High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Whole Numbers Integers Decimal number line FractionsCoordinate plane
Here you will learn about a coordinate plane, including the general form of a coordinate plane, plotting coordinates on different axes, and determining the coordinates of a point.
Students will first learn about coordinate planes as part of the number system in 6th grade.
What is a coordinate plane?
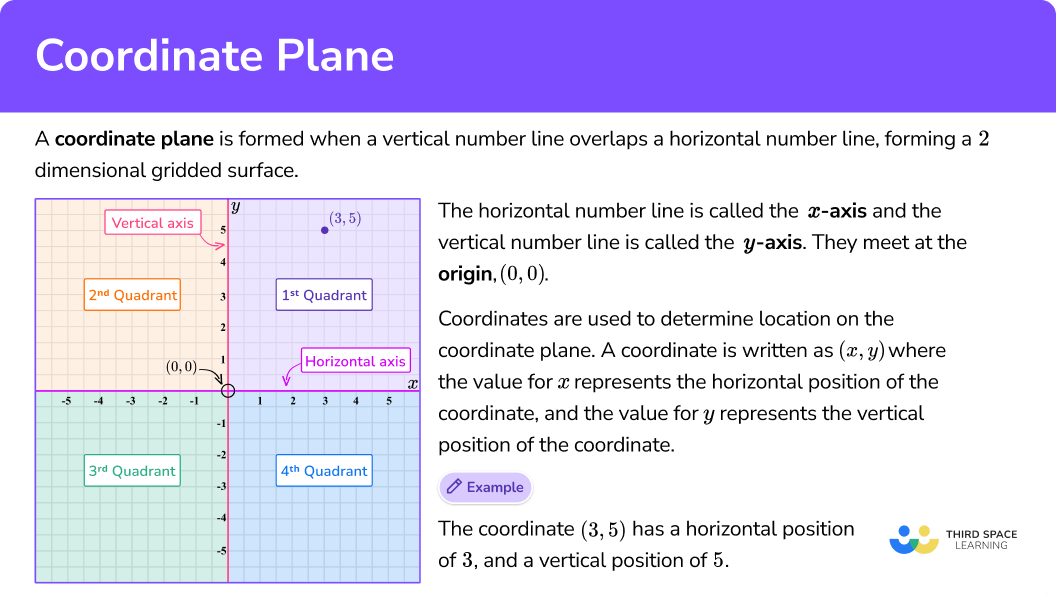
A coordinate plane is formed when a vertical number line overlaps a horizontal number line, forming a 2 dimensional gridded surface. It can also be called a coordinate grid.
The horizontal number line is called the \textbf{x} -axis and the vertical number line is called the \textbf{y} -axis. They intersect at the origin, (0,0).
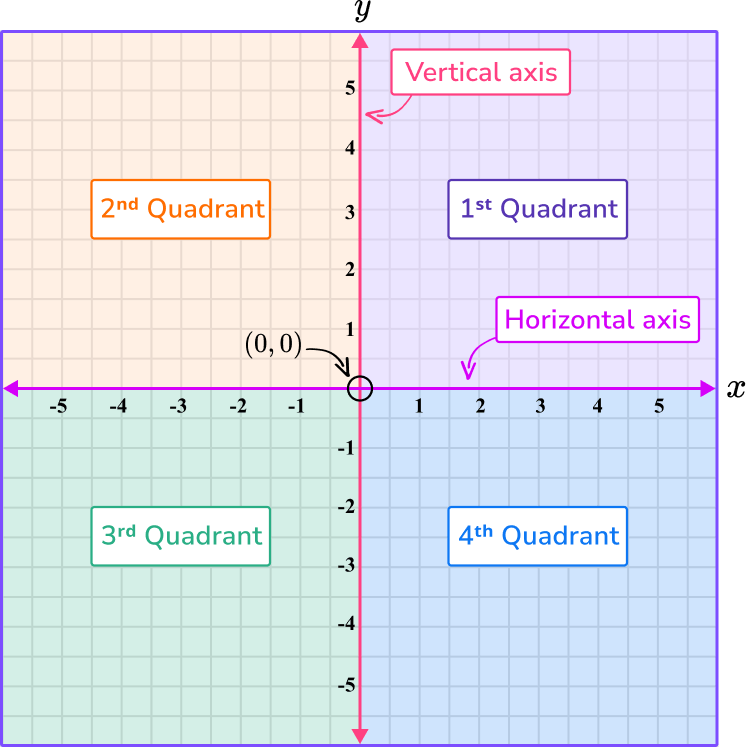
In a coordinate plane there are four quadrants. The values on the x and y axes are different in each quadrant:
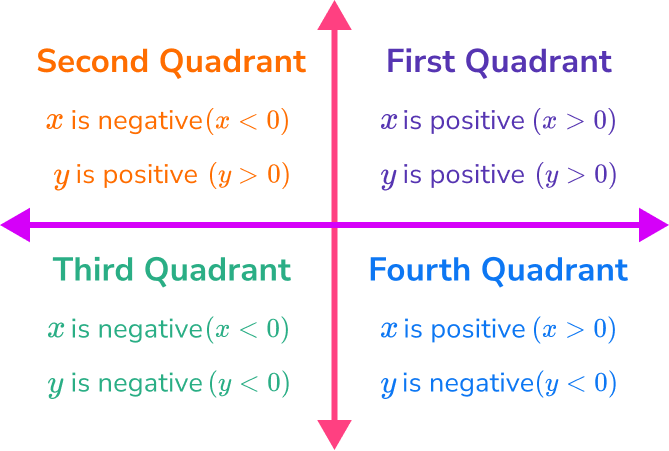
Note, it is also common for the names of the quadrants to be written with Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV).
Each axis has a scale. The scale must increase in equal amounts, but the scale does not have to be the same for both axes.
For example,
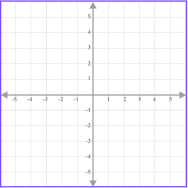 Here, both the x -axis and | 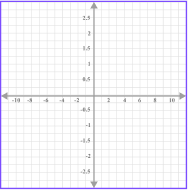 Here, the x -axis increases |  Here, the x -axis increases |
Coordinates are used to determine location on the coordinate plane.
A coordinate is written as (x,y), where the value for the x -coordinate represents the horizontal position of the coordinate, the value for the y -coordinate represents the vertical position of the coordinate and they are enclosed with parentheses.
These can also be referred to as ordered pairs.
For example, the coordinate (3,5) has a horizontal position of 3, and a vertical position of 5.
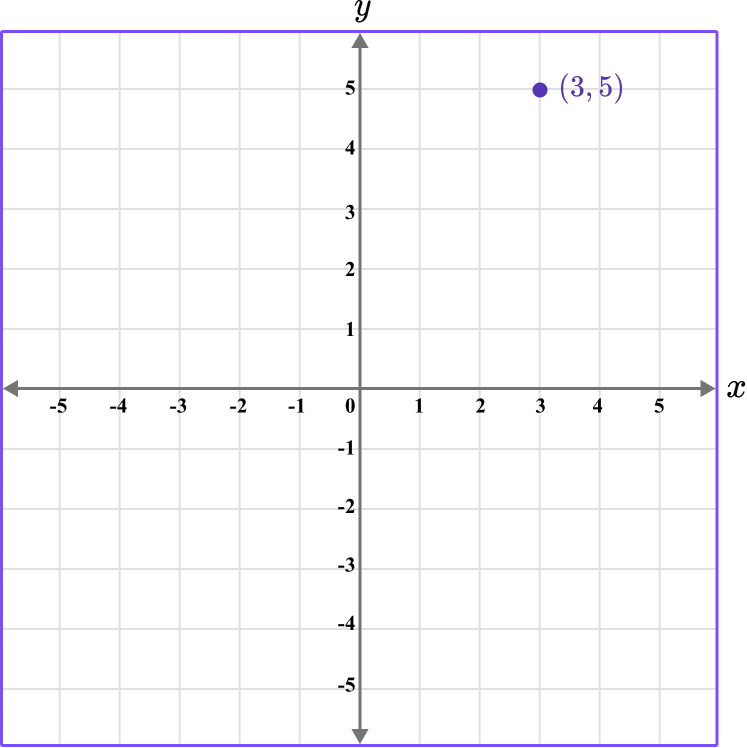
Besides locating the position of a coordinate, you can also plot coordinates within all four quadrants.
To do this, determine the horizontal and vertical position of the coordinate on the axes, and follow these values until the two values meet.
For example,
Draw the point A \, (4,2).
To draw the point, locate 4 on the x -axis, and then 2 on the y -axis. Follow the straight lines from these points to the coordinate A \, (4,2).
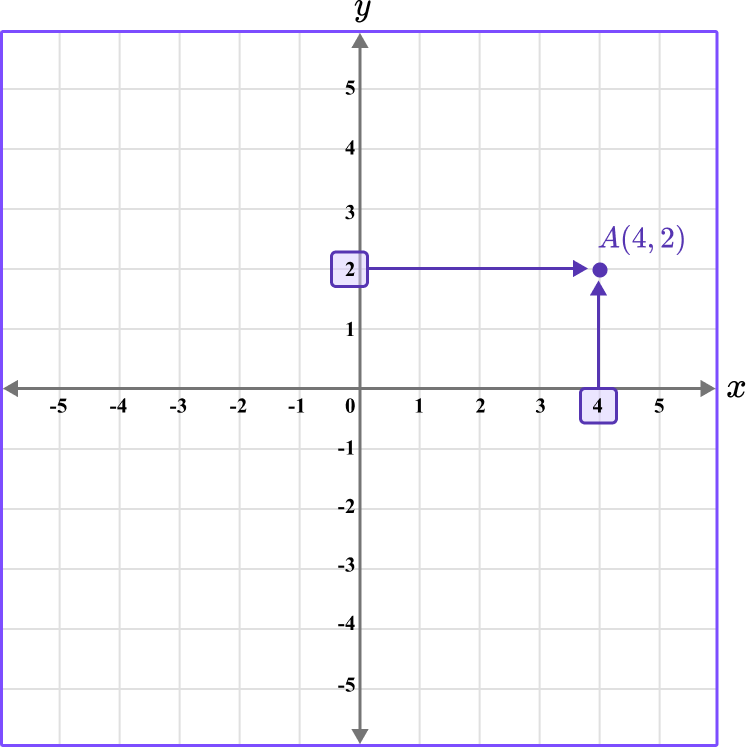
Note, to give a coordinate a specific name, label it as a point by using a capital letter.
Repeating this process by plotting points B \, (-4,4), \, C \, (-5,-3), and D \, (1,-2)…
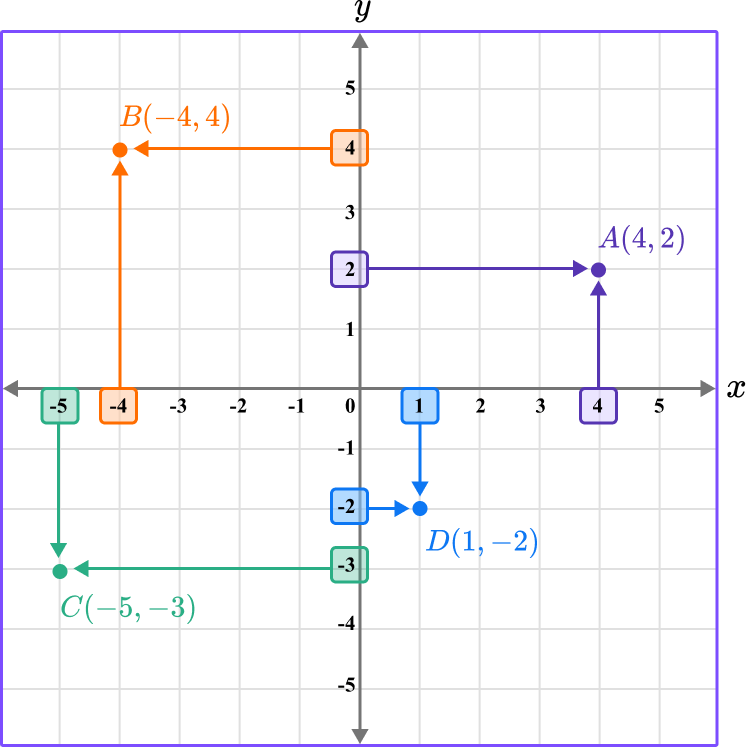
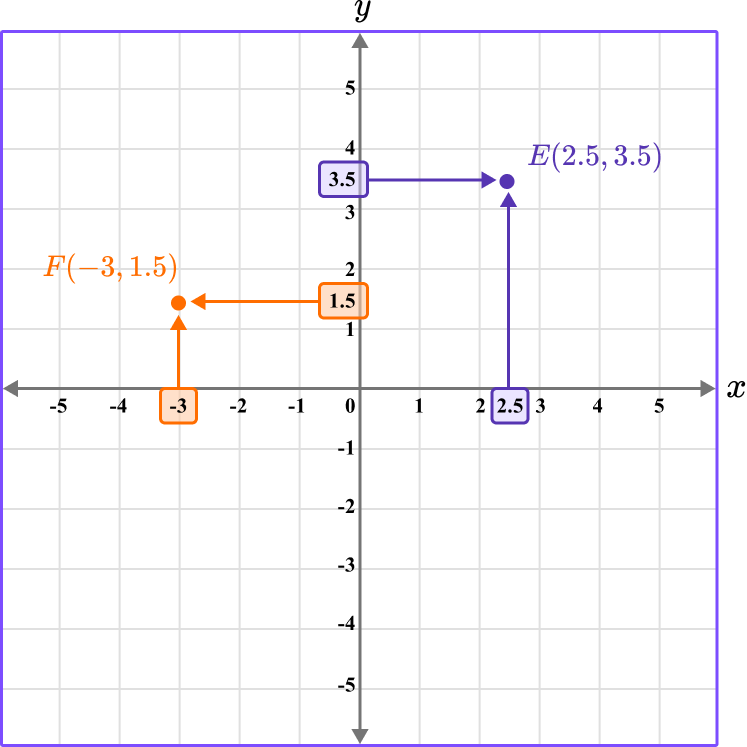
Note that coordinates can have decimal values. It is common to only see integer coordinates that lie on a grid line, however, you can also plot coordinates that have a decimal value, such as E \, (2.5, 3.5) and F \, (-3, 1.5).
These would lie within or on the edge of a grid square.
What is a coordinate plane?
![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 8 students’ understanding of algebra. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 8th grade algebra topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 8 students’ understanding of algebra. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 8th grade algebra topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREECommon Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6th grade math?
- Grade 6 – The Number System (6.NS.C.8)
Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate.
How to plot on a coordinate plane
In order to plot on a coordinate plane:
- Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
- Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
- Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Coordinate plane examples
Example 1: plot a coordinate
Plot the coordinate A \, (-12, 4).
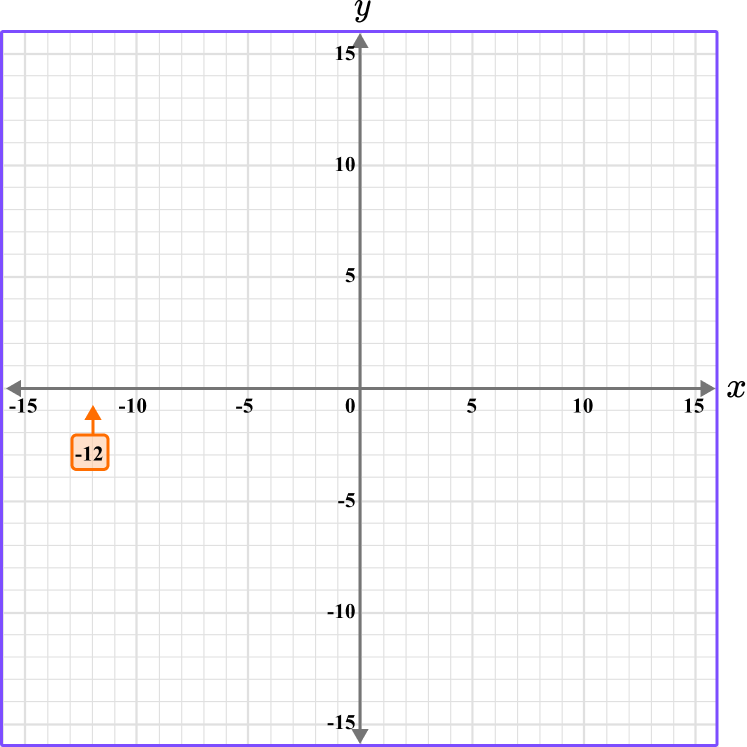
- Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
The x value is -12, so locate -12 on the x -axis. The scale is 1, so -12 is two gridlines after -10.
2Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
The y value is 4, so locate 4 on the y -axis. The scale is 1, so 4 is one gridline before 5.
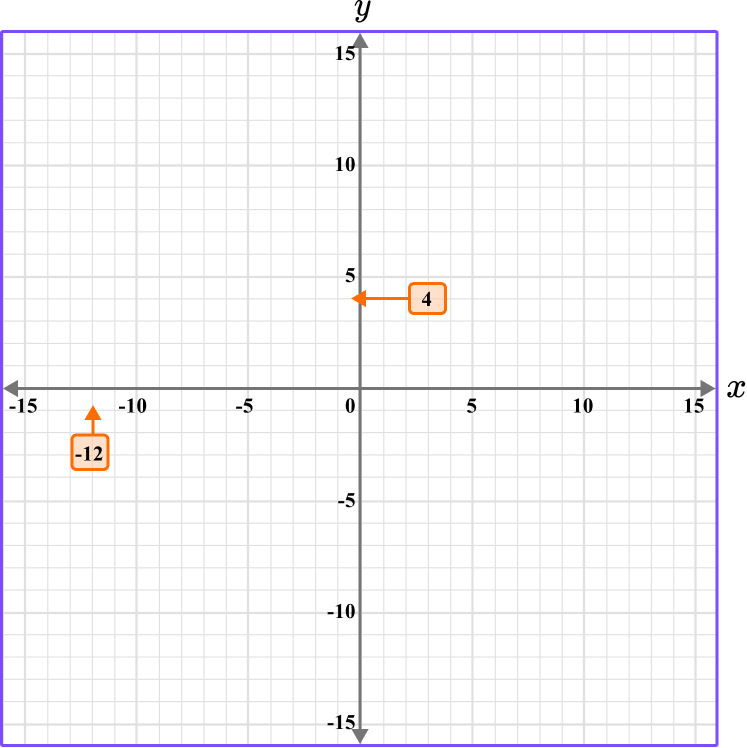
3Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Following the gridlines…
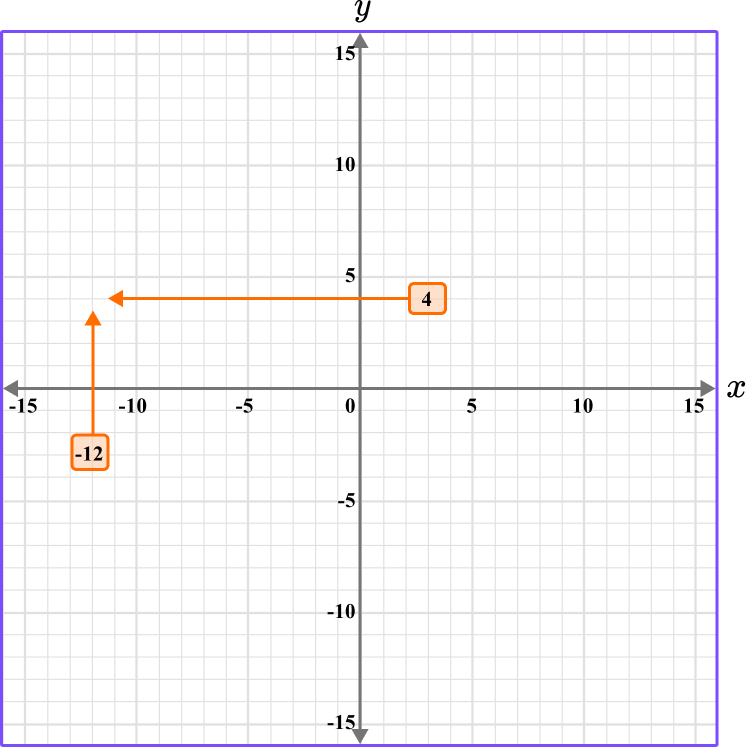
This gives us the final solution.
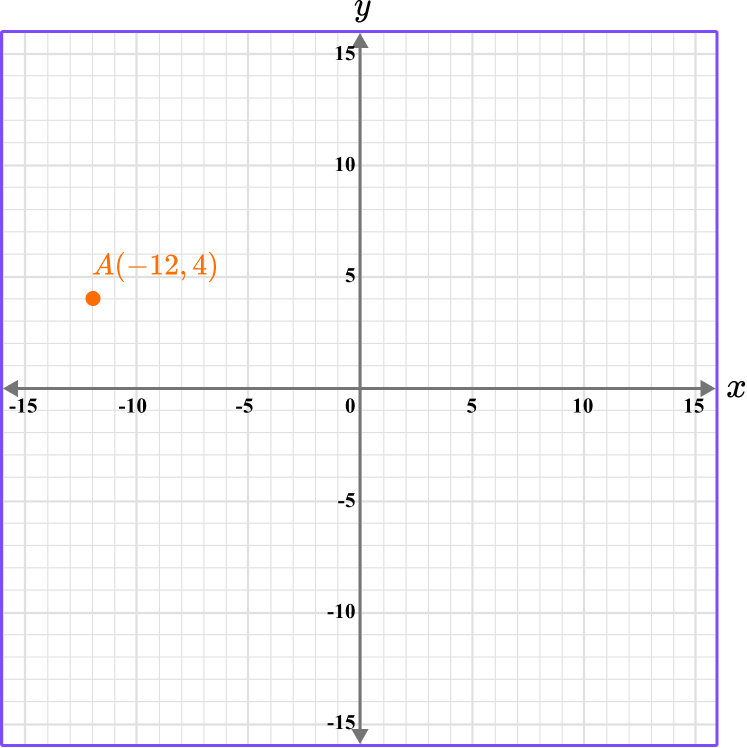
Example 2: plot a coordinate
Plot the coordinate H \, (-5, -7).
Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
The x value is -5, so locate -5 on the x -axis. The scale is 2, so -5 is between -4 and -6.
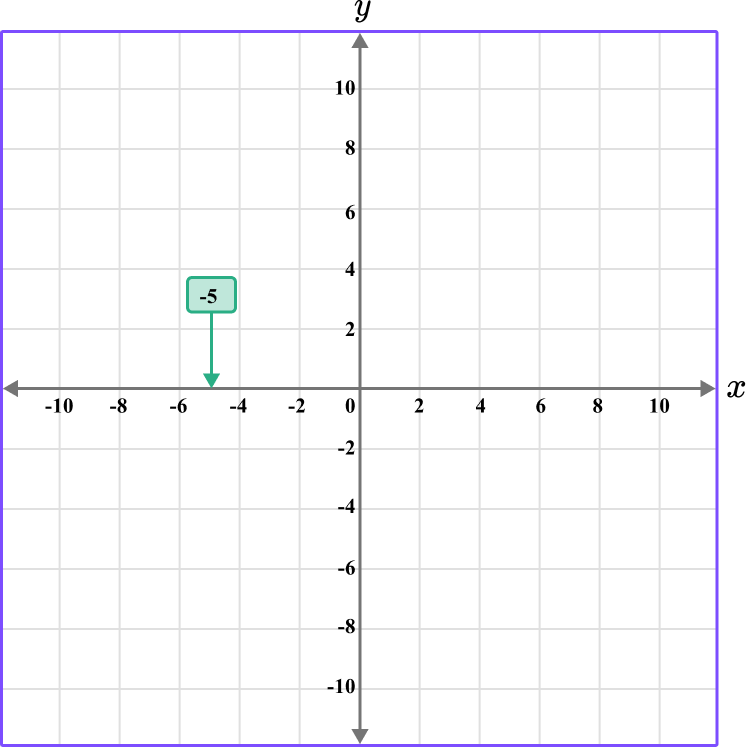
Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
The y value is -7, so locate -7 on the y -axis. The scale is 2, so -7 is between -6 and -8.
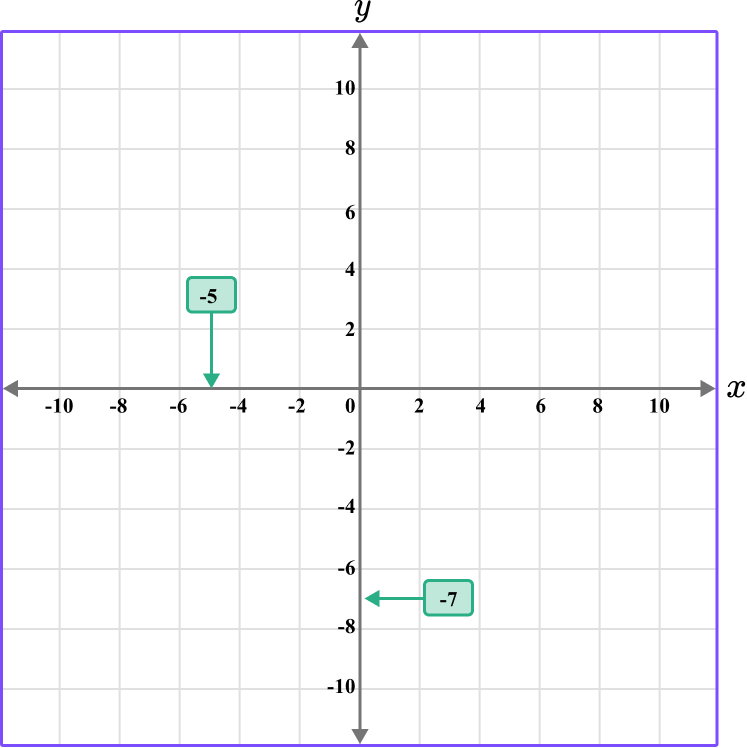
Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Following between the gridlines…
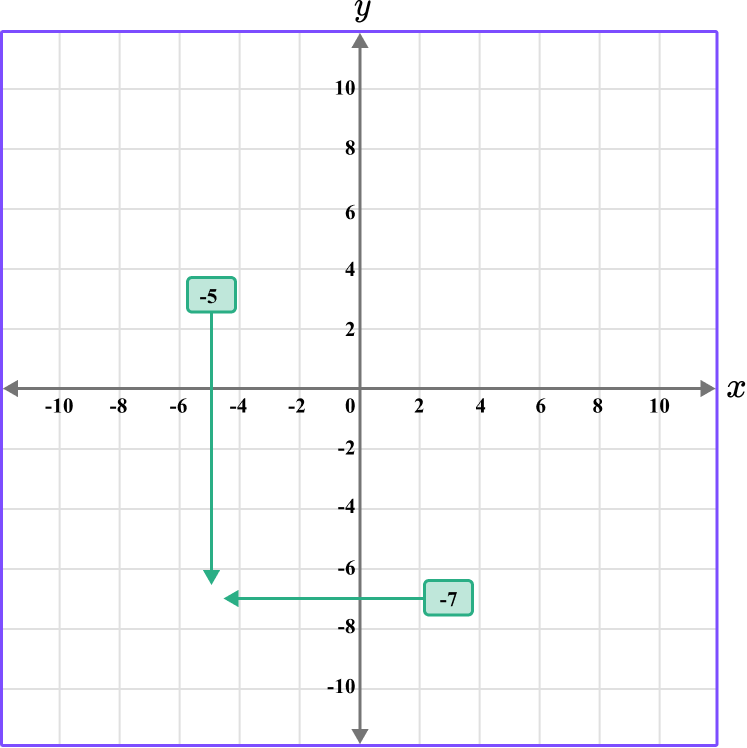
This gives us the final solution.
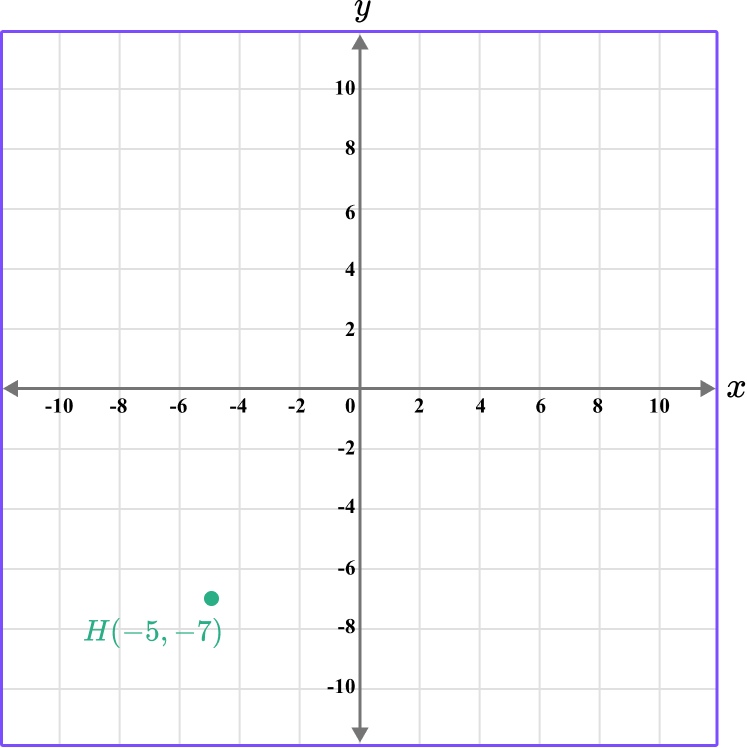
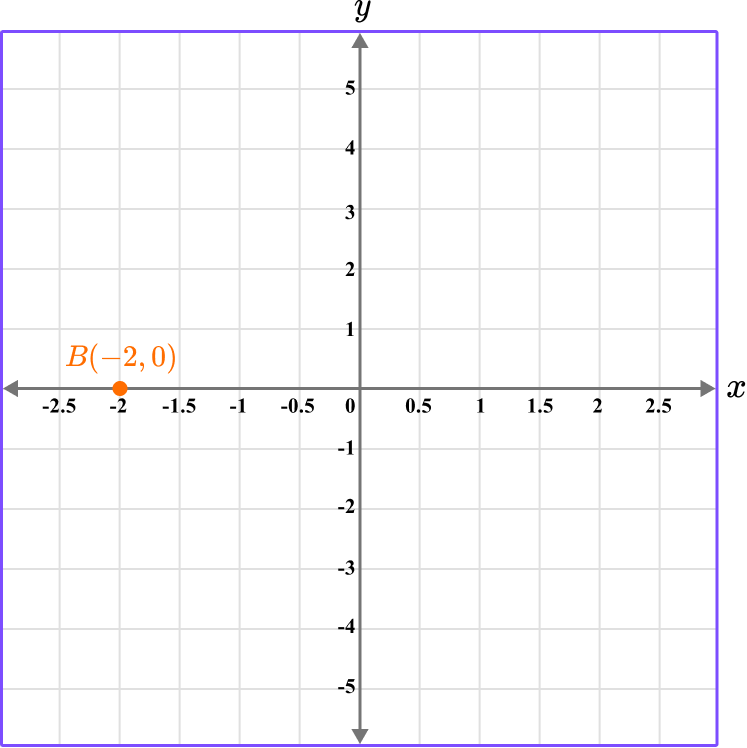
Example 3: plot a coordinate on the x -axis
Plot the coordinate B \, (-2,0).
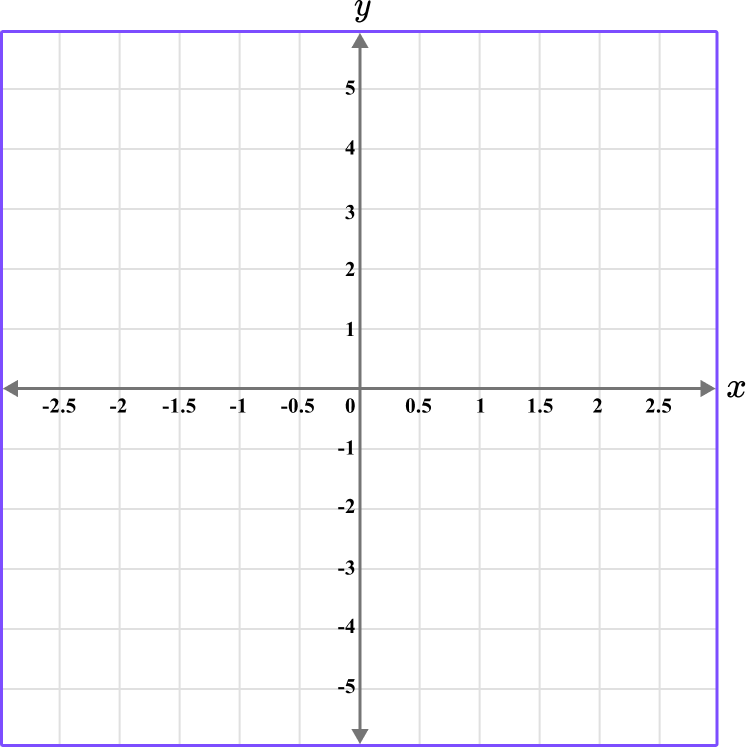
Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
The x value is -2, so locate -2 on the x -axis.
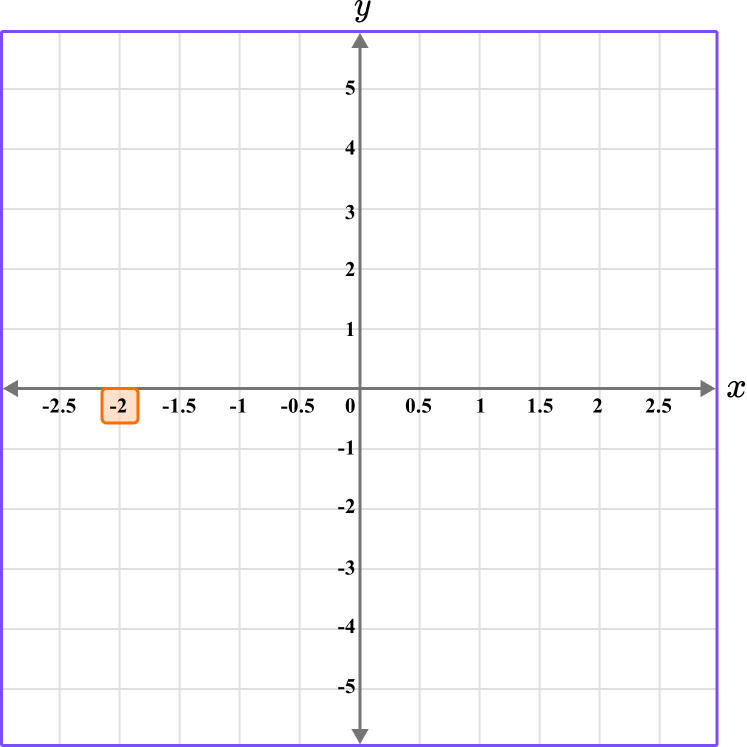
Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
The y value is 0, so locate 0 on the y -axis.
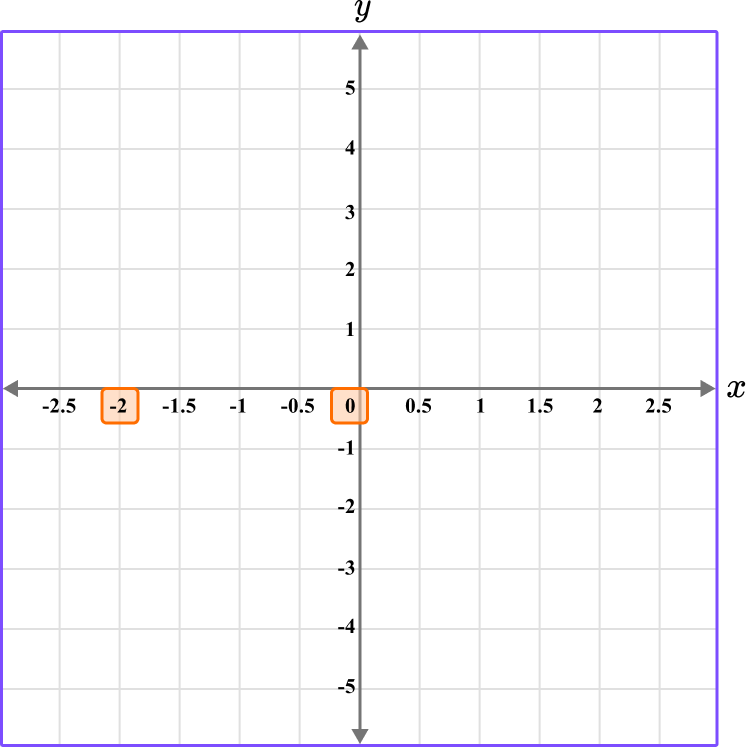
Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Following the gridlines…
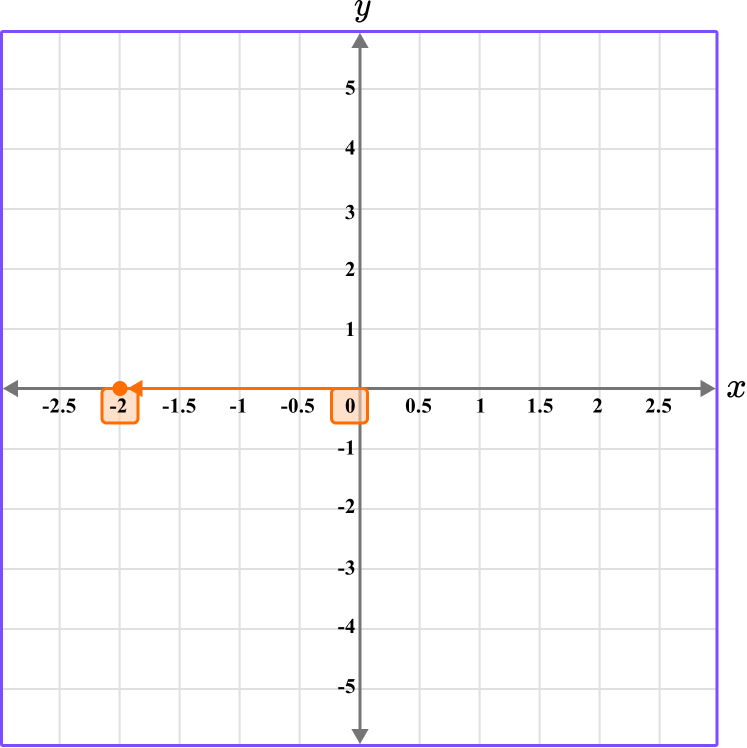
This gives us the final solution.
Example 4: plot a coordinate on the y -axis
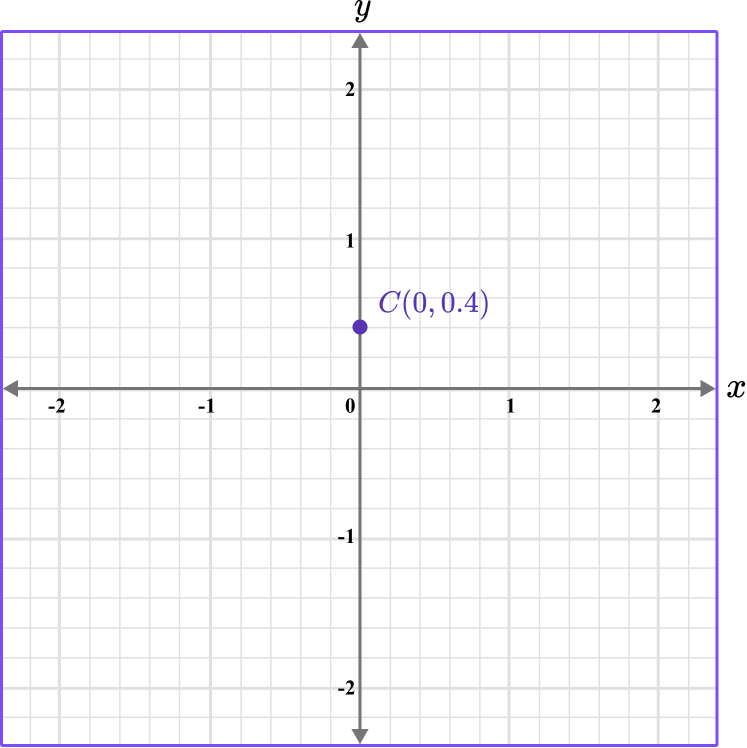
Plot the coordinate C \, (0,0.4).
Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
The x value is 0, so locate 0 on the x -axis.
Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
The y value is 0.4, so locate 0.4 on the y -axis. The scale is 0.2, so 0.4 is two gridlines above 0.
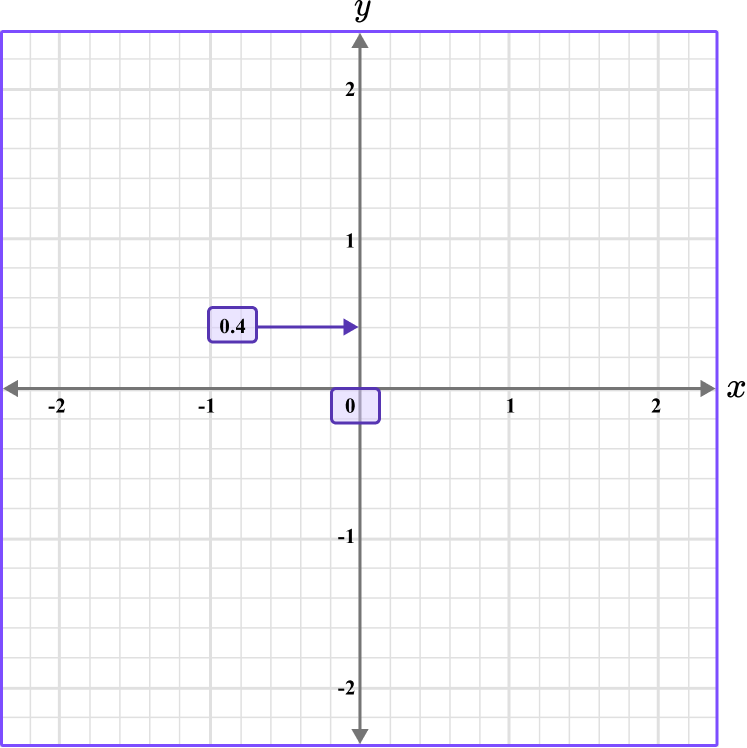
Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Following the gridlines…
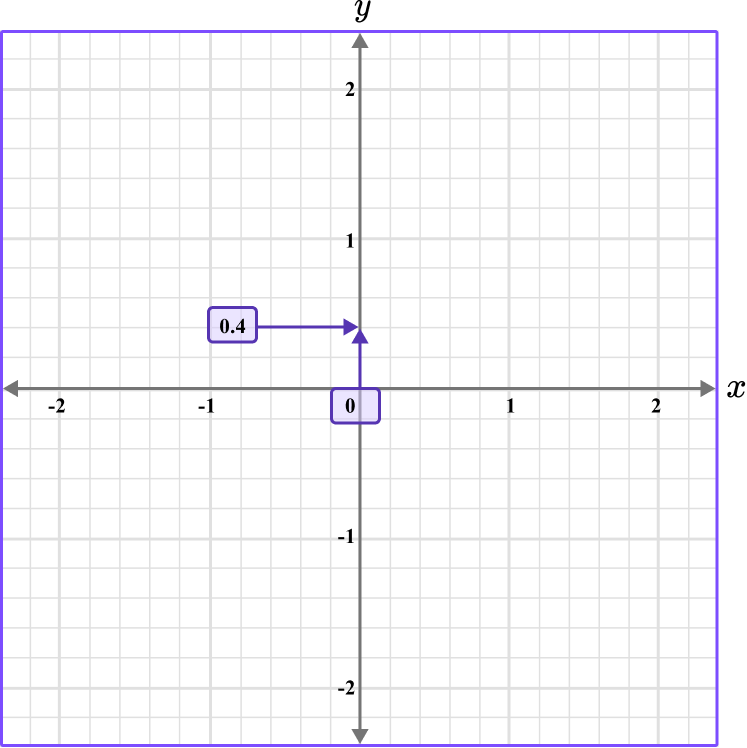
This gives us the final solution.
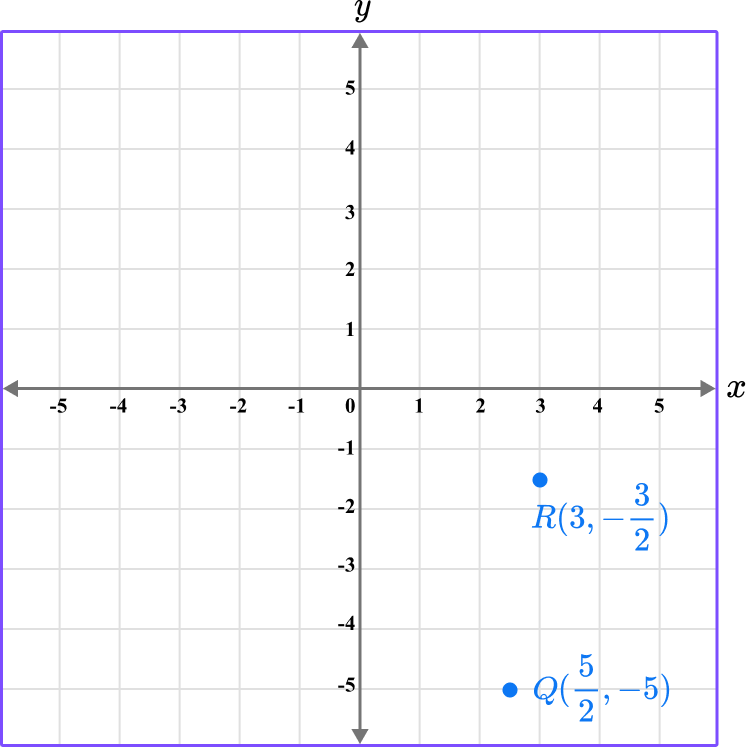
Example 5: plotting two coordinates
Plot the coordinates R \left(3,- \, \cfrac{3}{2} \, \right) and Q \left(\cfrac{5}{2},- \, 5 \right).
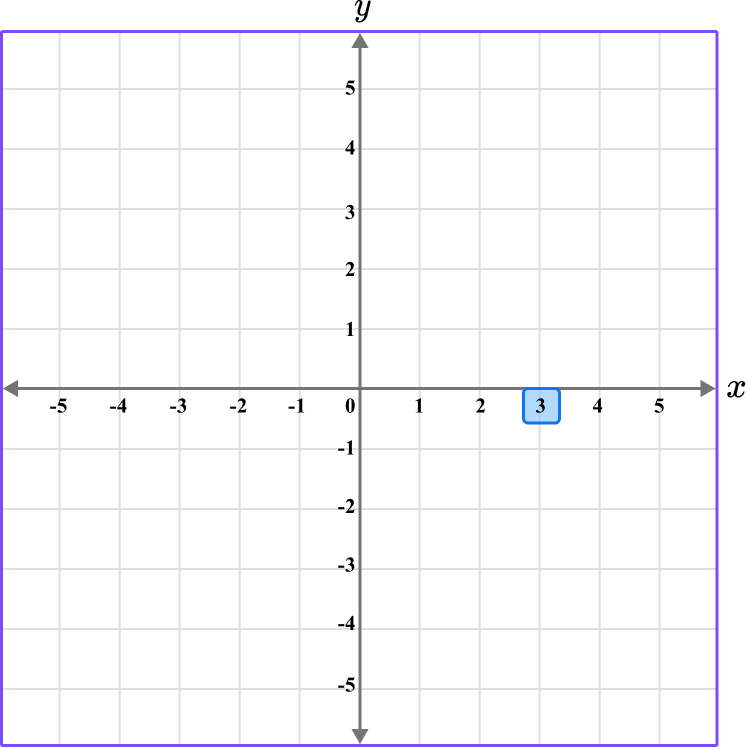
Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
Since there are two coordinates, plot each point one at a time.
The x value of the point R is 3, so locate 3 on the x -axis.
Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
The y value of the point R is -\cfrac{3}{2} \, , so locate -\cfrac{3}{2} \, on the y -axis.
Since -\cfrac{3}{2}= -1 \, \cfrac{1}{2} \, , it is in between -1 and -2.
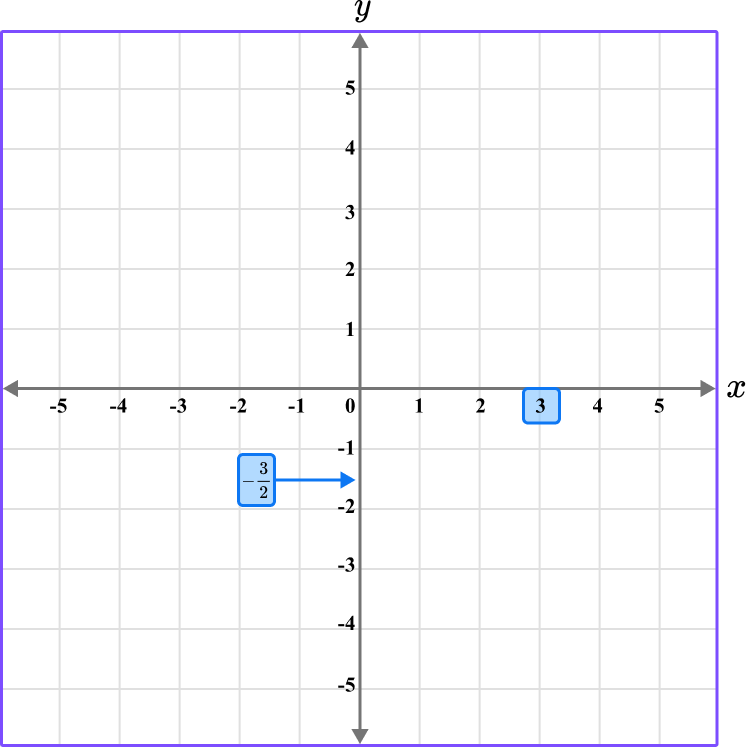
Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Following the gridlines (and between them)…
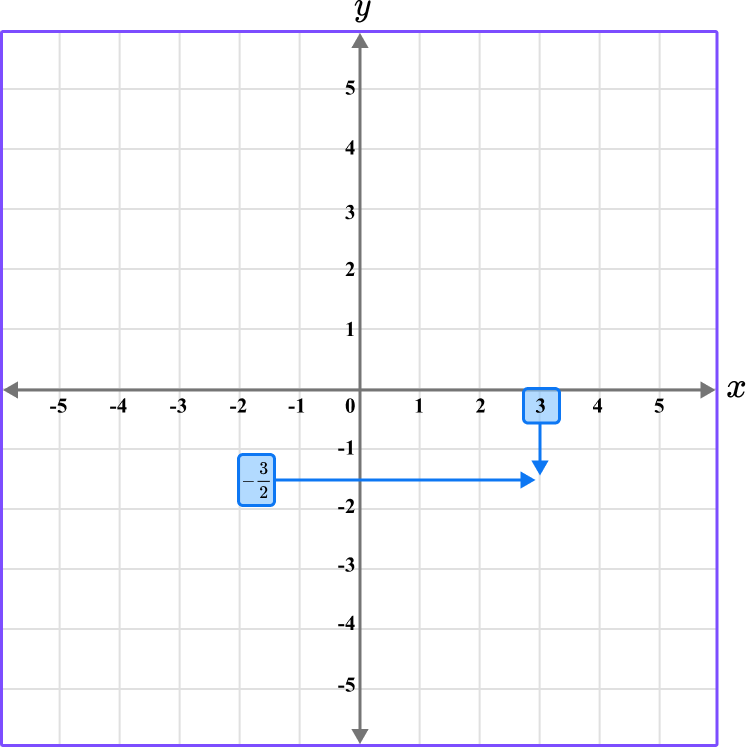
The point R is located here.
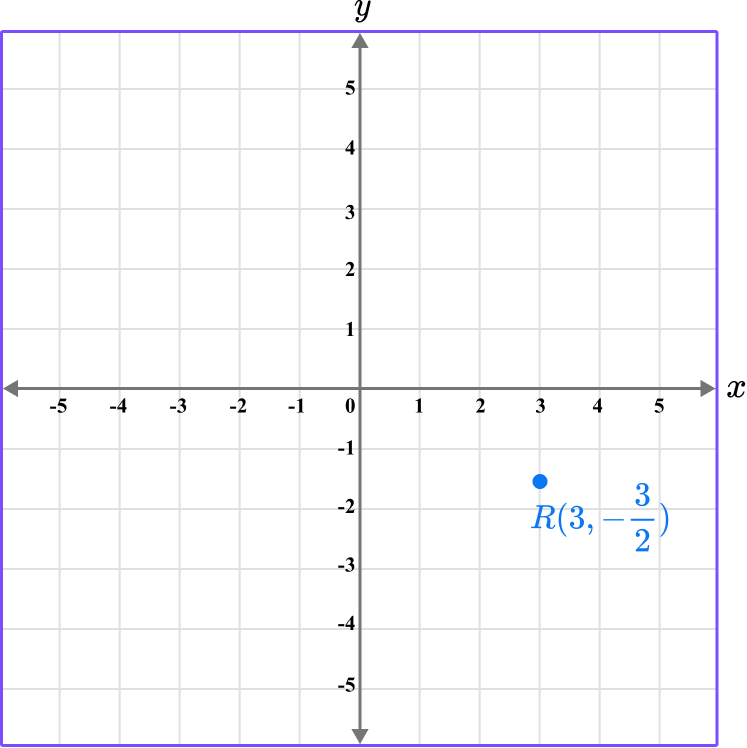
Repeat this process for the point Q \left(\cfrac{5}{2},- \, 5 \right).
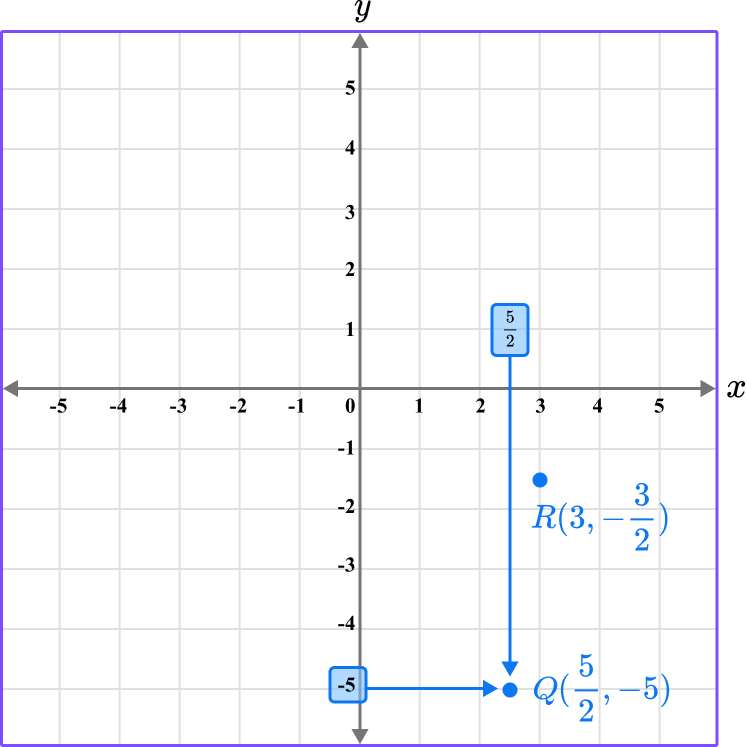
This gives us the final solution.
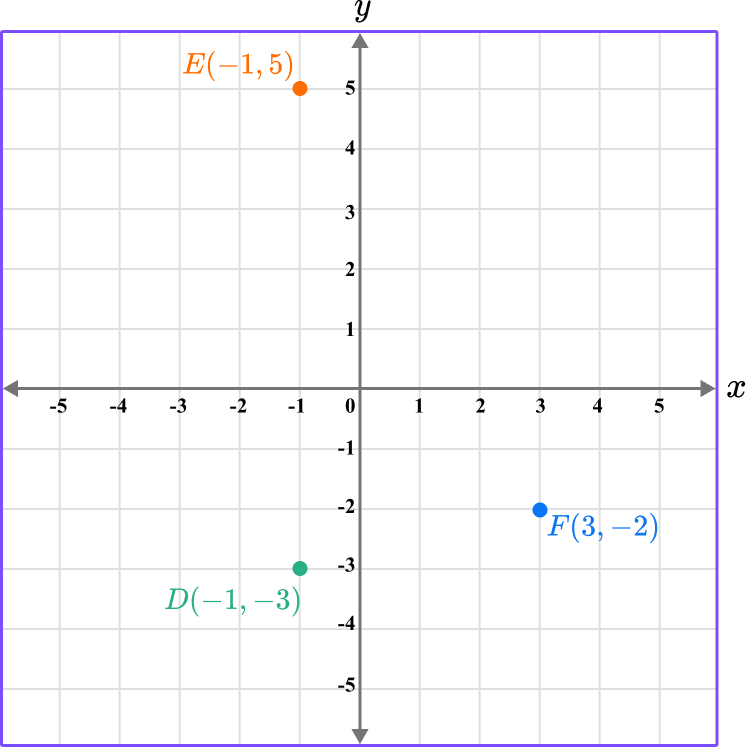
Example 6: plotting coordinates in three quadrants
Plot the coordinates D \, (-1,-3), \, E \, (-1,5) , and F\, (3,-2) on the set of axes below.
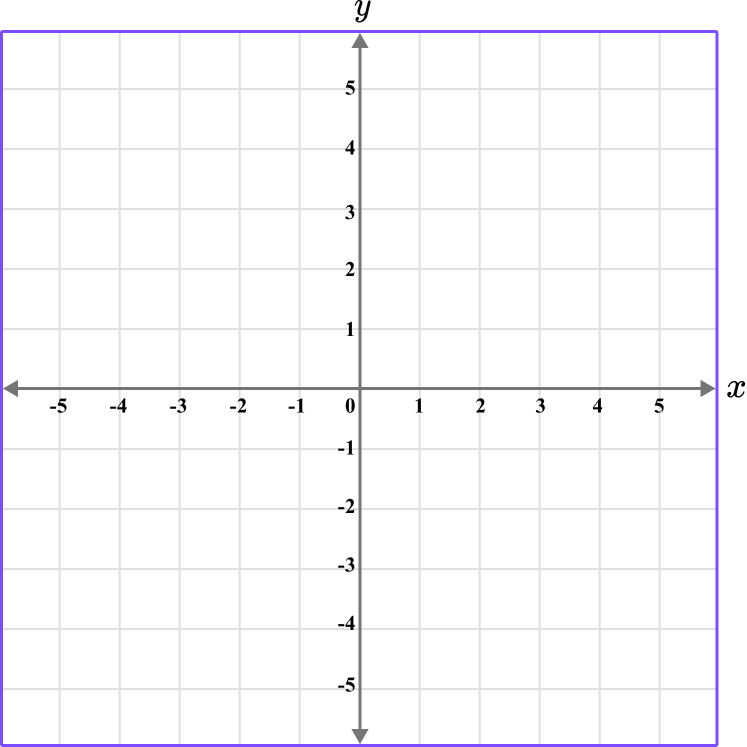
Determine the horizontal position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{x} ).
Since there are three coordinates, plot each point one at a time.
The x value of the point D is -1, so locate -1 on the x -axis.
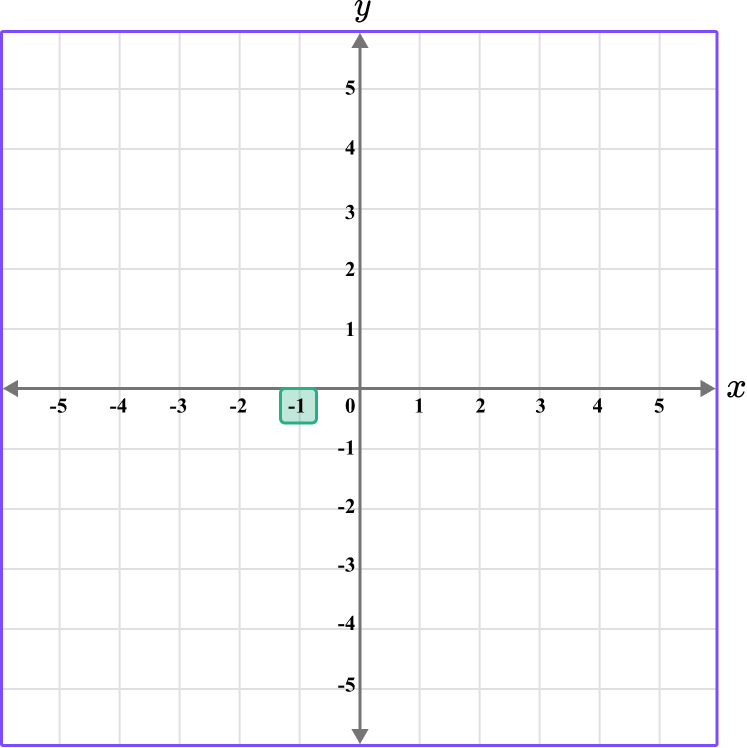
Determine the vertical position of the coordinate (the value of \textbf{y} ).
The y value of the point D is -3, so locate -3 on the y -axis.
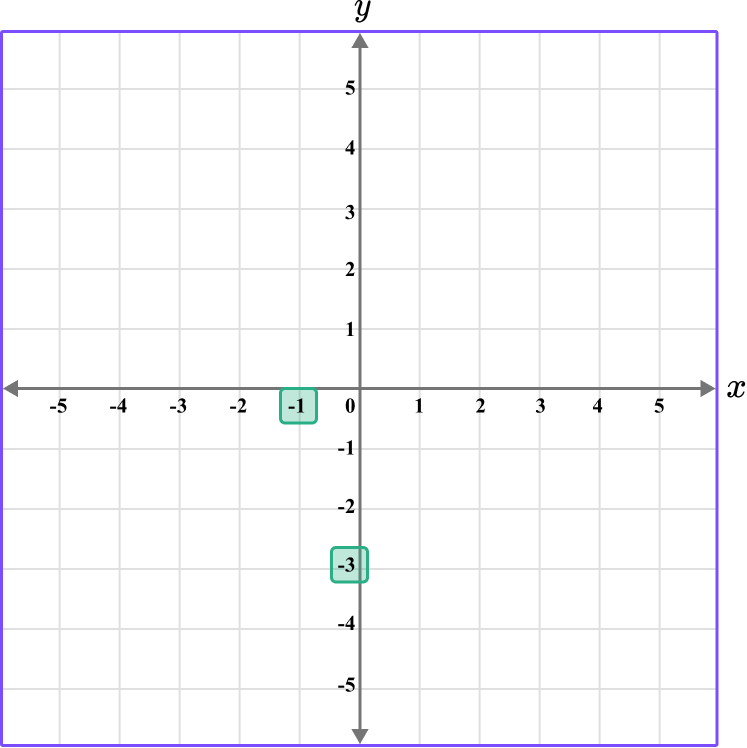
Follow the gridlines until the two values meet and draw a point.
Following the gridlines…
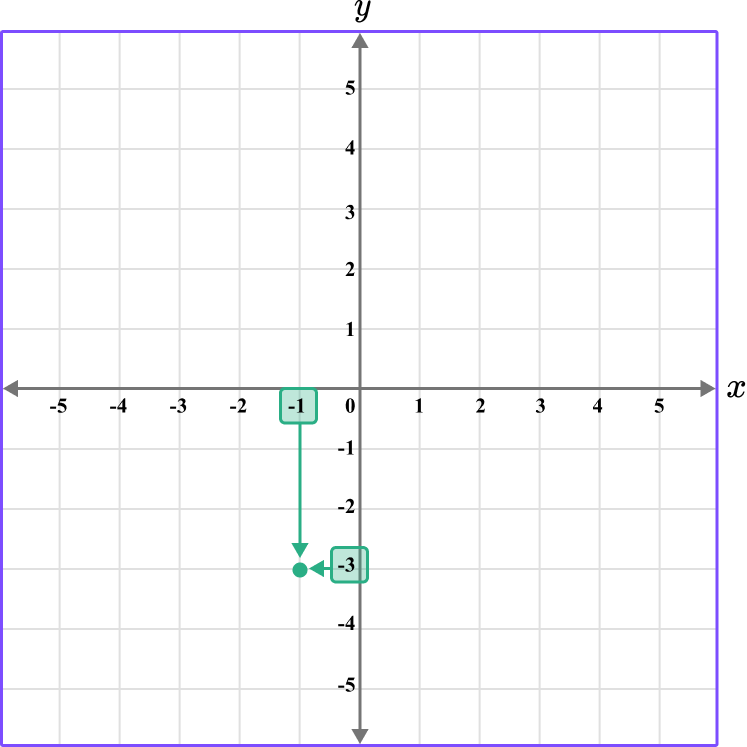
The point D is located here.
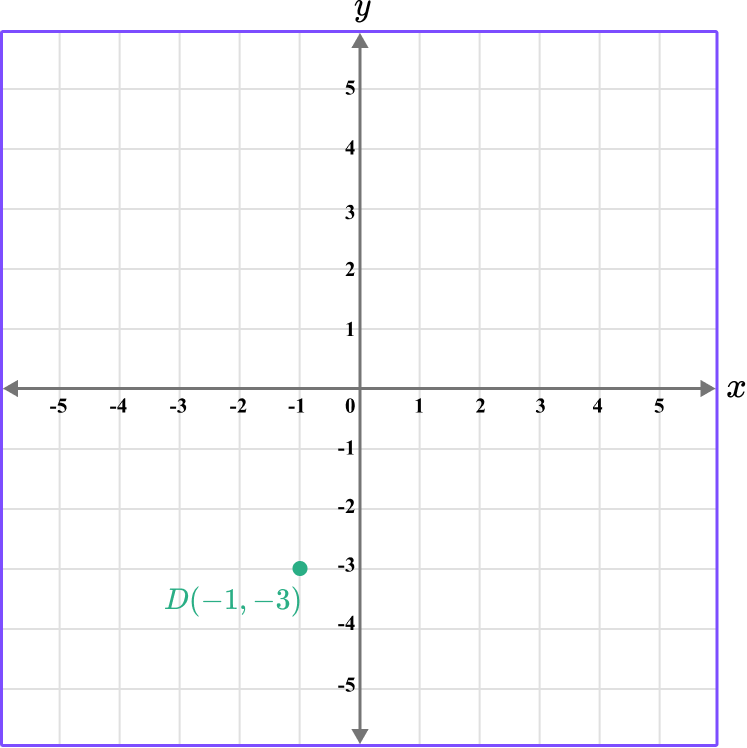
Repeat this process for the point E…
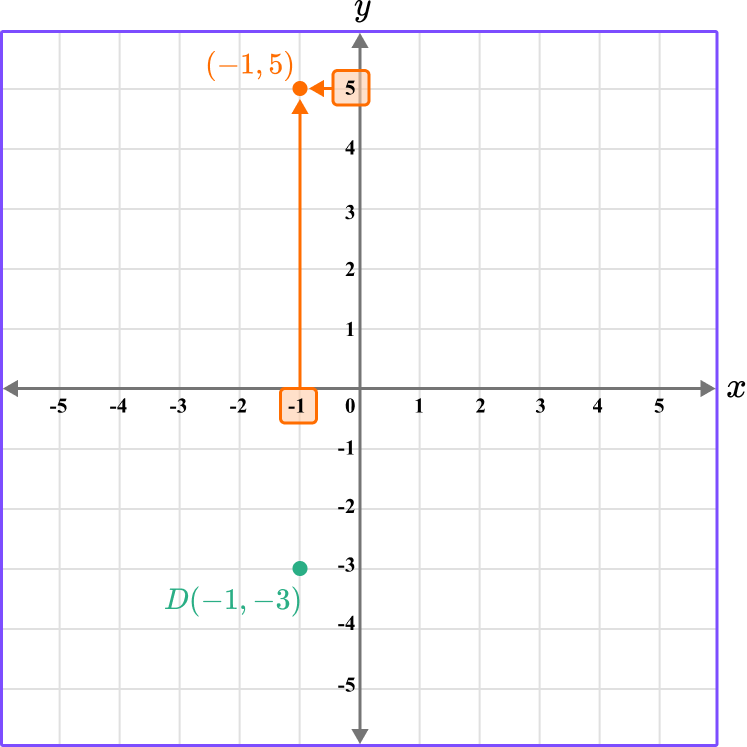
Repeating the process for the point F…
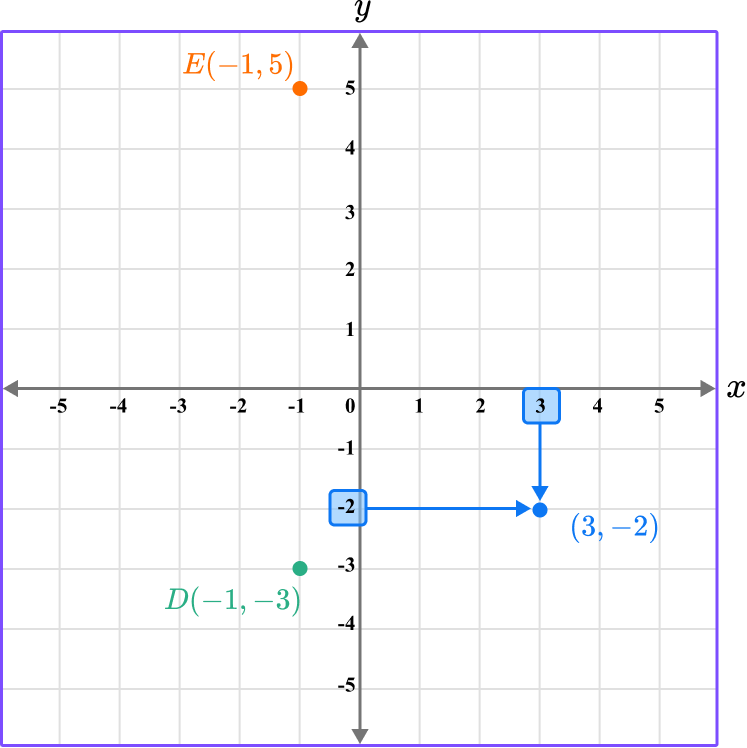
This gives us the final solution.
Teaching tips for the coordinate plane
- Worksheets play an important role when students are learning to plot on a coordinate plane, but they are not the only option. There are digital coordinate planes available where students can easily change the scale and explore grids with very small or very large scales that would be harder to represent on paper. You can also utilize a tiled floor or wall to create a physical version of the coordinate plane within the classroom.
- Coordinate planes have so many real life uses, and students understand them best with repeated use. To make the repeated practice more engaging, give students the opportunity to create and use a coordinate plane to solve a real world problem. It could be physical, for example, using string and stakes to create a grid in the school garden for proper plant distances. Or using a program to code a video game that requires students to indicate the position of the characters and items in each frame of the game.
Easy mistakes to make
- Mixing up the values in the coordinate
It is important to remember that the first number is x and represents the horizontal axis. The second number is y and represents the vertical axis. Confusing these, in most cases, will affect the location of the coordinate.
- Forgetting the values between the gridlines
Each axis is created by a number line, which has infinite rational values on it. If a coordinate lies between gridlines, rather than on a gridline, a smaller ratio of the scale can be used to find the exact position. Continuing to use the original scale or guessing, will lead to an incorrect answer.
- Not using parentheses and a comma
The parentheses and the comma are required when writing a coordinate. Coordinates can be incorrectly written as 3,2 without the parentheses, this is just a list of numbers; (3,2) is a coordinate.
Related coordinate plane lessons
- Interpreting graphs
- x and y axis
- Graph transformations
- Plot points on a graph
- Independent and dependent variables
Practice coordinate plane questions
1. What is the coordinate shown below?
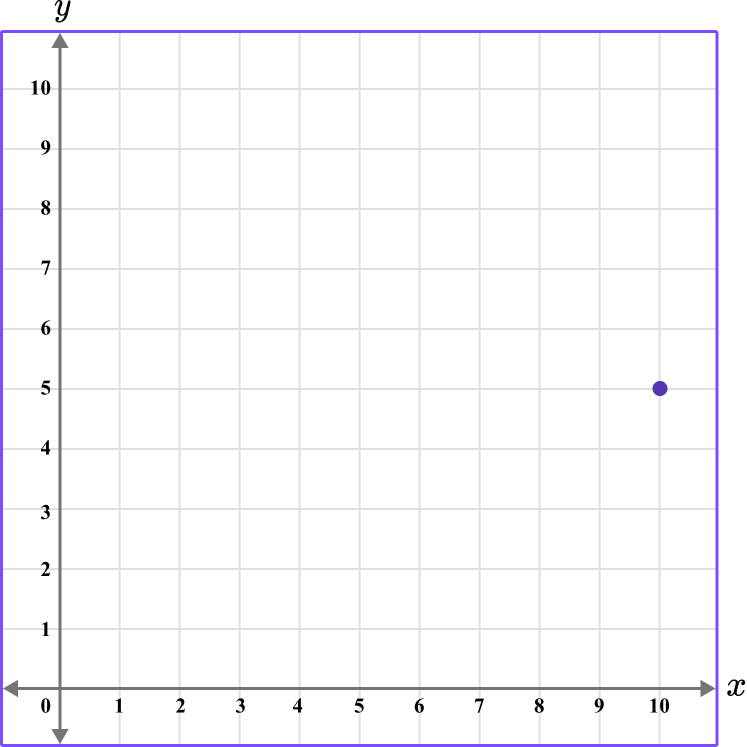




The first value is along the x axis and the second value is along the y axis.
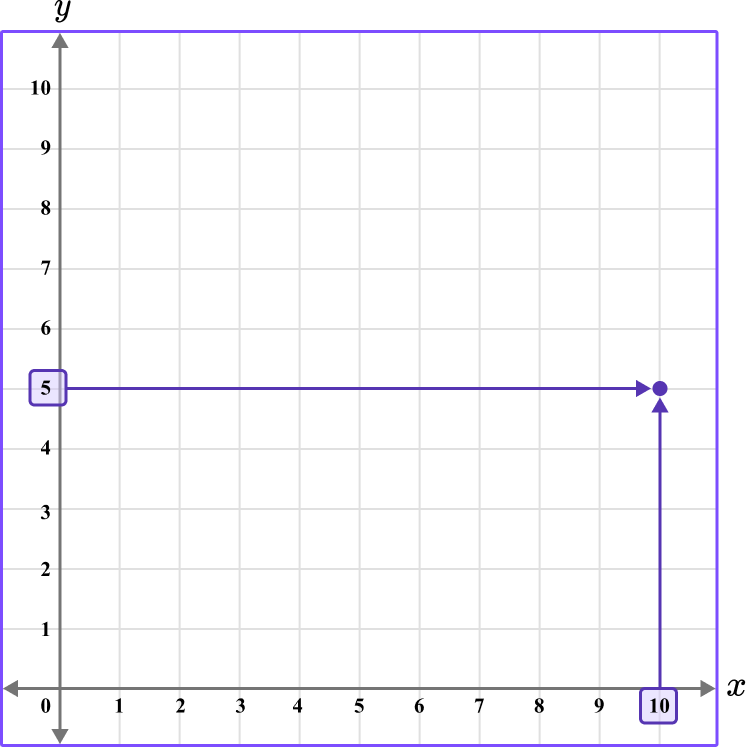
The x value of the coordinate is 10.
The y value of the coordinate is 5.
The coordinate is written as (10,5).
2. What is the coordinate shown below?
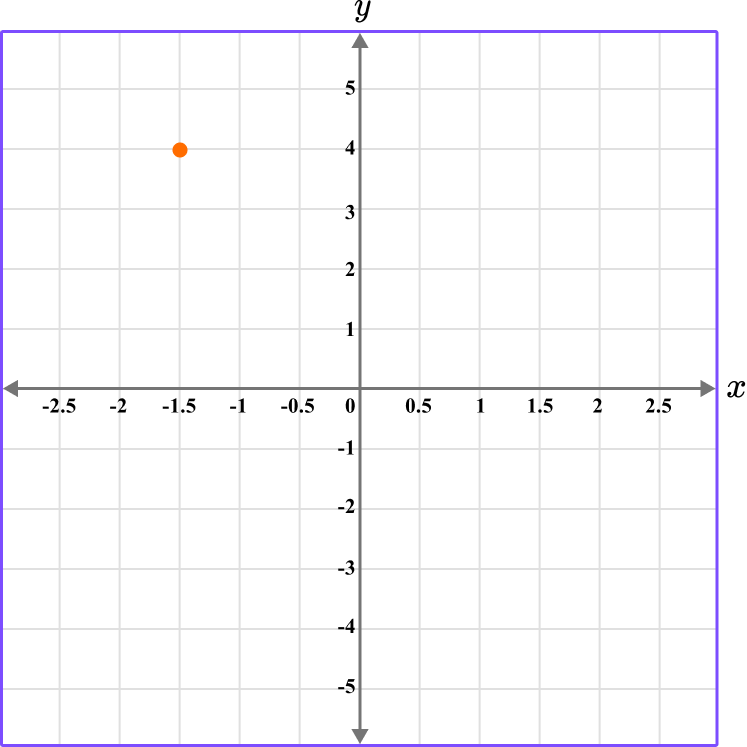




The first value is along the x axis and the second value is along the y axis.
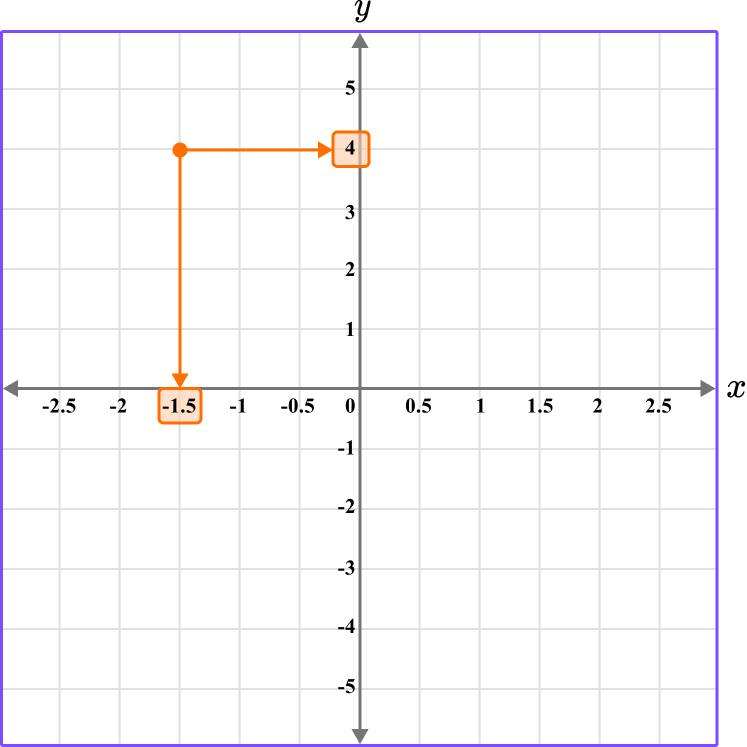
The coordinate is written as (-1.5,4).
3. Which diagram correctly shows the location of the point (2.5,4.5)?
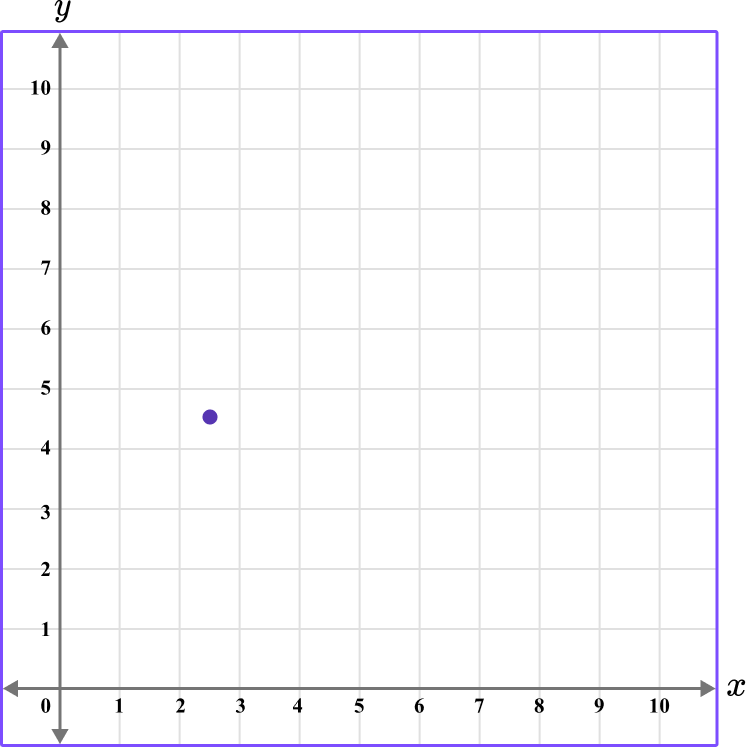

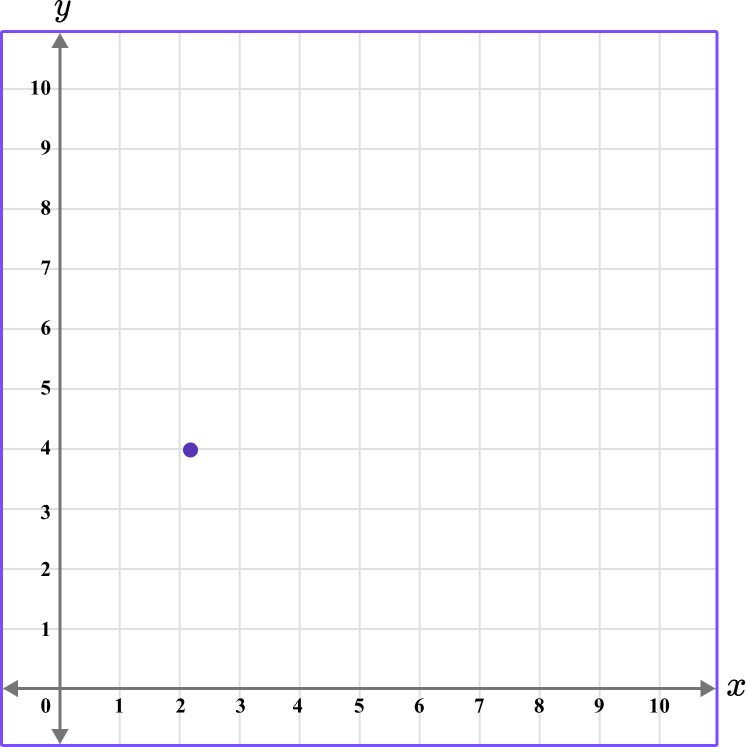

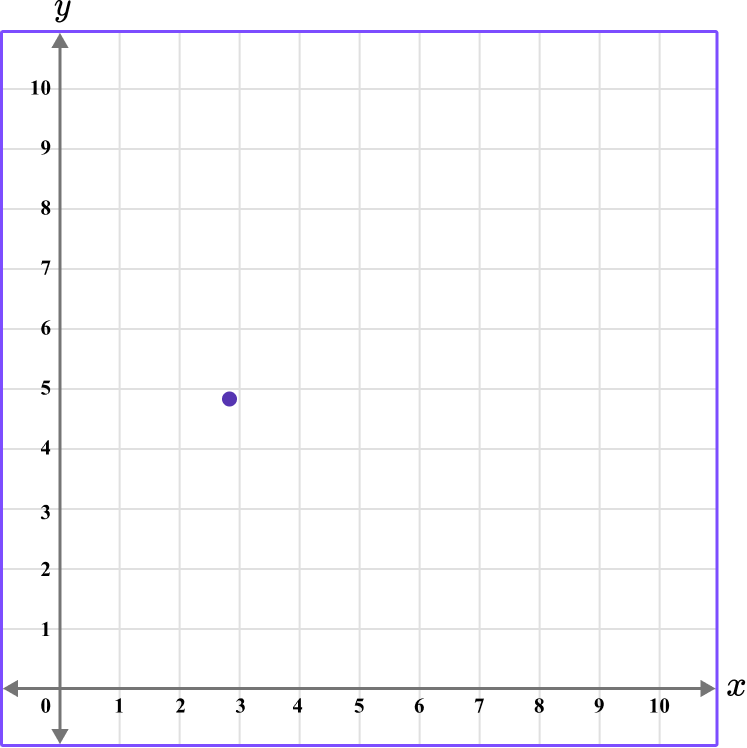

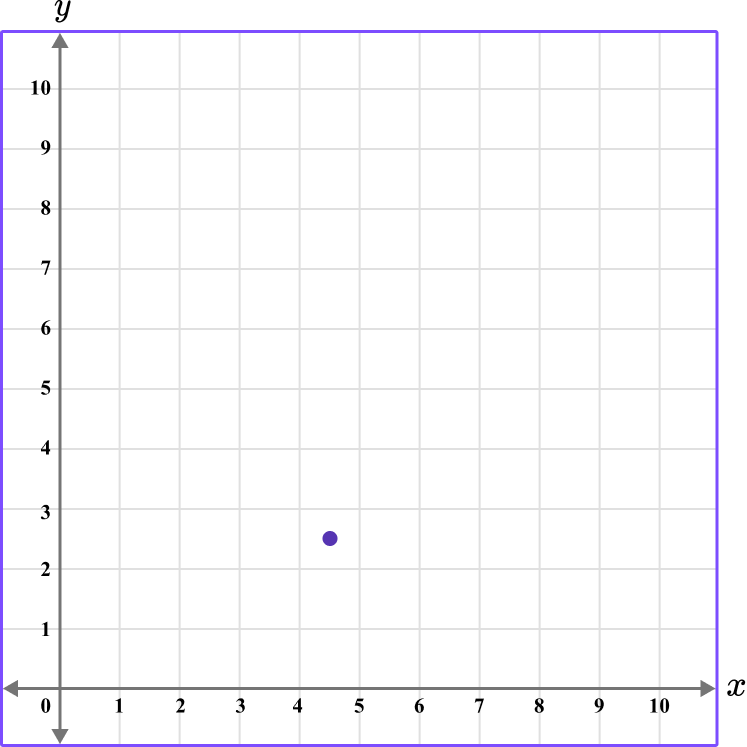

The first value is along the x axis and the second value is along the y axis.
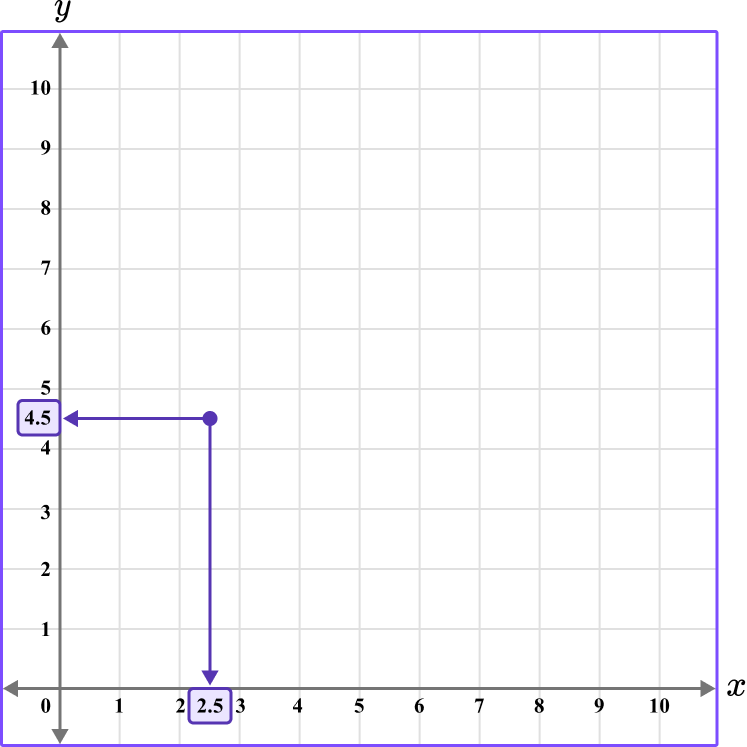
This graph shows the coordinate (2.5,4.5).
4. Which diagram correctly shows the location of the point A \, (-3,-1)?
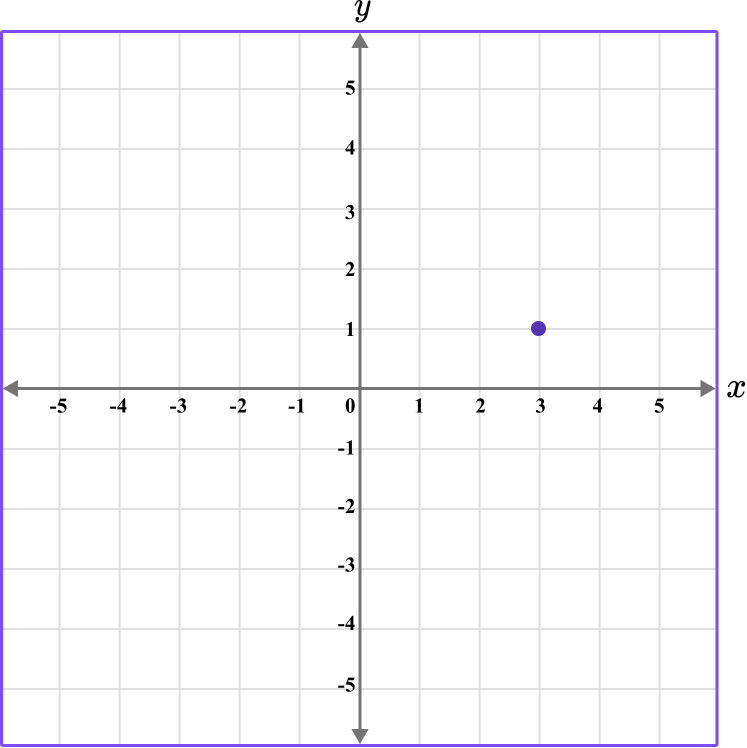

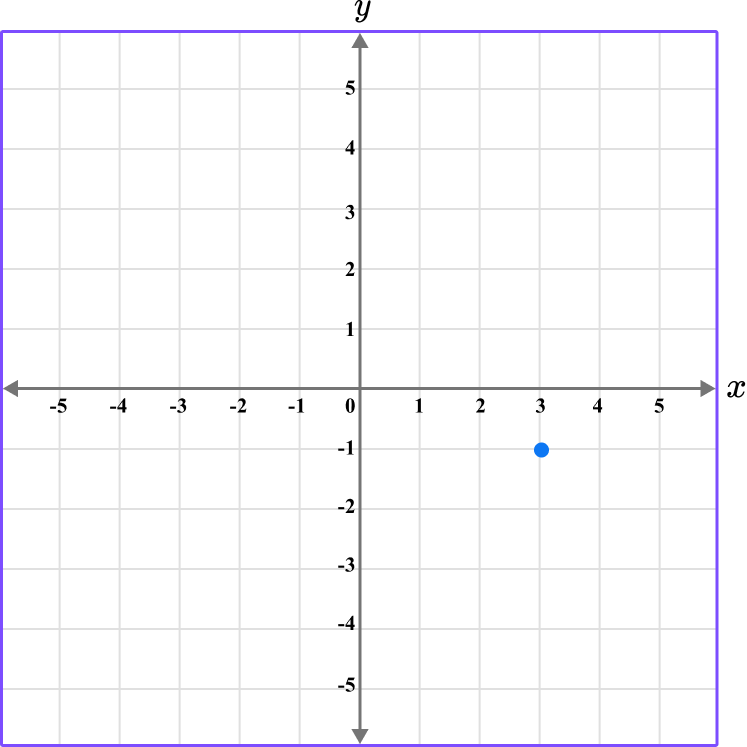

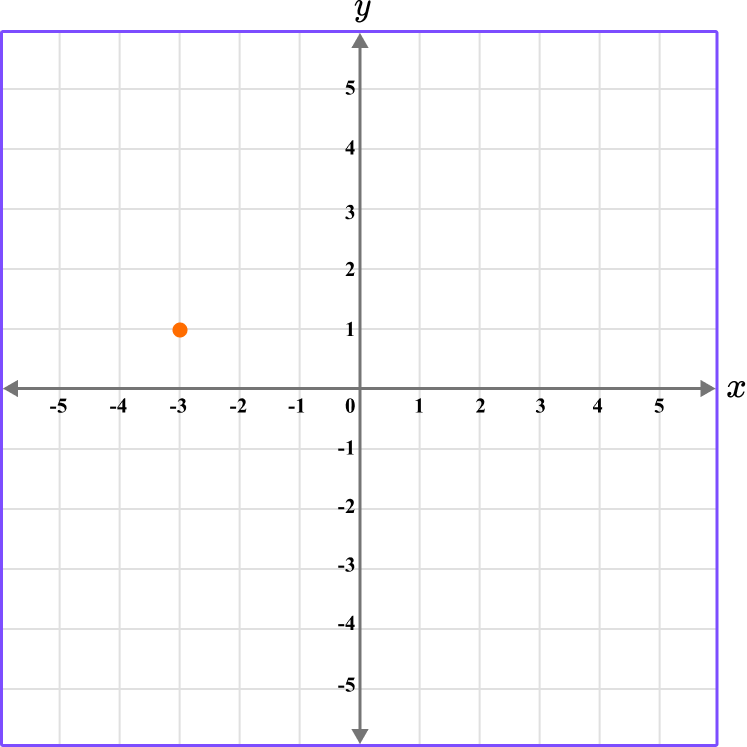

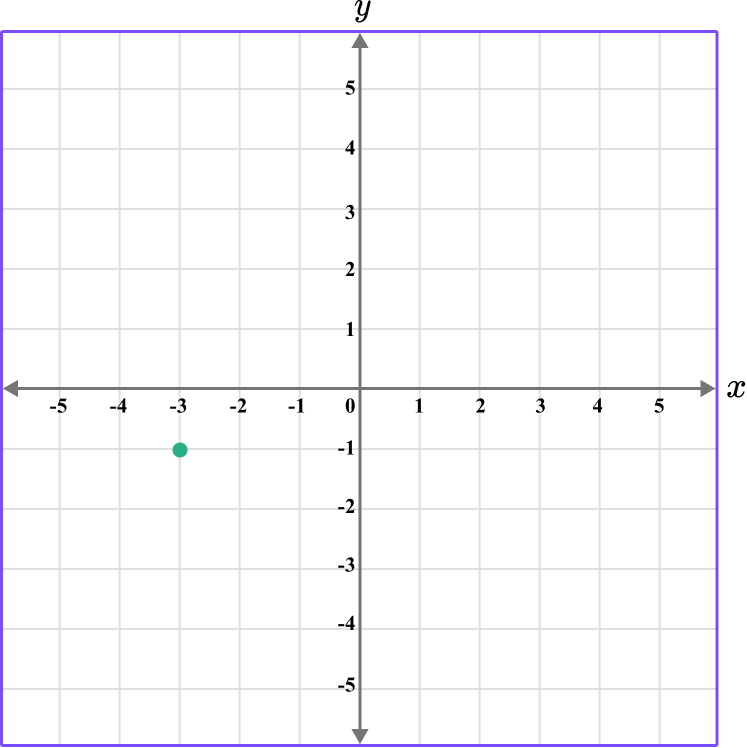

The first value is along the x axis and the second value is along the y axis.
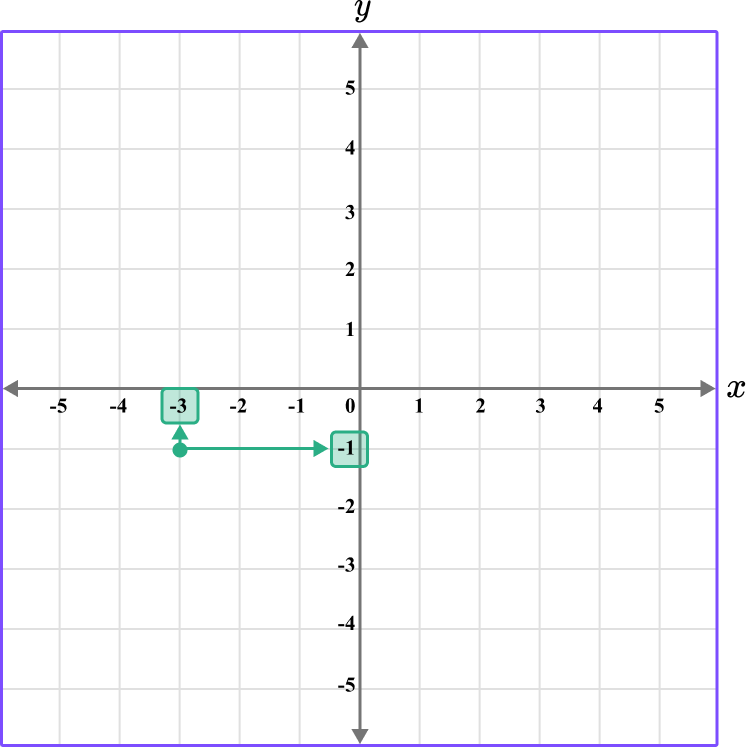
This graph shows the coordinate (-3,-1).
5. What is the coordinate shown below?
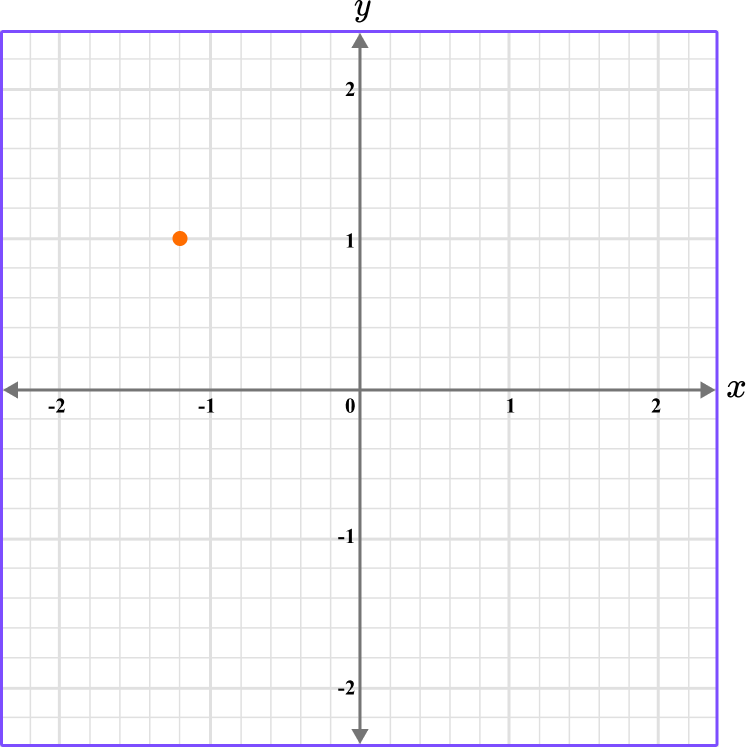




The first value is along the x axis and the second value is along the y axis.
The scale for the x and y axes is 0.2.
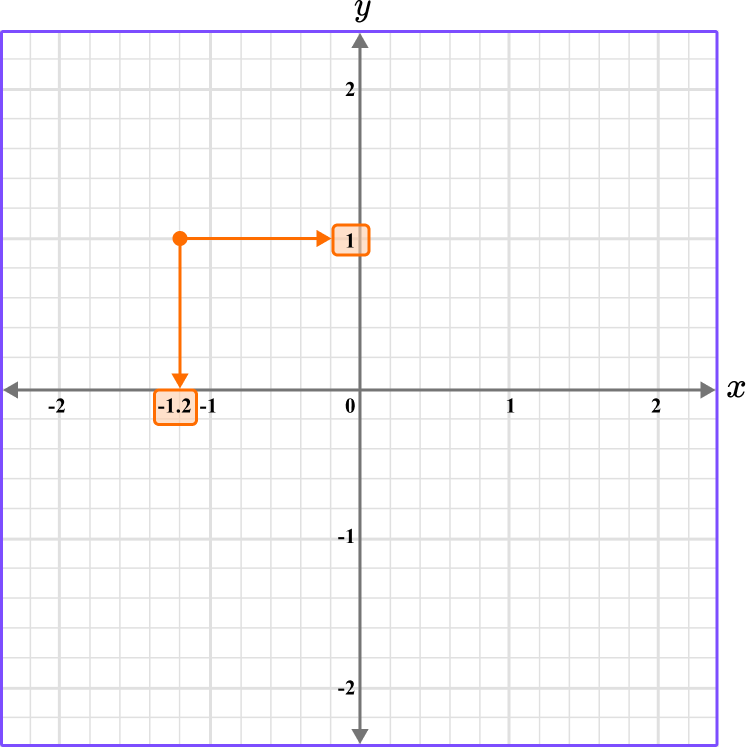
This graph shows the coordinate (-1.2,1).
6. What is the coordinate shown below?
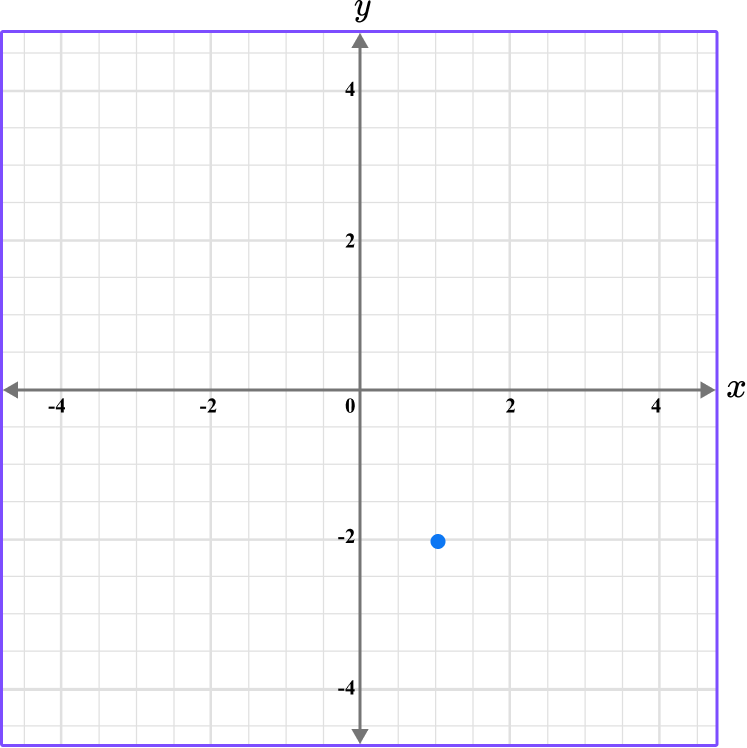




The first value is along the x axis and the second value is along the y axis.
The scale for the x and y axes is 0.5.
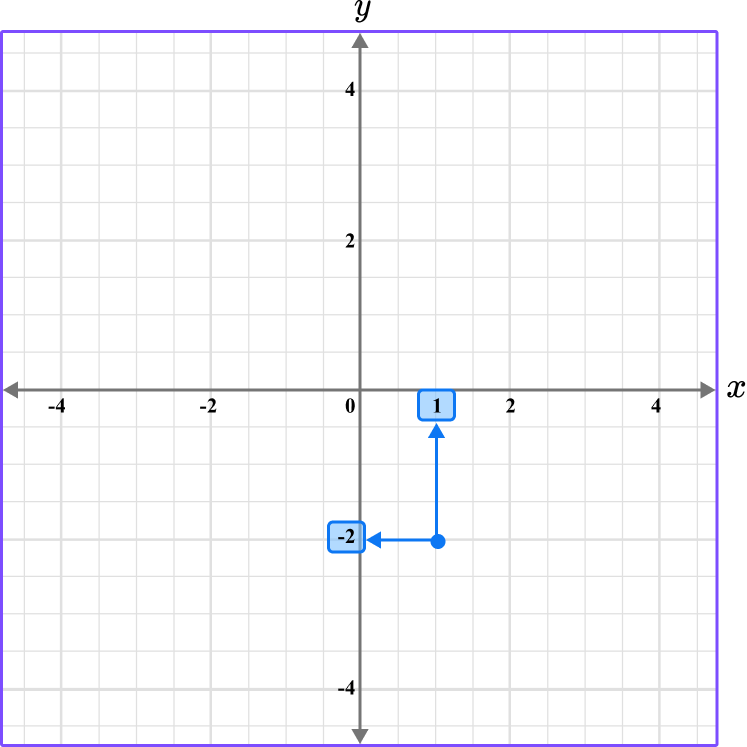
This graph shows the coordinate (1,-2).
Coordinate plane FAQs
This is the same as a coordinate plane. This name refers to the French mathematician Rene Descartes who is credited with incorporating the use of the coordinate plane into mathematics.
Coordinate planes have many uses in the real world and come up extensively in upper level math topics like geometry, algebra, and statistics.
The next lessons are
- Types of graphs
- Graphing linear equations
- Rate of change
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!