GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Multiplication and division
Converting units of timeConverting units of length (distance)
Rearranging the subject of a formula
Substitution into formulae
This topic is relevant for:

Speed Distance Time Triangle
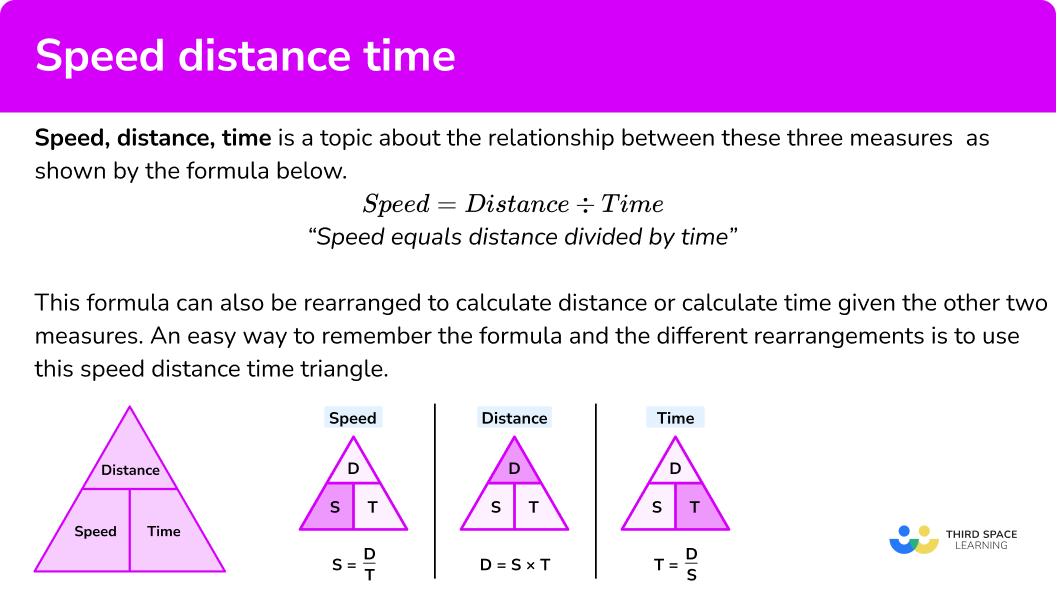
Here we will learn about the speed distance time triangle including how they relate to each other, how to calculate each one and how to solve problems involving them.
There are also speed distance time triangle worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is speed distance time?
Speed distance time is the formula used to explain the relationship between speed, distance and time. That is speed = distance ÷ time. Or to put it another way distance divided by speed will give you the time. Provided you know two of the inputs you can work out the third.
For example if a car travels for 2 hours and covers 120 miles we can work out speed as 120 ÷ 2 = 60 miles per hour.
The units of the the distance and time tell you the units for the speed.
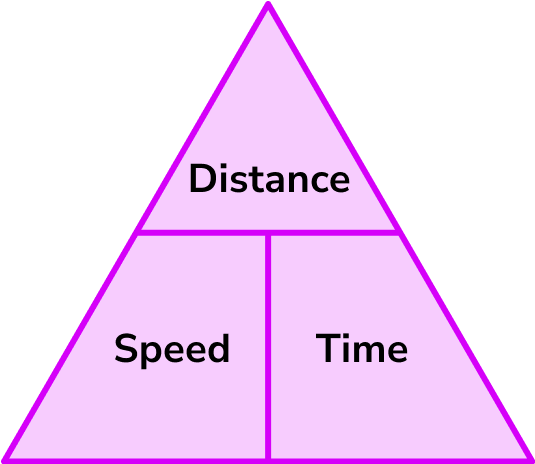
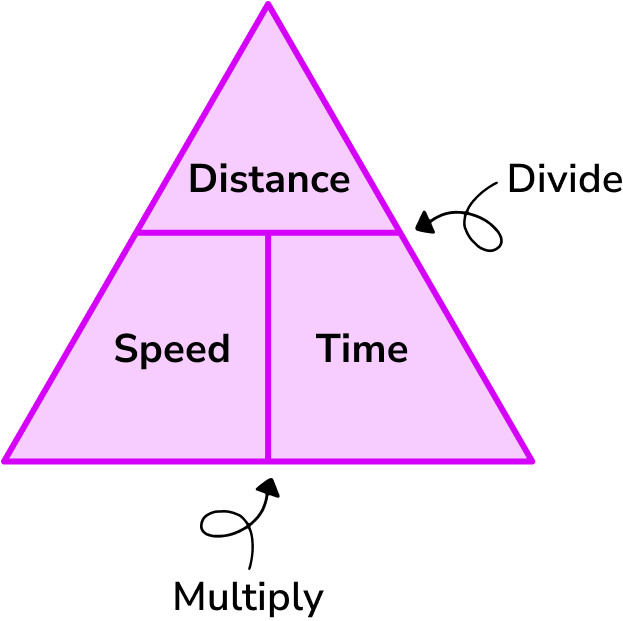
What is the speed distance time triangle?
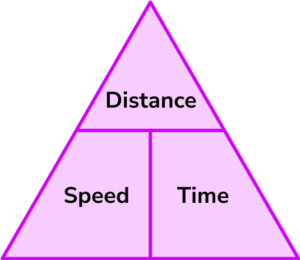
The speed distance time triangle is a way to describe the relationship between speed, distance and time as shown by the formula below.
\textbf{Speed } \bf{=} \textbf{ distance } \bf{\div} \textbf{ time}
“Speed equals distance divided by time”
Let’s look at an example to calculate speed.
If a car travels 66km in 1.5 hours then we can use this formula to calculate the speed.
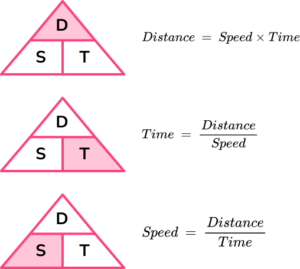
Speed = distance \div time = 66 \div 1.5 = 44km/hThis formula can also be rearranged to calculate distance or calculate time given the other two measures. An easy way to remember the formula and the different rearrangements is to use this speed distance time triangle.
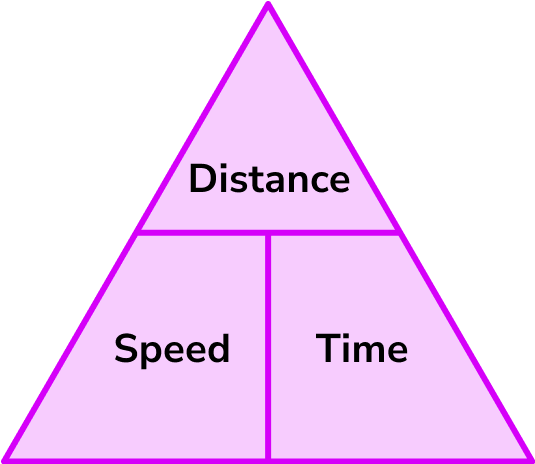
From this triangle we can work out how to calculate each measure: We can ‘cover up’ what we are trying to find and the formula triangle tells us what calculation to do.
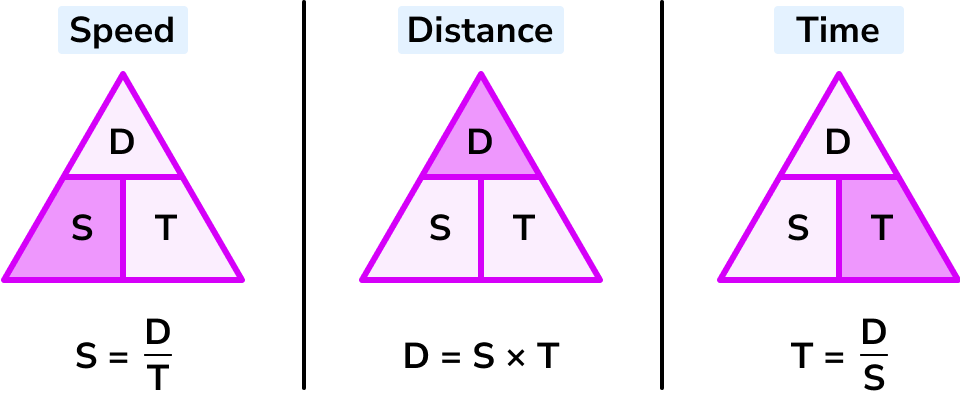
Let’s look at an example to calculate time.
How long does it take for a car to travel 34 miles at a speed of 68 miles per hour?
Time = distance \div speed = 34 \div 68 = 0.5 \ hoursLet’s look at an example to calculate distance.
What distance does a bike cover if it travels at a speed of 7 metres per second for 50 seconds?
Distance = speed \times time = 7 \times 50 = 350 \ metresWhat is the speed distance time triangle?
What is the speed distance time formula?
The speed distance time formula is just another way of referring to the speed distance time triangle or calculation you can use to determine speed, time or distance.
i.e.
- speed = distance ÷ time
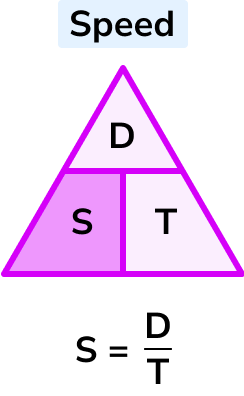
- S = D/T
- time = distance ÷ speed
- T = D/S
- distance = speed x time
- D = ST
Time problem
We can solve problems involving time by remembering the formula for speed, distance and time.
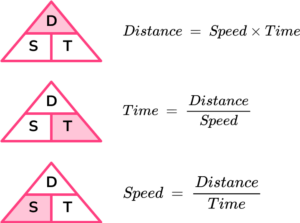
E.g.
Calculate the time if a car travels at 15 miles at a speed of 36 mph.
Time = distance ÷ speed
Time = 15 ÷ 36 = 0.42 hours
0.42 ✕ 60 = 25.2 minutes
E.g.
A train travels 42km between two stops at an average speed of 36 km/h.
If the train departs at 4 pm, when does the train arrive?
Time = distance ÷ speed
Time = 42 ÷ 36 = 1.17 hours
1.17 ✕ 60= 70 minutes = 1 hour 10 minutes.
E.g.
The average speed of a scooter is 18 km/h and the average speed of a cycle is 10 km/h.
When both have travelled 99 km what is the difference in the time taken?
Time = distance ÷ speed
Time A = 99 ÷ 18 = 5.5 hours
Time B= 99 ÷ 10 = 9.9 hours
Difference in time = 9.9 – 5.5 = 4.4 hours
4.4 hours = 4 hours and 24 minutes
Units of speed, distance and time
- The speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity.
We measure speed most commonly in metres per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph) and kilometres per hour (km/hr).
E.g.
The average speed of a small plane is 124mph.
The average walking speed of a person is 1.4m/s.
- We measure the distance an object has travelled most commonly in millimetres (mm), centimetres (cm), metres (m) and kilometres (km).
E.g.
The distance from London to Birmingham is 162.54km.
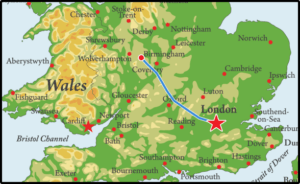
- We measure time taken in milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years.
E.g.
The time taken for the Earth to orbit the sun is 1 year or 365 days. We don’t measure this in smaller units like minutes of hours.
A short bus journey however, would be measured in minutes.
Speed, distance and time are proportional.
If we know two of the measurements we can find the other.
E.g.
A car drives 150 miles in 3 hours.
Calculate the average speed, in mph, of the car.
Distance = 150 miles
Time = 3 hours
Speed = 150÷ 3= 50mph
Speed, distance, time and units of measure
It is very important to be aware of the units being used when calculating speed, distance and time.
- Examples of units of distance: mm, \ cm, \ m, \ km, \ miles
- Examples of units of time: seconds (sec), minutes, (mins) hours (hrs), days
- Examples of units of speed: metres per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph)
Note that speed is a compound measure and therefore involves two units; a combination of a distance in relation to a time.
When you use the speed distance time formula you must check that each measure is in the appropriate unit before you carry out the calculation. Sometimes you will need to convert a measure into different units. Here are some useful conversions to remember.
Units of length
\begin{aligned} &1cm = 10mm \\\\ &1m = 100cm \\\\ &1km = 1000m \\\\ &8km \approx 5 miles \end{aligned}Units of time
1 minute = 60 seconds
1 hour = 60 minutes
1 day = 24 hours
Let’s look at an example.
What distance does a bike cover if it travels at a speed of 5 metres per second for 3 minutes?
Note here that the speed involves seconds, but the time given is in minutes. So before using the formula you must change 3 minutes into seconds.
1 minute = 60 seconds
3 minutes = 3\times 60 =180 seconds
Distance = speed \times time = 5 \times 180 = 900 \ metresNote also that sometimes you may need to convert an answer into different units at the end of a calculation.
Constant speed / average speed
For the GCSE course you will be asked to calculate either a constant speed or an average speed. Both of these can be calculated using the same formula as shown above.
However, this terminology is used because in real life speed varies throughout a journey. You should also be familiar with the terms acceleration (getting faster) and deceleration (getting slower).
Constant speed
A part of a journey where the speed stays the same.
Average speed
A journey might involve a variety of different constant speeds and some acceleration and deceleration. We can use the formula for speed to calculate the average speed over the course of the whole journey.
Average Speed Formula
Average speed is the total distance travelled by an object divided by the total time taken. To do this we can use the formula
Average speed =\frac{Total\, distance}{Total\, time}
If we are calculating an average speed in mph or km/h, we will need to ensure we have decimalised the time before we divide.
How to calculate speed distance time
In order to calculate speed, distance or time:
- Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
- Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.
- Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
- Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
- Write your final answer with the required units.
Explain how to calculate speed distance time

Speed distance time triangle worksheet

Get your free speed distance time triangle worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Speed distance time triangle worksheet

Get your free speed distance time triangle worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on compound measures
Speed distance time is part of our series of lessons to support revision on compound measures. You may find it helpful to start with the main compound measures lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Speed distance time triangle examples
Example 1: calculating average speed
Calculate the average speed of a car which travels 68 miles in 2 hours.
- Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
Speed: unknown
Distance: 68 miles
Time: 2 hours
2Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.
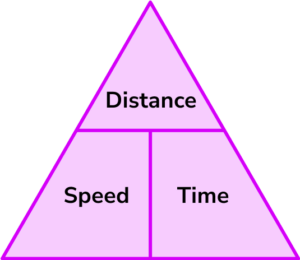
3Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
The distance is in miles and the time is in hours. These units are compatible to give the speed in miles per hour.
4Substitute the values into the formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
\begin{aligned} &Speed = 68 \div 2 \\\\ &Speed = 34 \end{aligned}5Write your final answer with the required units.
34 \ mphExample 2: calculating time
A golden eagle can fly at a speed of 55 kilometres per hour. Calculate the time taken for a golden eagle to fly 66 \ km, giving your answer in hours.
Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
Speed: 55 \ km/hour
Distance: 66 \ km
Time: unknown
Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.
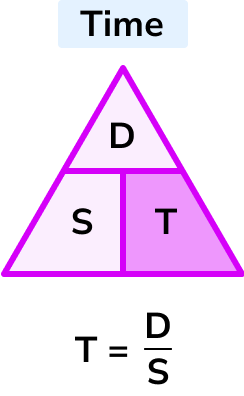
T=\frac{D}{S}
Time = distance \div speed
Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
Speed is in km per hour and the distance is in km, so these are compatible to give an answer for time in hours.
Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
Write your final answer with the required units.
1.2 hours
Example 3: calculating distance
Calculate the distance covered by a train travelling at a constant speed of 112 miles per hour for 4 hours.
Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
Speed: 112 \ mph
Distance: unknown
Time: 4 hours
Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.

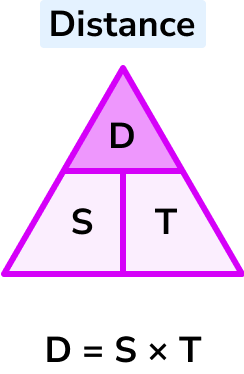
D= S \times T
Distance = speed \times time
Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
Speed is in miles per hour. The time is in hours. These units are compatible to find the distance in miles.
Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
Write your final answer with the required units.
448 miles
Example 4: calculating speed with unit conversion
A car travels for 1 hour and 45 minutes, covering a distance of 63 miles. Calculate the average speed of the car giving your answer in miles per hour (mph) .
Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
Speed: unknown
Distance: 63 miles
Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes
Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.

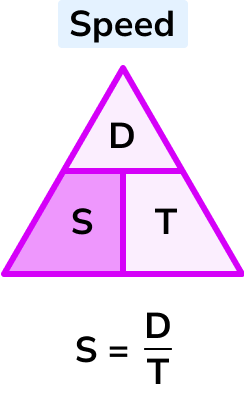
S = \frac{D}{T}
Speed = distance \div time
Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
The distance is in miles. The time is in hours and minutes. To calculate the speed in miles per hour, the time needs to be converted into hours only.
1 hour 45 minutes = 1\frac{3}{4} hours = 1.75 hours
Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
Write your final answer with the required units.
Example 5: calculating time with unit conversion
A small plane can travel at an average speed of 120 miles per hour. Calculate the time taken for this plane to fly 80 miles giving your answer in minutes.
Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
Speed: 120 \ mph
Distance: 80 \ miles
Time: unknown
Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.

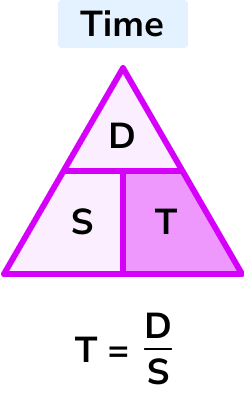
T = \frac{D}{S}
Time = distance \div speed
Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
Speed is in miles per hour and the distance is in miles. These units are compatible to find the time in hours.
Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
Write your final answer with the required units.
\frac{2}{3} hours in minutes
\frac{2}{3} \times 60 = 40
40 minutes
Example 6: calculating distance with unit conversion
A train travels at a constant speed of 96 miles per hour for 135 minutes. Calculate the distance covered giving your answer in miles.
Write down the values of the measures you know with the units.
Speed: 96 \ mph
Distance: unknown
Time: 135 minutes
Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.

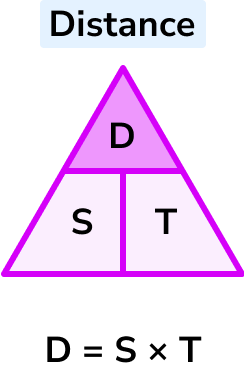
D = S \times T
Distance = speed \times time
Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
The speed is in miles per hour, but the time is in minutes. To make these compatible the time needs changing into hours and then the calculation will give the distance in miles.
135 minutes
135 \div 60 = \frac{9}{4} = 2\frac{1}{4} = 2.25
2.25 hours
Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
Write your final answer with the required units.
216 miles
Common misconceptions
- Incorrectly rearranging the formula Speed = distance \div time
Make sure you rearrange the formula correctly. One of the simplest ways of doing this is to use the formula triangle. In the triangle you cover up the measure you want to find out and then the triangle shows you what calculation to do with the other two measures.
- Using incompatible units in a calculation
When using the speed distance time formula you must ensure that the units of the measures are compatible.
For example, if a car travels at 80 \ km per hour for 30 minutes and you are asked to calculate the distance, a common error is to substitute the values straight into the formula and do the following calculation.
Distance = speed \times time = 80 \times 30 = 2400 \ km
The correct way is to notice that the speed uses hours but the time given is in minutes. Therefore you must change 30 minutes into 0.5 hours and substitute these compatible values into the formula and do the following calculation.
Distance = speed \times time = 80 \times 0.5 = 40 \ km
Practice speed distance time triangle questions
1. A car drives 120 miles in 3 hours. Calculate its average speed.




2. A cyclist travels 100 miles at an average speed of 20 \ mph. Calculate how long the journey takes.
2000 hours

0.2 hours

5 hours

12 hours

5 hours
3. An eagle flies for 30 minutes at a speed of 66 \ km per hour. Calculate the total distance the bird has flown.




30 minutes = 0.5 hours
\begin{aligned} &Distance = speed \times time \\\\ &Distance = 66 \times 0.5 = 33 \\\\ &33 \ km \end{aligned}4. Calculate the average speed of a lorry travelling 54 miles in 90 minutes. Give your answer in miles per hour (mph).




Firstly convert 90 minutes to hours.
90 minutes = 1.5 hours
5. Calculate the time taken for a plane to fly 90 miles at an average speed of 120 \ mph. Give your answer in minutes.
180 minutes

45 minutes

80 minutes

75 minutes

0.75 hours
Convert 0.75 hours to minutes
0.75 \times 6045 minutes
6. A helicopter flies 18 \ km in 20 minutes. Calculate its average speed in km/h .




Firstly convert 20 minutes to hours.
20 minutes is a third of an hour or \frac{1}{3} hours.
\begin{aligned}
&Speed = distance \div time \\\\
&Speed =18 \div \frac{1}{3} \\\\
&Speed = 54 \\\\
&54 \ km/h
\end{aligned}
Speed distance time triangle GCSE questions
1. A commercial aircraft travels from its origin to its destination in a time of 2 hours and 15 minutes. The journey is 1462.5 \ km.
What is the average speed of the plane in km/hour?
(3 marks)
2 hours 15 minutes = 2\frac{15}{60} = 2\frac{1}{4} = 2.25
(1)
Speed = distance \div time = 1462.5 \div 2.25(1)
650(1)
2. John travelled 30 \ km in 90 minutes.
Nadine travelled 52.5 \ km in 2.5 hours.
Who had the greater average speed?
You must show your working.
(3 marks)
90 minutes = 1.5 hours
John = 30 \div 1.5 = 20 \ km/h
(1)
Nadine = 52.5 \div 2.5 = 21 \ km/h
(1)
Nadine has the greater average speed.
(1)
3. The distance from Birmingham to Rugby is 40 miles.
Omar drives from Rugby to Birmingham at 60 \ mph.
Ayushi drives from Rugby to Birmingham at 50 \ mph.
How much longer was Ayushi’s journey compared to Omar’s journey? Give your answer in minutes.
(3 marks)
For calculating time in hours for Omar or Ayushi.
(1)
For converting hours into minutes for Omar or Ayushi.
(1)
For correct final answer of 8 minutes.
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Use compound units such as speed
- Solve simple kinematic problem involving distance and speed
- Change freely between related standard units (e.g. time, length) and compound units (e.g. speed) in numerical contexts
- Work with compound units in a numerical context
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.