High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Fractions Numerator and denominator Place valueDecimal place value
Here you will learn about decimal place value, including the names and values of the different positions.
Students will first learn about decimal place value as part of their work with numbers and operations in base ten in elementary school.
What is decimal place value?
Decimal place value extends our understanding of place value to the decimal system, which are the digits to the right of the decimal point.
To do this, look at the connection between fractions and decimals.
For example,
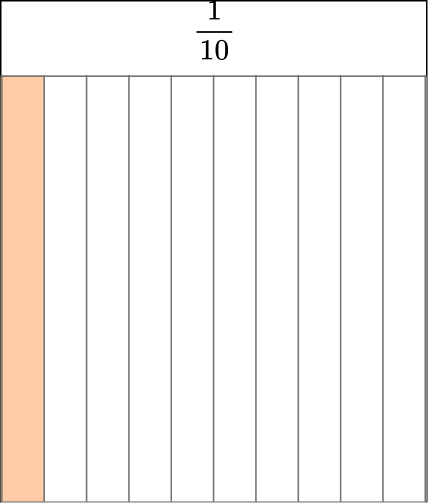
This model shows \cfrac{4}{10}.
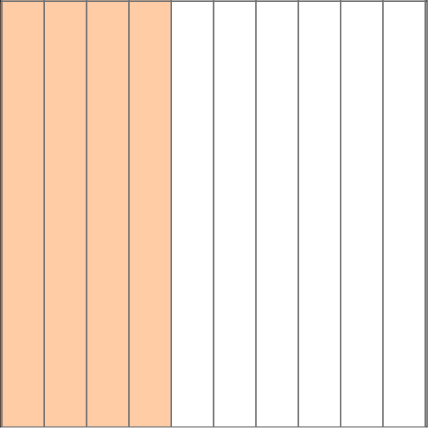
We can also write this as the decimal 0.4. We read it as “four-tenths,” just like the fraction.
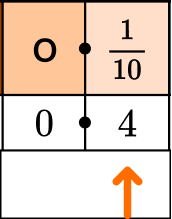
That is because the first decimal place is tenths.
Let’s look at the next decimal place.
For example,
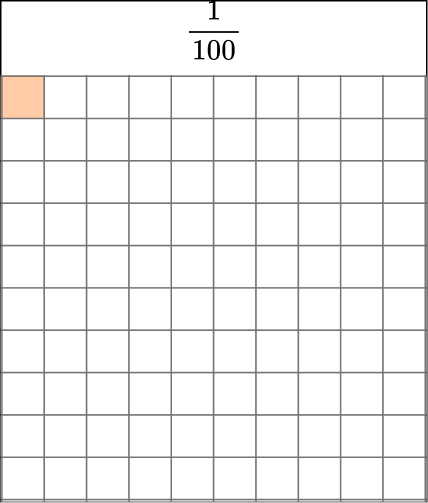
This model shows \cfrac{4}{100}.
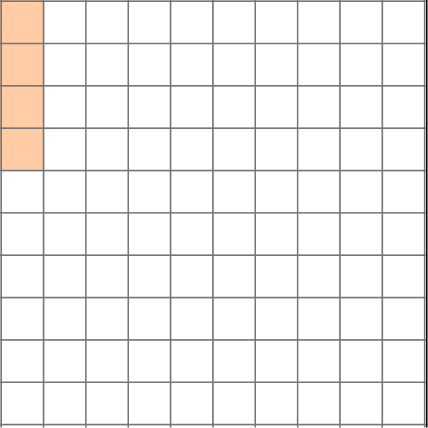
We can also write this as the decimal 0.04. We read it as “four-hundredths,” just like the fraction.
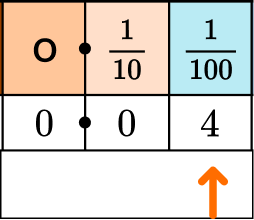
That is because the second decimal place is hundredths.
Let’s look at the next decimal place.
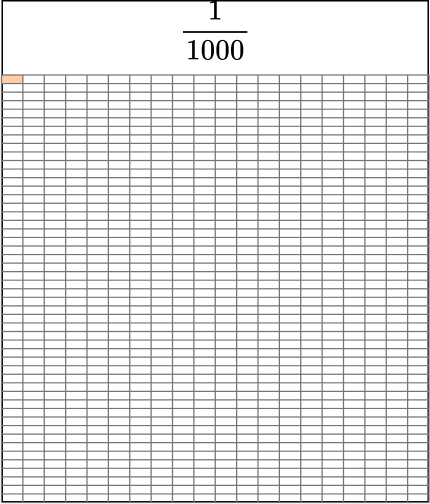
For example,
This model shows \cfrac{4}{1,000}.

We can also write this as the decimal 0.004. We read it as “four-thousandths,” just like the fraction.
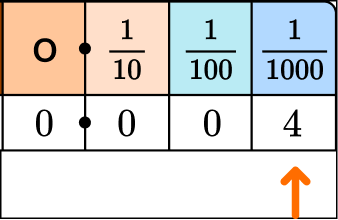
That is because the third decimal place is thousandths.
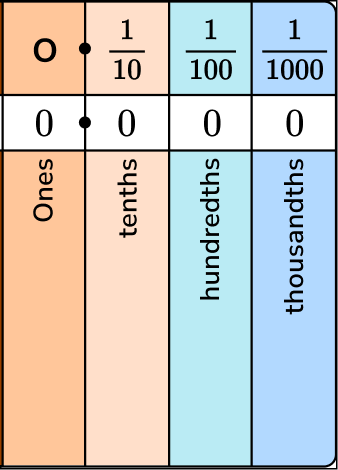
Here are the first three decimal place values. They show us the value of each digit in the number.
Notice the pattern in the denominators:
to to
As the places become smaller, each is \cfrac{1}{10} the size of the place to its left.
As the places become larger, each is 10 times the size of the place to its right.
These are the same patterns you see with whole numbers.
What is decimal place value?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 4th grade math and 5th grade math?
- Grade 4 – Numbers and Operations – Fractions (4.NF.C.6)
Use decimal notation for fractions with denominators 10 or 100. For example, rewrite 0.62 as \cfrac{62}{100} ; describe a length as 0.62 meters; locate 0.62 on a number line diagram.
- Grade 5 – Numbers and Operations in Base 10 (5.NBT.A.1)
Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and \cfrac{1}{10} of what it represents in the place to its left.
How to use decimal place value
In order to write a fraction as a decimal:
- Write the fraction in words.
- Place the numerator of the fraction on the place value chart.
- Write the decimal number.
In order to write a fraction as a decimal:
- Write the decimal in words using a place value chart.
- The digits of the decimal will be the numerator, and the denominator is where the last digit of the decimal is in the place value chart.
- Write the fraction.
In order to write the value of a digit in a decimal number:
- Locate the digit within the number.
- Use the place value chart to find the position.
- Write the value of the digit.
In order to compare the value of a digit in two decimal numbers:
- Locate the digits within the number(s).
- Use the place value chart to find the positions.
- Compare how many times bigger or smaller the positions are.
![[FREE] Decimal Place Value Worksheet (Grade 4 and 5)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Decimal-Place-Value-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Decimal Place Value Worksheet (Grade 4 and 5)
![[FREE] Decimal Place Value Worksheet (Grade 4 and 5)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Decimal-Place-Value-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 4 and 5 students’ understanding of decimal place value. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Decimal Place Value Worksheet (Grade 4 and 5)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Decimal-Place-Value-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Decimal Place Value Worksheet (Grade 4 and 5)
![[FREE] Decimal Place Value Worksheet (Grade 4 and 5)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Decimal-Place-Value-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 4 and 5 students’ understanding of decimal place value. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEDecimal place value examples
Example 1: write a fraction as a decimal
Write \cfrac{2}{10} as a decimal.
- Write the fraction in words.
\cfrac{2}{10} is 2 tenths.
2Place the numerator of the fraction on the place value chart.
Put a 2 in the tenths place.
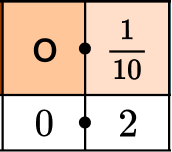
3Write the decimal number.
\cfrac{2}{10} written as a decimal is 0.2
Example 2: write a fraction as a decimal
Write \cfrac{51}{100} as a decimal.
Write the fraction in words.
\cfrac{51}{100} is 51 hundredths.
Place the numerator of the fraction on the place value chart.
The model shows \cfrac{51}{100}.
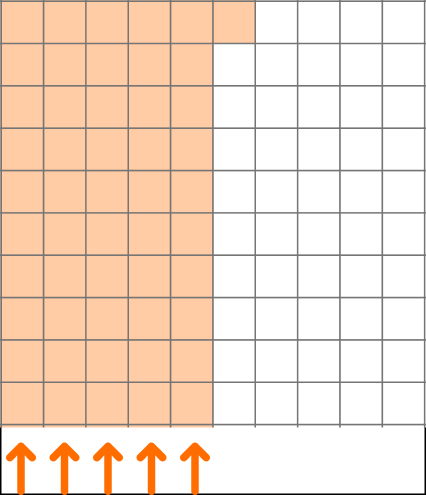
In the model there are 5 full columns of 10, which is equal to 5 tenths.
So to write this decimal, put a 5 in the tenths place and 1 in the hundredths place.
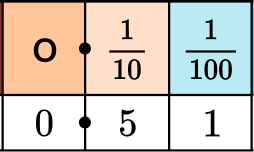
Write the decimal number.
\cfrac{51}{100} written as a decimal is 0.51
*Notice there is only one digit in each place, just like with whole numbers.
Example 3: writing a decimal as a fraction
Write 0.22 as a fraction.
Write the decimal in words using a place value chart.
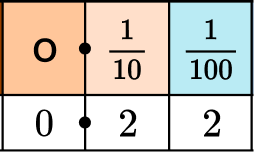
0.22 is 22 hundredths.
The digits of the decimal will be the numerator, and the denominator is where the last digit of the decimal is in the place value chart.
The model shows 22 hundredths.
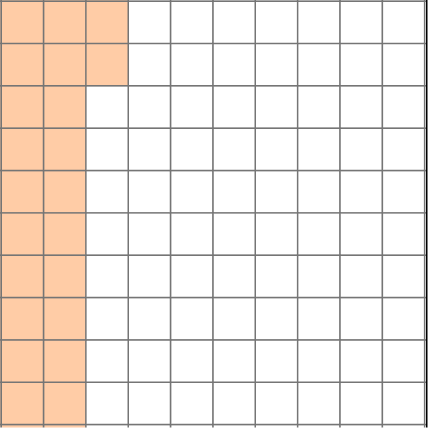
The 22 in the decimal is the numerator.
The last place value position is hundredths (which is also the size of the 22 parts), so this is the denominator.
Write the fraction.
0.22=\cfrac{22}{100}
Example 4: write the value of a decimal digit
What is the value of the digit 3 in 0.13?
Locate the digit within the number.
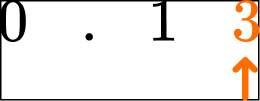
Use the place value chart to find the position.
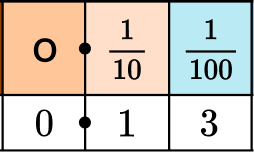
Write the value of the digit.
The value of the digit 3 is 0.03 or \cfrac{3}{100}.
Example 5: write the value of a decimal digit
What is the value of the digit 7 in 0.75?
Locate the digit within the number.

Use the place value chart to find the position.
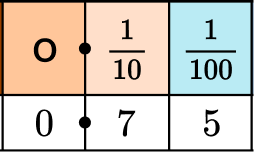
Write the value of the digit.
The value of the digit 7 is 0.7 or \cfrac{7}{10}.
Example 6: compare the value of the same digit in a different place
Compare the value of each digit 1 in the number 0.101.
Locate the digits within the number(s).
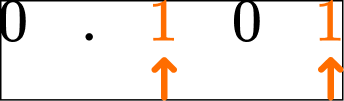
Use the place value chart to find the positions.
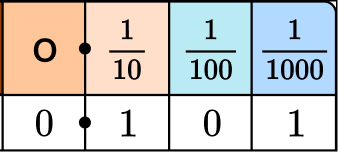
Compare how many times bigger or smaller the positions are.
In 0.101, there is a digit 1 in the tenths position and in the thousandths position.
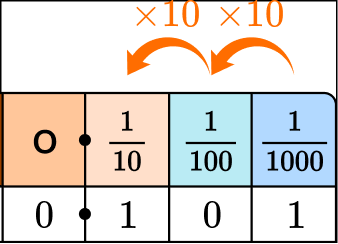
0.1 is 100 times greater than 0.001.
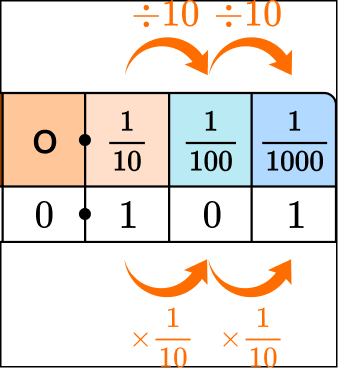
0.001 is 100 times smaller than 0.1. The 1 in the thousandths is \cfrac{1}{100} the value of the 1 in the tenths.
Teaching tips for decimal place value
- Instead of relying on just worksheets, use manipulatives to help students visualize the size of each place value and see how each position relates to the others. For smaller positions, especially thousandths, digital representations may be the best option.
- Decimal place values in our number system are based on patterns, which many students will discover as they work. Ask questions such as “What do you notice about these numbers?” or “If you change the place value of the digits, how does the value of the number change?” to guide all students to see the underlying structure of our place value system.
- Incorporate decimal place value ideas daily. It can be something as simple as a quick place value game. For example, say to students “I am thinking of a number that has more than 7 tenths, what could it be?” Daily activities like this help students to think flexibly about decimal place value.
- Ask students to show the standard form, expanded form, and word form for any given decimal to reinforce the connection between each representation.
- Have a decimal place value chart posted in the classroom or another way that is easily accessible to students. Seeing a chart regularly can help students remember it.
Our favorite mistakes
- Writing more than one digit in a place
Just like with whole number place value, decimal place only has one digit per place.
For example,
Writing \cfrac{51}{100} as 0.051 is read as 51 thousandths, not 51 hundredths. The digits 5 and 1 cannot both go into the hundredths place. You place 5 in the tenths place, because \cfrac{50}{100}=\cfrac{5}{10}.
- Thinking there is a “oneths” place
The first place value position to the right of the decimal point is the tenths column, not the “oneths” column.
For example, In the number 1.534, what is the value of the digit 3?
Three tenths or 0.03 \color{red} ✘ Three hundredths, or 0.03 \color{green} ✔
(Treating the first decimal (Treating first decimal place as tenths
place as “oneths” and the and the second as hundredths)
second as tenths)
- Confusing the hundredths and hundreds places
The numbers to the right of the decimal point end in ‘ths’ because they are parts of a whole. The numbers to the left of the decimal point do not end in ‘ths’ because they are whole.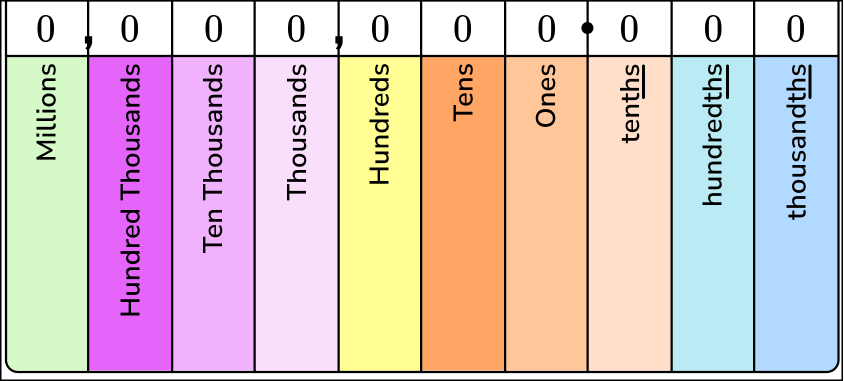
Practice decimal place value questions
1. Write \cfrac{8}{10} as a decimal.




\cfrac{8}{10} is 8 tenths. Put an 8 in the tenths place.
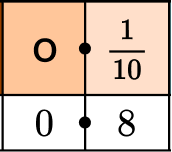
\cfrac{8}{10} written as a decimal is 0.8
2. Write \cfrac{62}{100} as a decimal.




\cfrac{62}{100} is 62 hundredths.
The model shows \cfrac{62}{100}.
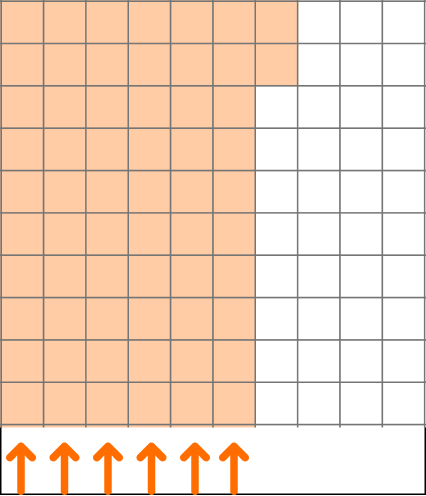
In the model there are 6 full columns of 10, which is equal to 6 tenths.
So to write this decimal, put a 6 in the tenths place and 2 in the hundredths place.
\cfrac{62}{100} written as a decimal is 0.62
3. Write 0.19 as a fraction.




0.19 is 19 hundredths.
The model shows 19 hundredths.
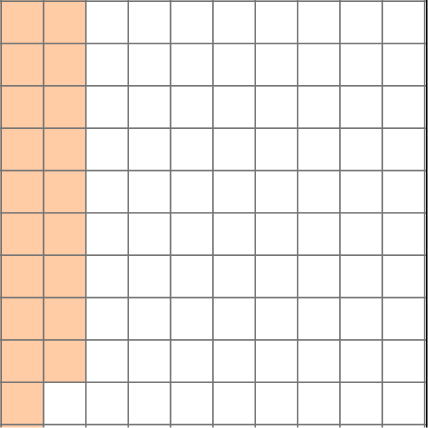
The 19 in the decimal is the numerator.
The last place value position is hundredths (which is also the size of the 19 parts), so this is the denominator.
0.19=\cfrac{19}{100}
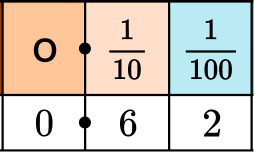
4. What is the value of the digit 4 in 0.054?

4 tenths

4 thousandths

4 hundredths

Locate the digit within the number.

Use the place value chart to find the position.
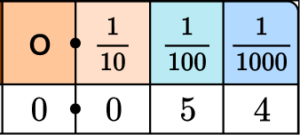
The value of the digit 4 is 4 thousandths (0.004 or \cfrac{4}{1,000}).
5. Choose the correct comparison of each digit 8’s value in the numbers 0.8 and 0.18.
The 8 in 0.8 is 100 times less

The 8 in 0.18 is 10 times more

The 8 in 0.8 is 10 times more

The 8 in 0.18 is 100 times less

Locate the digits within the number(s).
![]()
Use the place value chart to find the positions.

In 0.8, \, 8 is in the tenths position. In 0.18, \, 8 is in the hundredths position.
Tenths are 10 times more than hundredths, so the 8 in 0.8 is 10 times more.
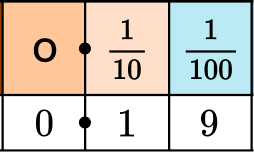
6. Choose the correct comparison of the digit 3’s values in the number 0.033.
The 3 in the thousandths is \cfrac{1}{10} the size of the 3 in the hundredths

The 3 in the thousandths is 100 times smaller than the 3 in the hundredths

The 3 in the hundredths is 10 times smaller than the 3 in the tenths

The 3 in the hundredths is \cfrac{1}{10} the size of the 3 in the thousandths

Locate the digits within the number(s).

Use the place value chart to find the positions.
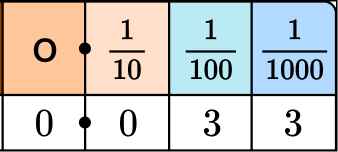
In 0.033, there is a digit 3 in the hundredths position and in the thousandths position.
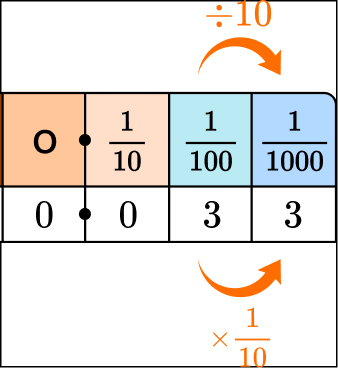
Thousandths are \cfrac{1}{10} the size of hundredths, so the 3 in the thousandths is \cfrac{1}{10} of the 3 in the hundredths.
Decimal place value FAQs
We use a Base Ten number system, meaning each place value position is a grouping of 10. That is why all of the place value positions (like the tenths place or hundredths place) are multiples of 10.
They are similar because they can both be used to represent parts. For example, the fraction \cfrac{3}{10} represents a part ( 3 tenths) and the decimal 0.3 represents a part ( 3 tenths).
Decimal place value gives meaning to the digits in each position and helps you understand the size of a number. Understanding decimal place value can help you when comparing or ordering decimals and is also necessary to know when calculating with decimal numbers.
In the Common Core, fifth grade students are expected to know and use the tenths place, the hundredths place, and the thousandths place. Sixth graders extend this to even smaller positions. However, it can vary from state to state, so be mindful of your state’s standard expectations.
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!