High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
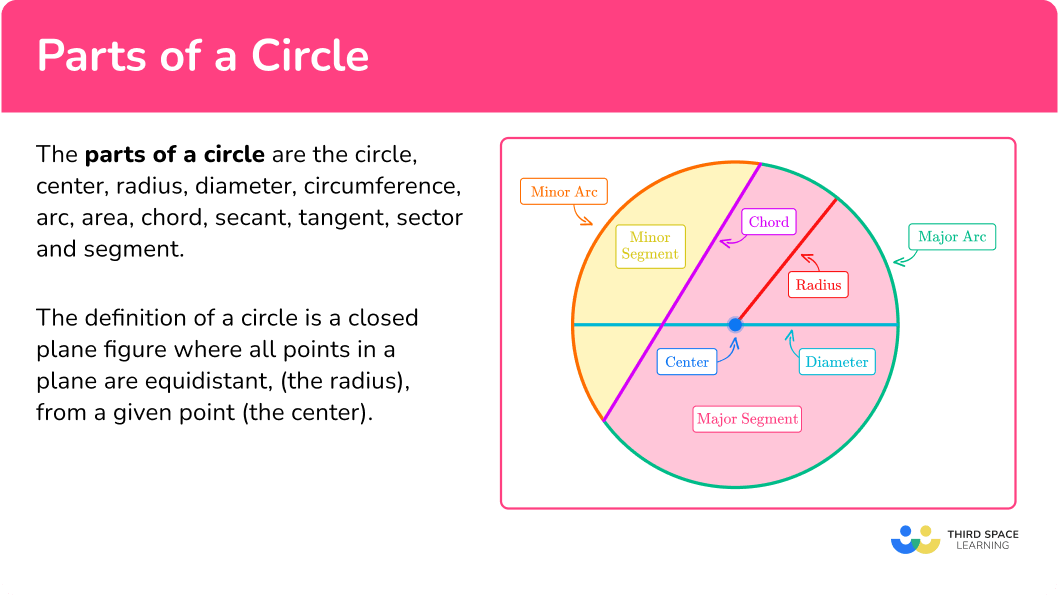
Parts of a circle
Here you will learn about the different parts of a circle including how to identify the key parts of a circle from a diagram, how to identify the key parts of a circle from a definition and how to draw a circle with the different parts labeled, such as the diameter of a circle.
Students will first learn about parts of a circle as part of geometry in high school.
What are the parts of a circle?
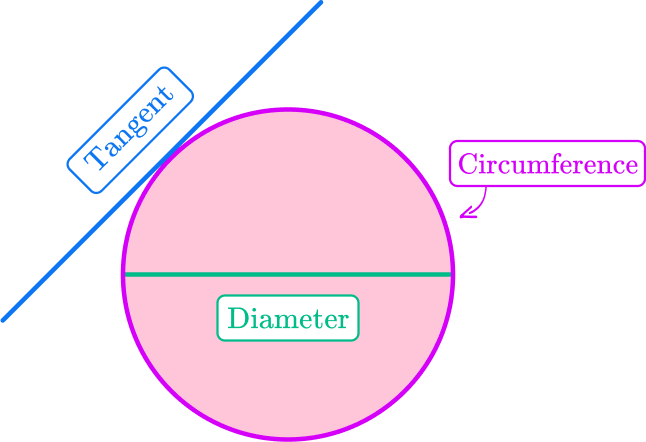
The parts of a circle are the circle, center, radius, diameter, circumference, arc, area, chord, secant, tangent, sector and segment.
The definition of a circle is a closed plane figure where all points in a plane are equidistant, (the radius), from a given point (the center).
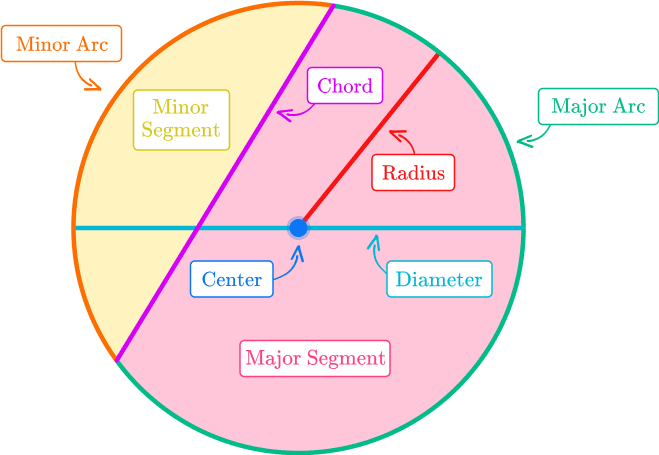
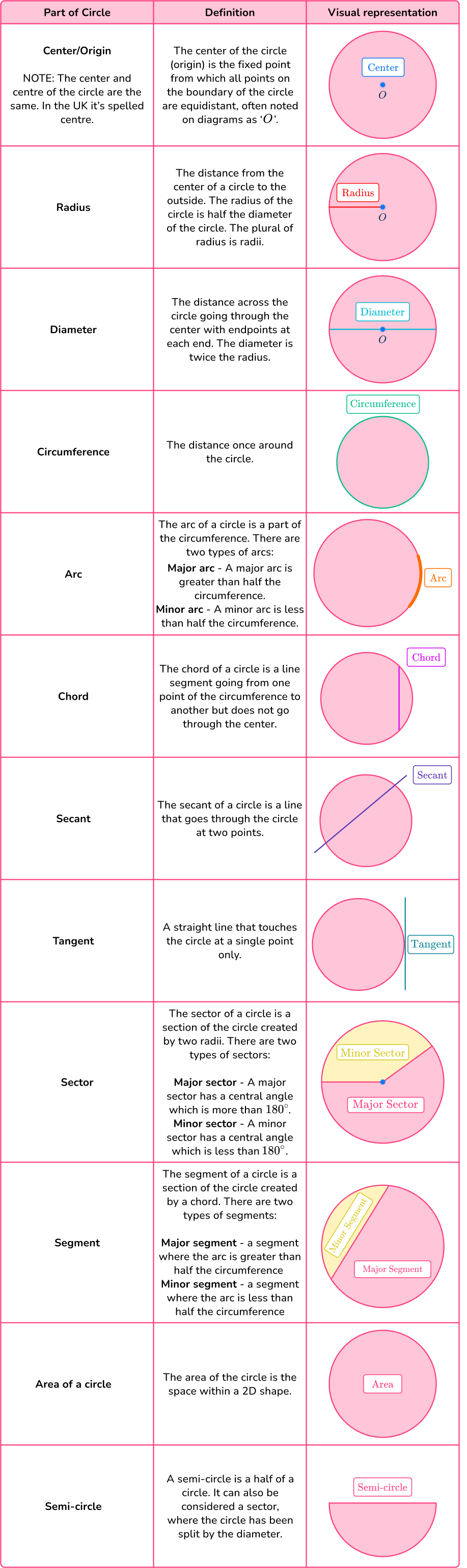
What are the parts of a circle?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to high school math?
- High School: Geometry (HS.G.CO.A.1)
Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
- High School: Geometry (HS.G.C.A.2)
Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle.
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents. 40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents. 40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to identify parts of a circle
In order to identify and label parts of a circle:
- Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
- Clearly state your answer, using specific mathematical language.
Parts of a circle examples
Example 1: identifying a part of a circle from a diagram
Name the part of the circle shown in blue in the diagram below.
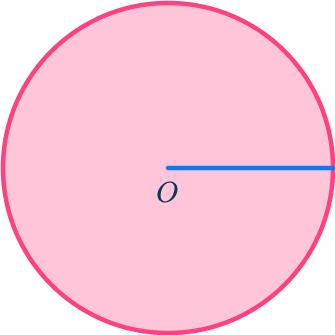
- Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
Here are some key questions you can ask yourself:
- Is it a line or part of the circle’s area? \hspace{2.75cm} Line
- If a line, does it go through the origin of the circle? \hspace{1cm} Yes
- If a line, is it part of the circle’s circumference? \hspace{1.6cm} No
2Clearly state your answer, using specific mathematical language.
The part of the circle shown in the diagram is the radius.
Example 2: identifying a part of a circle from a diagram
Name the part of the circle shown in yellow in the diagram below.
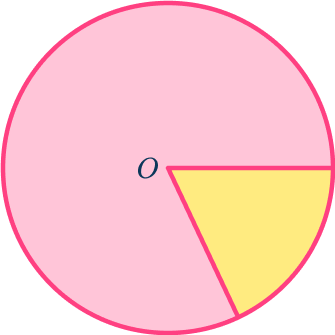
Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
Here are some key questions you can ask yourself:
- Is it a line or part of the circle’s area? \hspace{1.5cm} Part of the area
- If part of the circle’s area, is it \hspace{2.4cm} Sector as the radii
a segment or sector? \hspace{3.5cm} meet at the origin
Clearly state your answer, using specific mathematical language.
The part of the circle shown in the diagram is the sector, specifically the minor sector.
Example 3: identifying a part of a circle from a diagram
Name the part of the circle shown in blue in the diagram below.
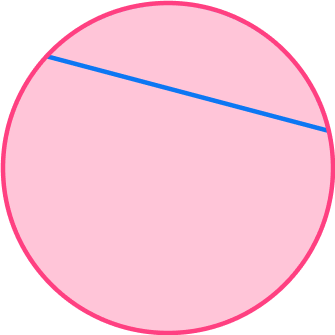
Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
Here are some key questions you can ask yourself:
- Is it a line or part of the circle’s area? \hspace{2.75cm} Line
- If a line, does it go through the origin of the circle? \hspace{1cm} No
- If a line, is it part of the circle’s circumference? \hspace{1.6cm} No
Clearly state your answer, using specific mathematical language.
The part of the circle shown in the diagram is the chord.
Example 4: identifying a part of a circle from a diagram
Name the part of the circle shown in yellow in the diagram below.

Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
Here are some key questions you can ask yourself?
- Is it a line or part of the circle’s area? \hspace{1.45cm} Part of the area
- If part of the circle’s area, is it \hspace{2.4cm} Segment as the line
a segment or sector? \hspace{3.5cm} shown is a chord
Clearly state your answer, using specific mathematical language.
The part of the circle shown in the diagram is the segment – specifically the minor segment.
Example 5: identifying a part of a circle from a diagram
Name the part of the circle shown in blue in the diagram below.
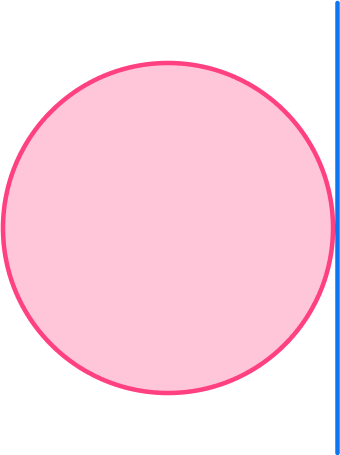
Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
Here are some key questions you can ask yourself?
- Is it a line or part of the circle’s area? \hspace{2.75cm} Line
- If a line, does it go through the origin of the circle? \hspace{1cm} No
- If a line, is it part of the circle’s circumference? \hspace{1.55cm} No, it touches the
\hspace{7.6cm} circumference of
\hspace{7.55cm} the circle at
\hspace{7.55cm} one point
Clearly state your answer, using specific mathematical language.
The part of the circle shown in the diagram is the tangent.
Example 6: labeling a part of a circle on a diagram
On the circle below:
Draw a diameter
Draw a tangent
Label the circumference
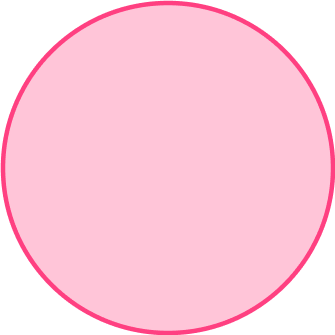
Identify the key aspects of the part of the circle.
Here you are being asked to draw the parts on the given circle, so you need to consider each key term:
- Diameter – The distance across the circle going through the center
- Tangent – A straight line that touches the circle at a single point only
- Circumference – The distance once around the circle
Clearly state your answer by labeling the diagram given.
Teaching tips for parts of a circle
- Instead of relying on worksheets for students to identify the parts of the circle, consider interactive activities for student practice. Provide students with real-world examples and have them measure the diameter and find the longest chord on that example.
- Use technology to allow students to interact with circles in a different way. There are many educational apps and interactive websites that offer simulations and exercises that lead to deeper understanding.
Easy mistakes to make
- Confusing the radius and the diameter
The radius is from the center of the circle to the circumference while the diameter goes across the whole circle. Both will pass through the origin.
- Confusing the segment and the sector
A segment is made from a chord while a sector will have lines (radii) coming from the origin.
Note: Some students like to consider a sector like a slice of pizza.
- Confusing the chord and the diameter
A chord of the circle will not go through the origin of the circle while the diameter will.
- Confusing the tangent and the secant
A tangent only touches the circumference at a single point, it does not cross the line. A secant will cross the circumference twice.
Related circle math lessons
Practice parts of a circle questions
1. If a circle has an ‘O’ noted on it, it normally notes the:
Circle is an O shape

Middle of the circle (origin)

Name of the circle is O

A circle inside a circle

The ‘O’ refers to the center of the circle which is called the origin of the circle.
2. Which will be the longest in length of any circle?
Radius

Diameter

Chord

Circumference

The circumference is the distance around the edge of the circle, this will always be longer than the radius, diameter or a chord.
3. What part of the circle is shown in the diagram below?
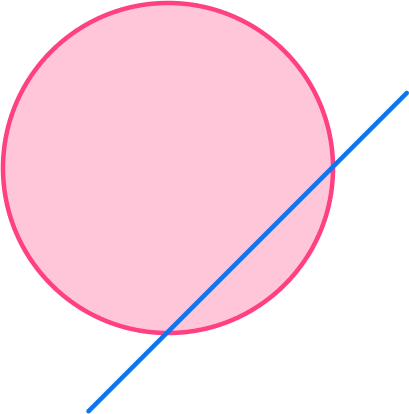
a secant

a sector

a tangent

a segment

The secant of a circle is a line that goes through the circle at two points.
4. A line that touches the circumference of a circle at one point is called a:
A secant

A segment

A tangent

An arc

A tangent is a straight line that touches the circle at a single point only.
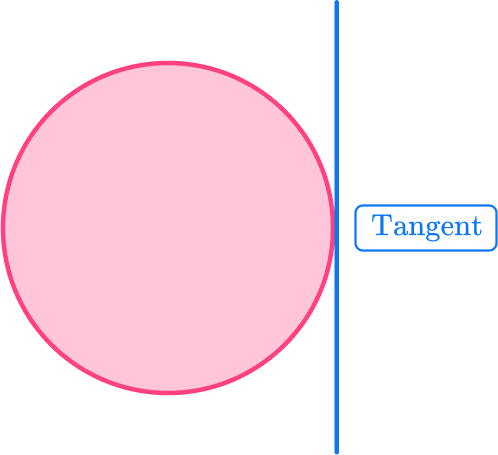
5. Which of the following statements is true?
The radius is twice the length of the diameter:

The diameter is twice the length of the radius.

The radius is half the length of the circumference.

The diameter is half the length of the circumference.

The diameter is twice the length of the radius. The distance from the center of the circle to the circumference is called the radius.
The distance across the circle passing through the center is called the diameter. This means that the diameter is twice as long as the radius.
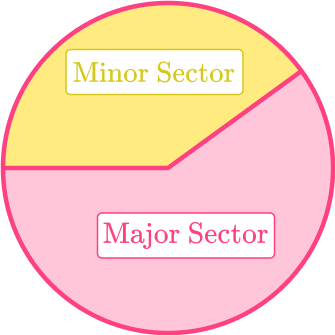
6. A sector is:
Part of a circle’s circumference

Part of a circle’s area

A line that goes through a circle

The middle of a circle

A sector consists of the area created by an arc and two radii.
Parts of a circle FAQs
The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to any point on the circle’s circumference. It is typically represented by an r.
Concentric circles are circles that share the same center but have a different radius. They are often circles that are nested within one another.
A cyclic quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices are located on the circumference of a circle.
The next lessons are
- Angles of a circle
- Circle theorems
- Prism shape
- Trigonometry
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!