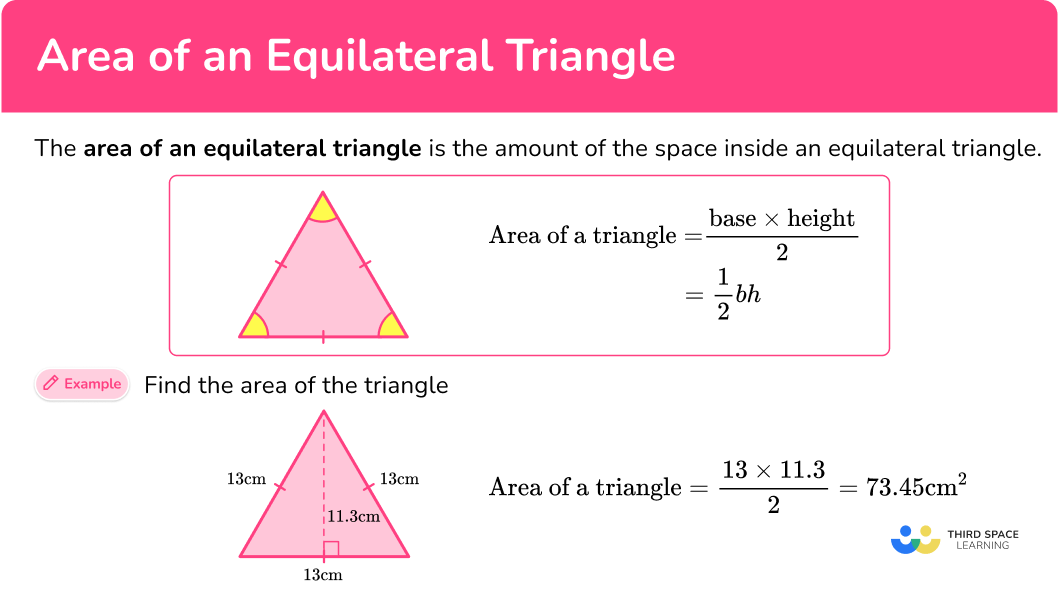
DOWNLOAD FREEThe general formula to find the area of any triangle is:
\text { Area of a triangle }=\cfrac{\text{ base } \times \text{ height }}{2}
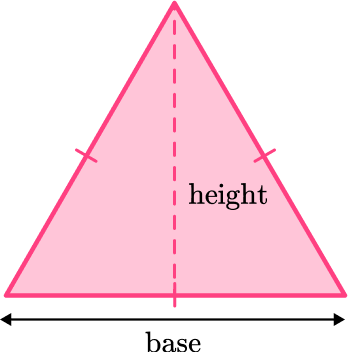
This can also be written as the following formula:
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
where b is the base length and h is the height of the triangle.
The space inside of shapes is measured in square units, so the final answer must be given in \text{units}^2. For example, \mathrm{cm}^2, \mathrm{~m}^2, or \mathrm{~mm}^2.
For example,
What is the area of the equilateral triangle?
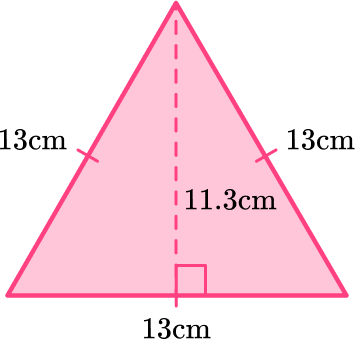
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
The base is 13 and the height is 11.3.
A few things to note:
- The height of an equilateral triangle is always a perpendicular line that starts at a vertex and intersects with the opposite side of the triangle at a 90 degree angle.
- The other side lengths of the triangle may be given, but they are extra information.
\begin{aligned} & A=\frac{1}{2} \times 13 \times 11.3 \\\\ & A=6.5 \times 11.3 \\\\ & A=73.45 \end{aligned}
The area of the equilateral triangle is 73.45 \, cm^2.
What is the area of an equilateral triangle?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Geometry (6.G.A.1)
Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
How to find the area of equilateral triangles
In order to find the area of equilateral triangles:
- Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
- Write the area formula.
- Substitute known values into the area formula.
- Solve the equation.
- Write the answer, including the units.
Area of equilateral triangles examples
Example 1: given base length and height
Find the area of the triangle below:
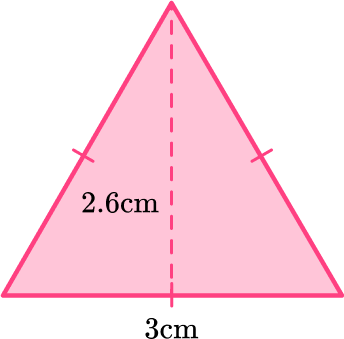
- Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
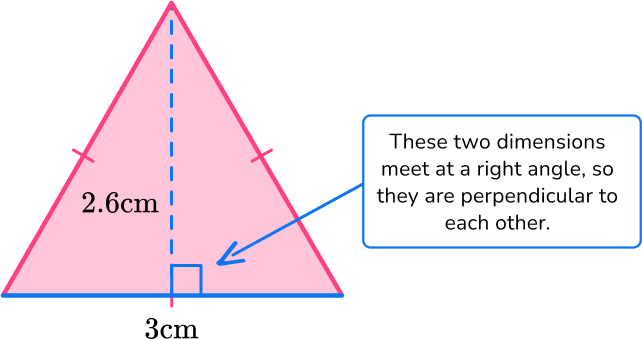
b = 3 \, cm
h = 2.6 \, cm
2Write the area formula.
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
3Substitute known values into the area formula.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (3)(2.6) \end{aligned}
4Solve the equation.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (3)(2.6)\\\\ &=3.9 \, cm^2 \end{aligned}
5Write the answer, including the units.
A=3.9 \mathrm{~cm}^2
Remember: Your final answer must be in units squared.
Example 2: given base length and height
Find the area of the triangle below:
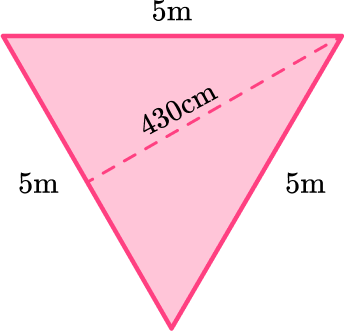
Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
Rotating the triangle makes it easier to identify the base and height.
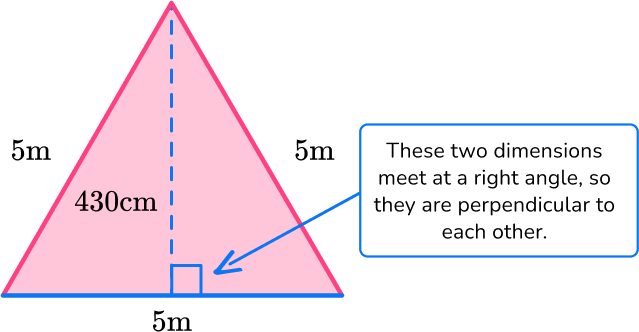
b = 5 \, m
h = 430 \, cm
Notice, there are 2 different units here. You must convert them to a common unit:
430 \, cm = 4.3 \, m
b = 5 \, m
h = 4.3 \, m
Write the area formula.
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
Substitute known values into the area formula.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (5)(4.3) \end{aligned}
Solve the equation.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (5)(4.3)\\\\ &=10.75 \end{aligned}
Write the answer, including the units.
A=10.75 \mathrm{~cm}^2
Example 3: given base length and height – fractions
Find the area of the triangle below:
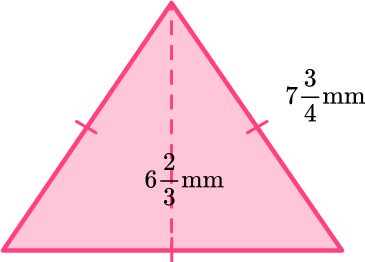
Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
Even though the base length is not labeled, since all sides of the equilateral triangle are the same the base will also be 7 \, \cfrac{3}{4} \mathrm{~mm}.
\mathrm{b}=7 \, \cfrac{3}{4} \mathrm{~mm}
\mathrm{h}=6 \, \cfrac{2}{3} \mathrm{~mm}
Write the area formula.
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
Substitute known values into the area formula.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, \left(7 \, \cfrac{3}{4} \, \right)\left(6 \, \cfrac{2}{3} \, \right) \end{aligned}
Solve the equation.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, \left(7 \, \cfrac{3}{4} \, \right)\left(6 \, \cfrac{2}{3} \, \right) \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, \left( \, \cfrac{31}{4} \, \right)\left( \, \cfrac{20}{3} \, \right) \\\\ & =\cfrac{620}{24} \\\\ & =25 \, \cfrac{20}{24} \\\\ & =25 \, \cfrac{5}{6} \end{aligned}
Write the answer, including the units.
A=25 \, \cfrac{5}{6} \mathrm{~mm}^2
Example 4: word problem
Shown below is a triangular shaped field. Each chicken needs 5 \mathrm{~m}^2 to graze. How many chickens can fit into this field?
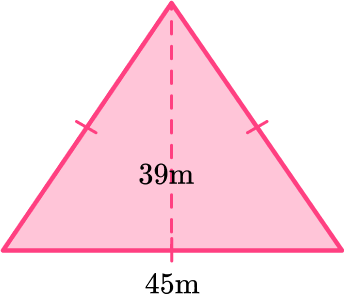
Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
b = 45 \, m
h = 39 \, m
Write the area formula.
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
Substitute known values into the area formula.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (45)(39) \end{aligned}
Solve the equation.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, (45)(39) \\\\ & =877.5 \end{aligned}
Write the answer, including the units.
A=877.5 \mathrm{~m}^2
Now to calculate how many chickens will fit into the field, take 877.5 \, m^2 and divide it by 5 \, m^2 because each chicken needs that much space to graze on the field.
877.5 \div 5=175.5
The quotient has 175 wholes and 5 tenths.
There cannot be part of a chicken and 175.5 is not enough for 176 chickens.
So, 175 chickens will fit in the field.
Example 5: compound shapes
Below is the layout for a new garden that needs to be filled with soil. Each bag of soil costs \$4.50 and covers an area of 2.5 \, m^2. How much would it cost to cover the entire garden with soil?
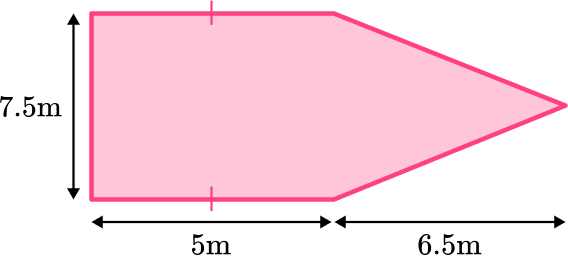
Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
Split the garden into 2 shapes; a rectangle and an equilateral triangle.
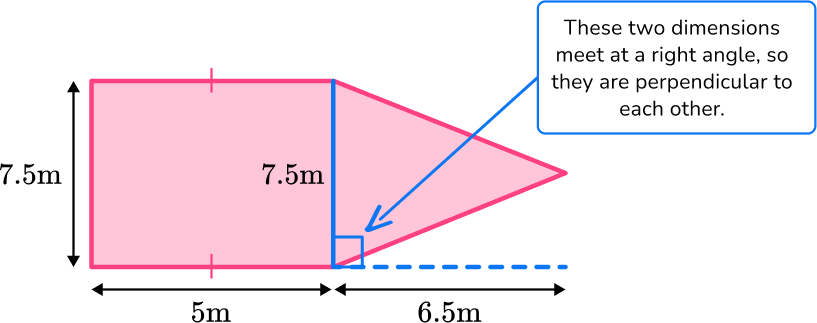
For the triangle:
b = 7.5 \, m
h = 6.5 \, m
Write the area formula.
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
Substitute known values into the area formula.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (7.5)(6.5) \end{aligned}
Solve the equation.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, (7.5)(6.5)\\\\ &=24.375 \, m^2 \end{aligned}
Now you must find the area of the rectangle.
\begin{aligned}
\text { Area of a rectangle }&=l \times w \\\\
&=5 \times 7.5 \\\\
&=37.5 \, m^{2}
\end{aligned}
Write the answer, including the units.
Total Area = 24.375+37.5=61.875 \, m^2
Now divide 61.875 by 2.5 since one bag of soil only covers an area of 2.5 \, m^2.
61.875 \div 2.5=24.75
The quotient has 24 wholes and 75 hundredths. You cannot buy part of a bag, so 25 bags are needed.
Multiply to find the costs: 25 bags of soil \times \$4.50 = \$112.50.
The total cost to fill the plot with soil is \$112.50.
Example 6: calculating base length
Triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle with an area of 173 \, cm^2. The height of the triangle is 17.3 \, cm. Find the length of the base of the triangle.
Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
A=173 \mathrm{~cm}^2
b = \, ?
h = 17.3 \mathrm{~cm}
Write the area formula.
A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h
Substitute known values into the area formula.
\begin{aligned} A &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & 173=\cfrac{1}{2} \, \times b \times 17.3 \\\\ & 173=\cfrac{1}{2} \, \times 17.3 \times b \\\\ & 173=8.65 \times b \end{aligned}
Solve the equation.
173=8.65 \times b
To solve, find what times 8.65 is equal to 173. You can use the inverse operation of division to solve. Divide both sides by 8.65.
\begin{aligned} &173 \quad \quad = \quad \; 8.65 \times b \\ & \div 8.65 \quad \quad \quad \div 8.65 \end{aligned}
20=b
Solve the original equation to check your work.
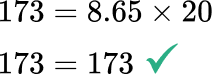
Write the answer, including the units.
b=20 \mathrm{~cm}
The units are not squared, because the base is the length of the bottom of the triangle (one-dimensional), not the square units within the triangle (two-dimensional).
Teaching tips for area of equilateral triangles
- Give students the opportunity to measure the length of the sides and the height of equilateral triangles. Once they have found one height measurement, encourage them to rotate the triangle to find the other two to see that the height of the equilateral triangle is the same no matter which side is used as a base. Understanding these attributes of an equilateral triangle helps students think flexibly when different measurements are given.
- Introduce how to find the area of an equilateral triangle by connecting the base of the triangle to the rectangle formed around it. This helps students understand why the area of a triangle is half the area of a rectangle, giving meaning to the formula and making it easier to remember.
- Worksheets are a useful tool, but be sure to choose ones that include a variety of types of triangles and scenarios. Triangles where all measurements are given, triangles where no measurements are given (either on grid paper or give students tools to measure), word problems that include a picture of the triangle, word problems that do not, etc.
Easy mistakes to make
- Thinking the height of an equilateral triangle is the same as the base
Even though the length of all sides are equal, the height will not be the same as the sides – which means the base and the height will never be equivalent.
- Forgetting to write the units
It is common to forget the units for area in the final answer. When calculating area, your answer must always include the square units.
Practice area of equilateral triangles questions
1. Find the area of the triangle below:
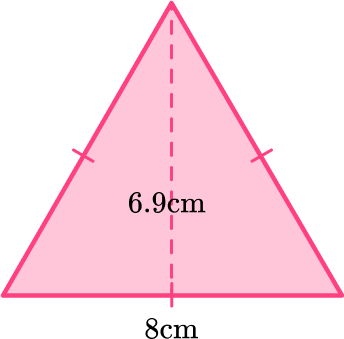




The area of a triangle is calculated with the formula: A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h.
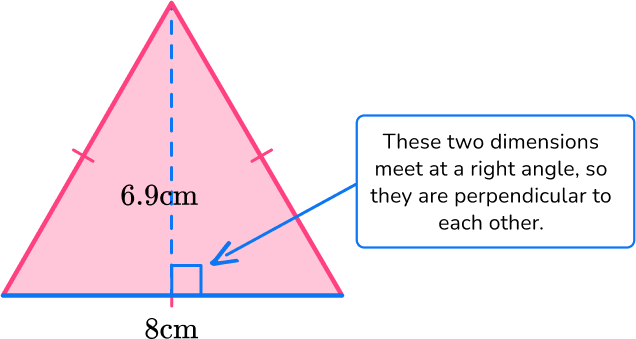
For this triangle:
b = 8 \, cm
h = 6.9 \, cm
Substitute the values into the formula.
\begin{aligned} A & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, (8)(6.9) \\\\ & =27.6 \mathrm{~cm}^2 \end{aligned}
2. Find the area of the triangle below:
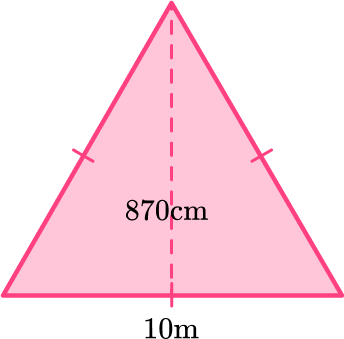




The area of a triangle is calculated with the formula: A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h.
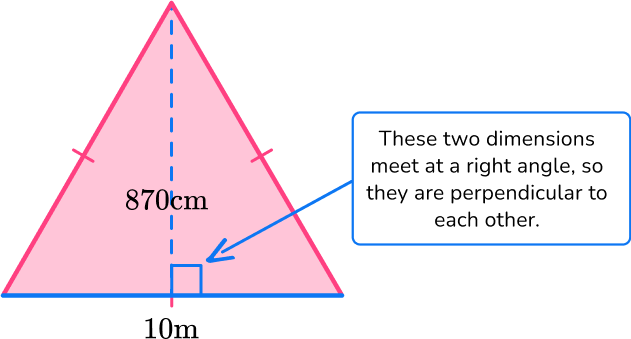
For this triangle:
b = 10 \, m
h = 870 \, cm
Since the measurements are in different units (m and cm), they need to be converted to the same unit: 870 \, cm = 8.7 \, m.
b = 10 \, m
h = 8.7 \, m
Substitute the values into the formula.
\begin{aligned} A & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, (10)(8.7) \\\\ & =43.5 \mathrm{~cm}^2 \end{aligned}
3. Find the area of the triangle below:
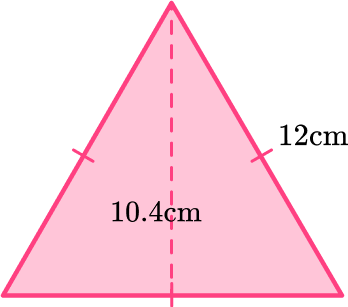




The area of a triangle is calculated with the formula: A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h.
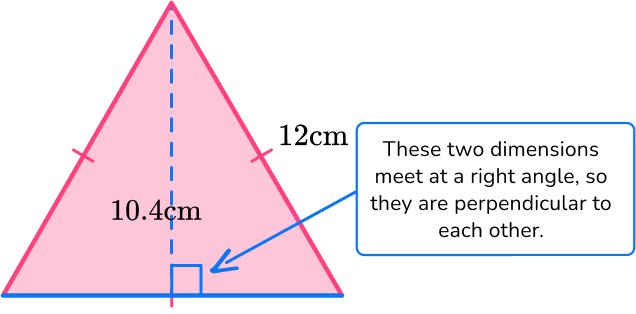
Even though the base length is not labeled, since all sides of an equilateral triangle are the same the base will also be 12 \, cm.
For this triangle:
b = 12 \, cm
h = 10.4 \, cm
Substitute the values into the formula.
\begin{aligned} A & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, (12)(10.4) \\\\ & =62.4 \mathrm{~cm}^2 \end{aligned}
4. The three equilateral triangles below are congruent and form a trapezoid. Find the area of the trapezoid:





The area of a triangle is calculated with the formula: A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h.
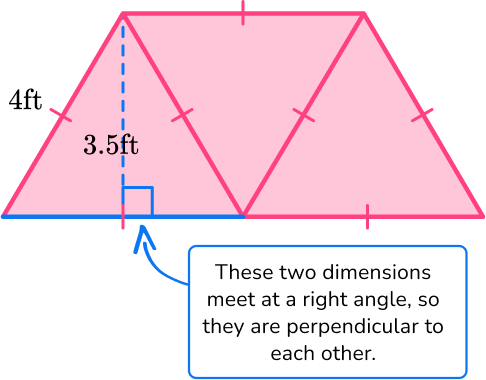
Even though the base length is not labeled, since all sides of an equilateral triangle are the same the base will also be 4 \, ft.
For this triangle:
b = 4 \, ft
h = 3.5 \, ft
Substitute the values into the formula.
\begin{aligned} A & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, (4)(3.5) \\\\ & =7 \, f t^2 \end{aligned}
7 \, ft^2 is the area of one triangle.
Multiply by 3 to find the area of all of the triangles together, which form the trapezoid.
7 \times 3=21 \mathrm{~ft}^2
5. Shown below is a compound shaped rhino enclosure. Each rhino needs a minimum of 9 \, m^2 to roam around. What is the maximum number of rhinos that can fit into this enclosure?
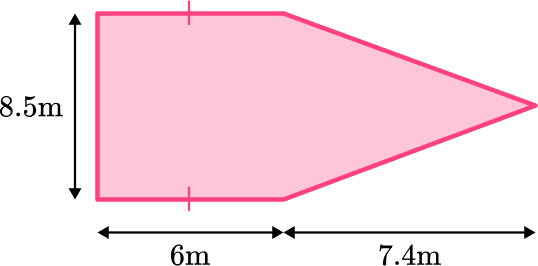
9 rhinos

10 rhinos

5 rhinos

18 rhinos

The shape can be split into a rectangle and a triangle. The opposite sides of the rectangle are congruent.
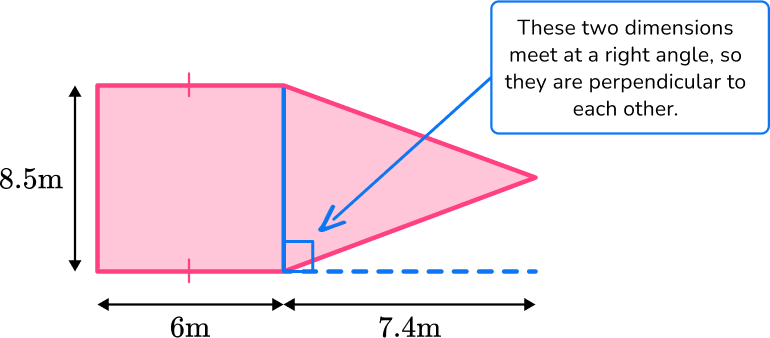
The area of the rectangle is 8.5 \times 6 = 43 \, m^{2}
The area of the triangle is \cfrac{1}{2} \times 8.5 \times 7.4 = 31.45 \, m^{2}
This means the total area is 43 + 31.45=82.45 \, m^{2}
Now to calculate how many rhinos will fit into the enclosure, take 82.45 \, m^2 and divide it by 9 \, m^2 because each rhino needs that much space to roam.
82.45 \div 9=9.161
The quotient has 9 wholes and 161 thousandths.
There cannot be part of a rhino and 9.161 is not enough for 10 rhinos.
So, 9 rhinos will fit in the enclosure.
6. Triangle TRF is an equilateral triangle with an area of 15.6 \, inch^2. The perimeter of the triangle is 18 inches. Find the height of the triangle.




Triangle TRF is made up of 3 equal sides, so if the perimeter is 18, each side is 6, since 6 + 6 + 6 = 18.
The area of a triangle is calculated with the formula: A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h.
A=15.6 \text { inches}^2
b=6 \text { inches}
h = \, ?
\begin{aligned} A & =\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ 15.6 &=\cfrac{1}{2} \, \times 6 \times h \\\\ 15.6 & =3 \times h \end{aligned}
To solve, find what times 3 is equal to 15.6.
You can use the inverse operation of division to solve.
Divide both sides by 3.
\begin{aligned} & 15.6 \quad = \quad 3 \times h \\ & \div 3 \; \quad \quad \quad \div 3 \end{aligned}
5.2 = h
Solve the original equation to check your work.
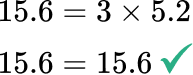
Area of equilateral triangles FAQs
The perimeter of equilateral triangles is found by adding all the side lengths together. Since the length of each side is the same, you can also multiply one side length of the equilateral triangle by 3.
Yes, no matter the type of triangle, the following formula: A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h will calculate the area.
The pythagorean theorem explains a relationship between the sides of all right triangles (right-angled triangles). It is represented by the formula a^2+b^2=c^2, where a and b are sides of the triangle and c is the hypotenuse.
How to find the area of an equilateral triangle in later grades
You will not always be given the height of the equilateral triangle, but if you know the side length there are ways to calculate the height or area using other methods.
To find the area of an equilateral triangle when only the side length has been given, we will need to calculate the height of the triangle using Pythagoras’ Theorem or Trigonometry (SOHCAHTOA).
Finding the height using Pythagoras’ Theorem
Let the side length of the equilateral triangle represent the base, b.
Drawing a perpendicular line from the top vertex to the base forms the height, h, and also forms a right angled triangle with hypotenuse b and short sides h and \cfrac{1}{2} \, b.
\begin{aligned} h &=\sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-{{\left( \frac{1}{2}b \right)}^{2}}} \\\\ & =\sqrt{\frac{3}{4}{{b}^{2}}} \\\\ & =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}b \end{aligned}
Finding the height using SOHCAHTOA
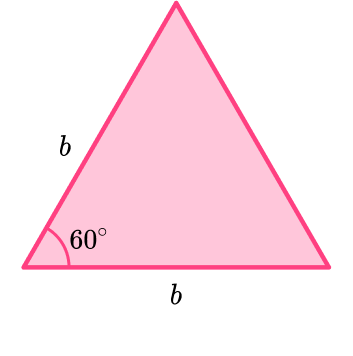
Let the side length of the equilateral triangle represent the base, b.
Drawing a perpendicular line from the top vertex to the base forms the height, h, and also forms a right angled triangle with hypotenuse b and angle 60^{\circ}.
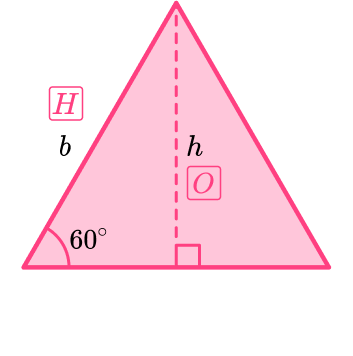
\sin \left( 60 \right)=\cfrac{h}{b}
So, h=b\sin \left( 60 \right)
We can also find the area of the equilateral triangle using the area of a triangle formula
\text{Area }=\cfrac{1}{2} \, ab\sin C
The formula would give the area as
\text{Area }=\cfrac{1}{2} \, {{b}^{2}}\sin \left( 60 \right)
Using the exact value of \sin \left( 60 \right)=\cfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, this gives us
Area of an equilateral triangle =\cfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{b}^{2}}
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!